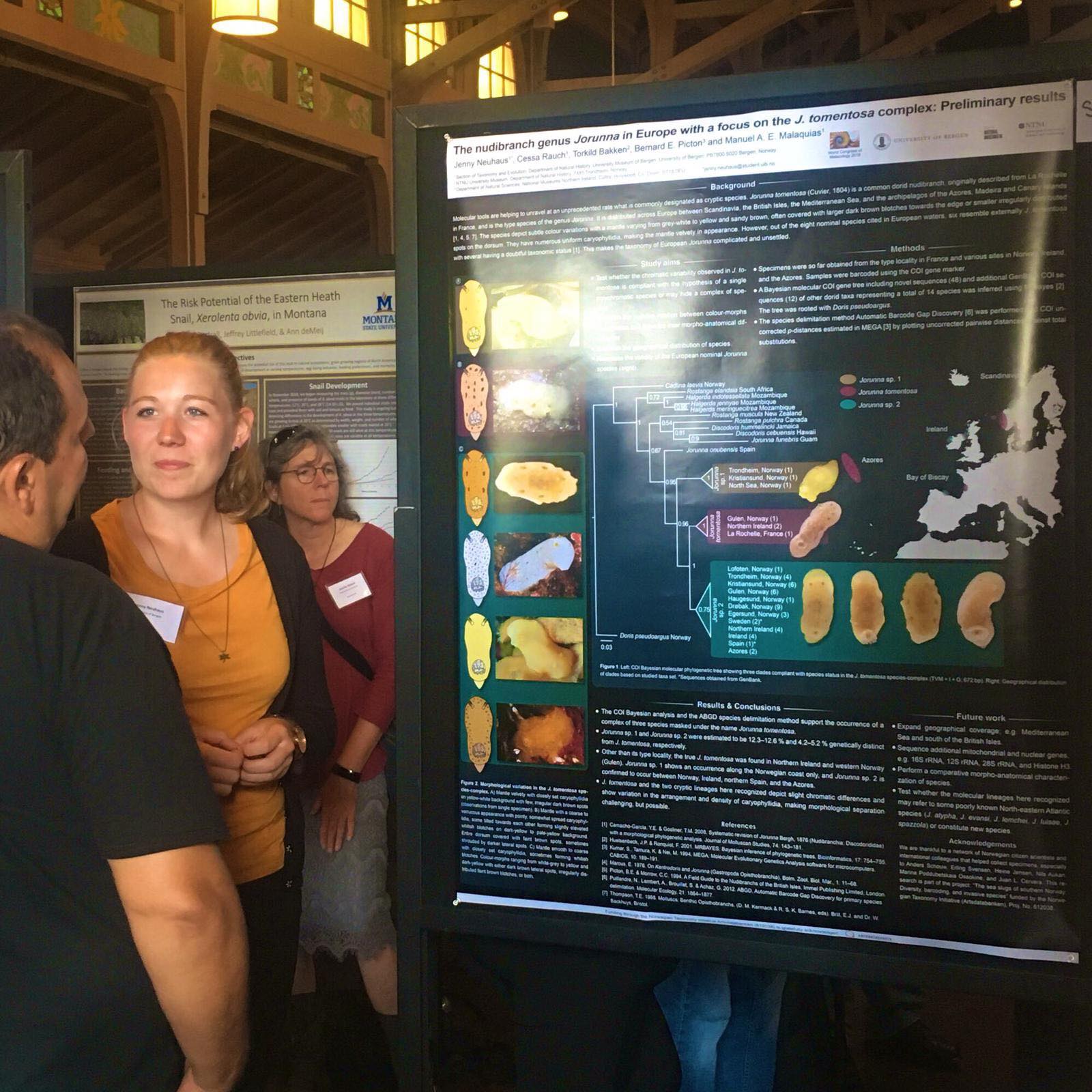
In 2018 former master student Jenny Neuhaus started working under supervision of Manuel Malaquias and Cessa Rauch on the sea slug species Jorunna tomentosa.
It was known already for some time that this sea slug occurs in a wide variety of colour patterns (morphotypes). With the increased discovery of cryptic species due to improved molecular techniques we wondered if we were dealing with a single species or several cryptic lineages.
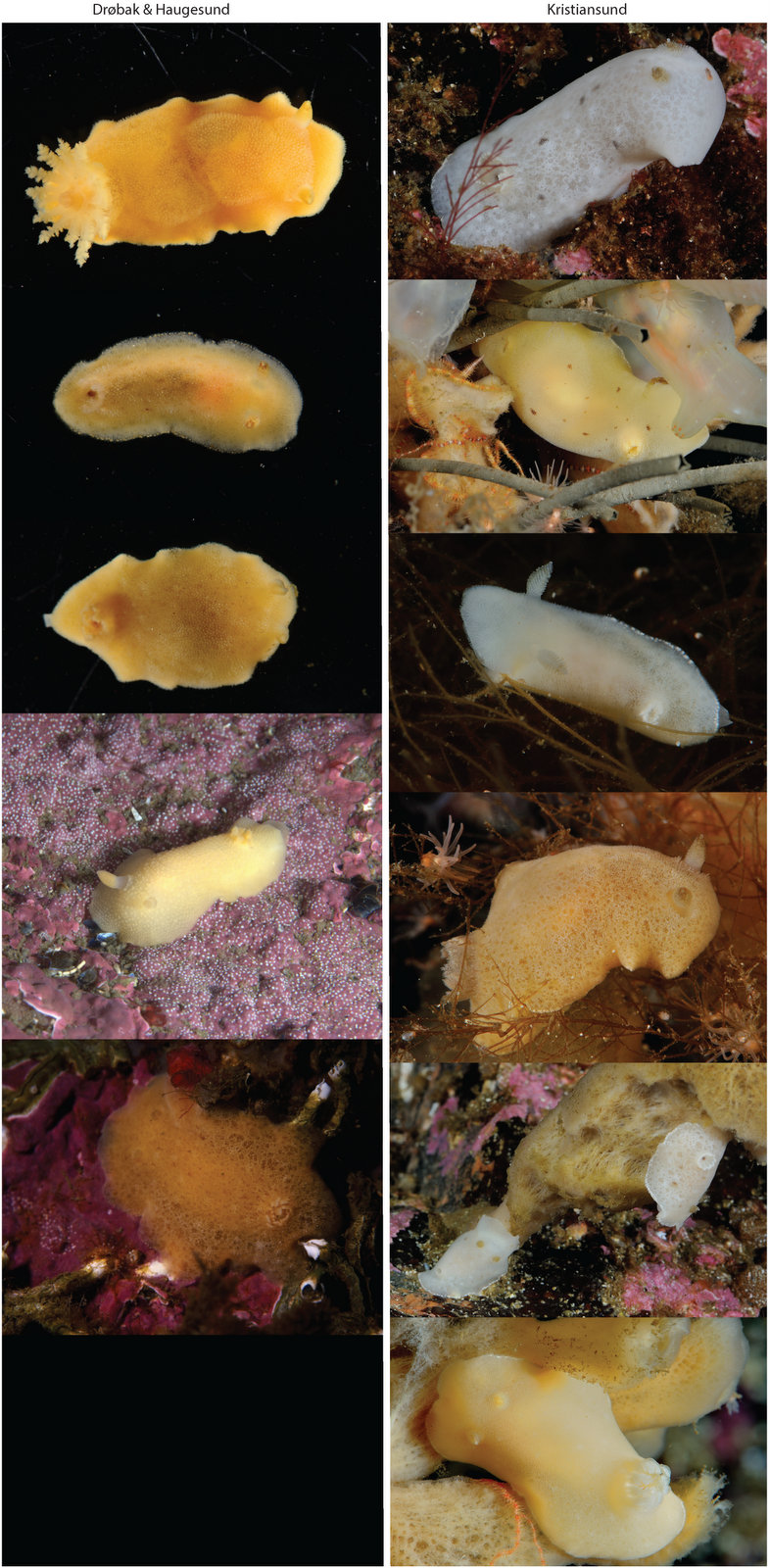
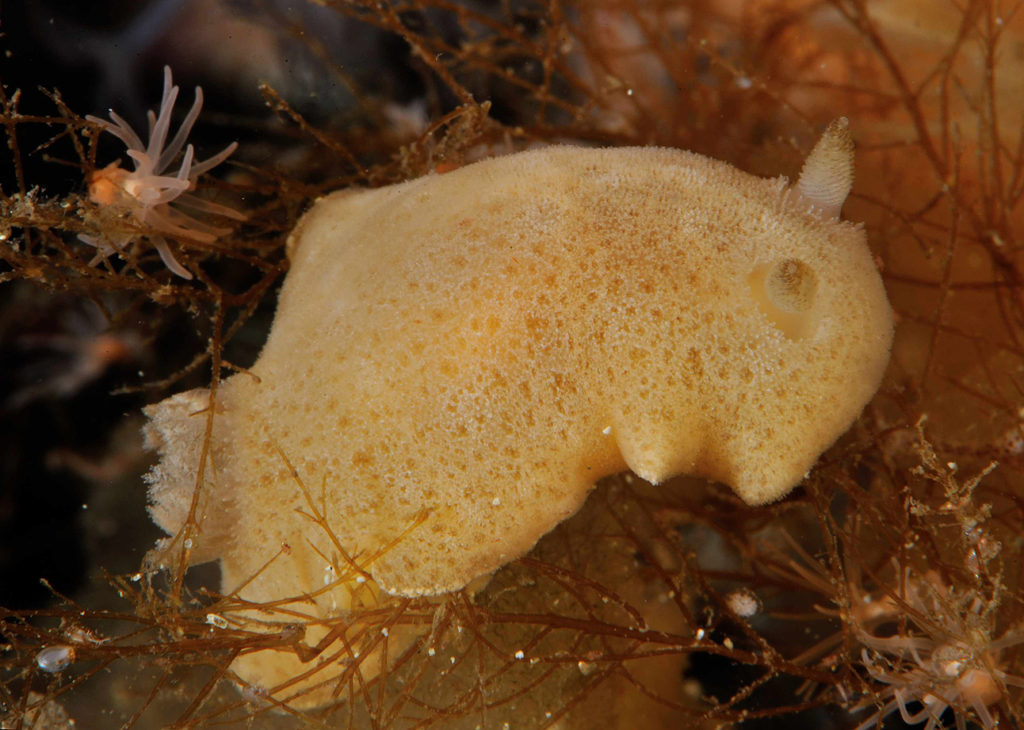
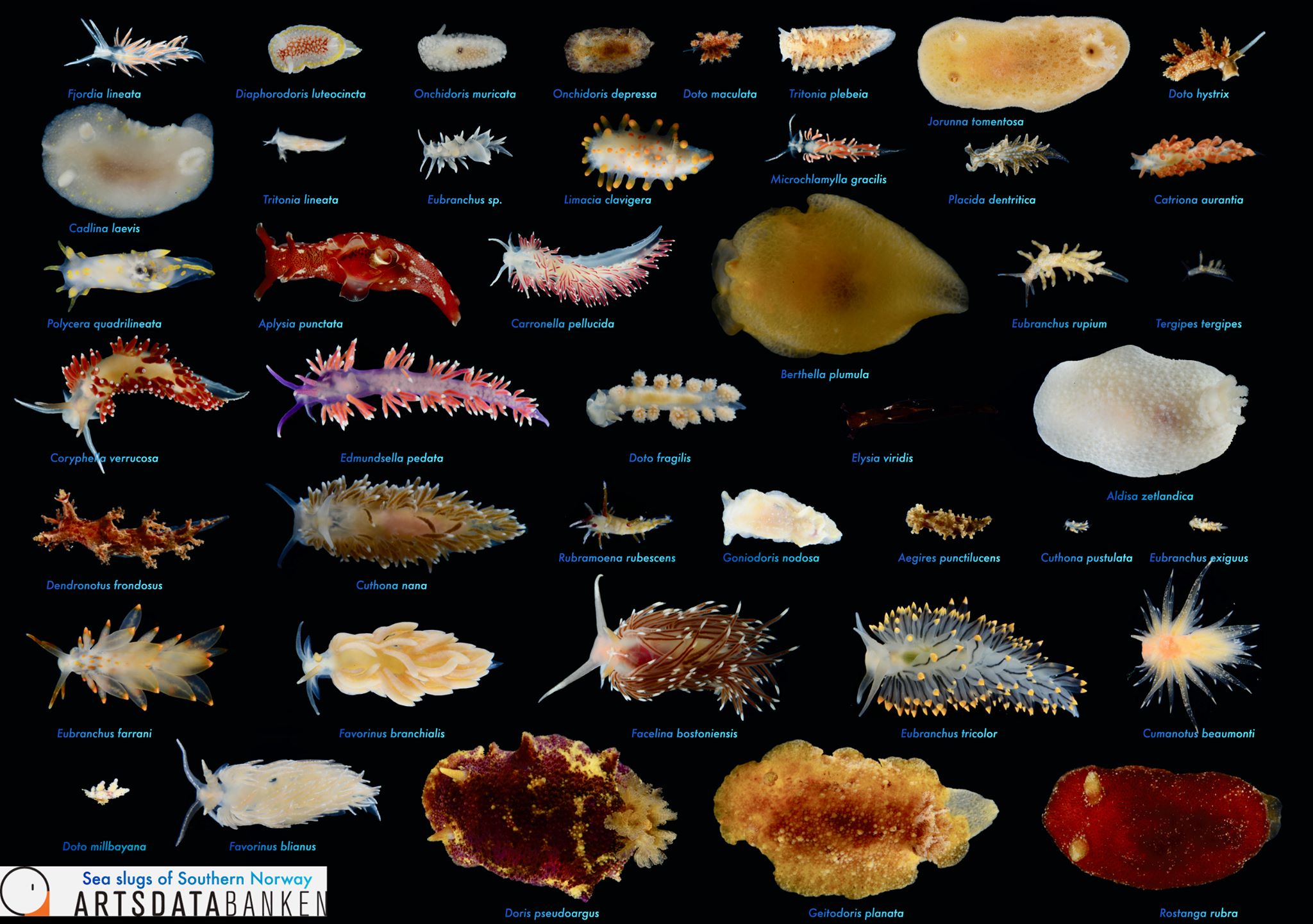
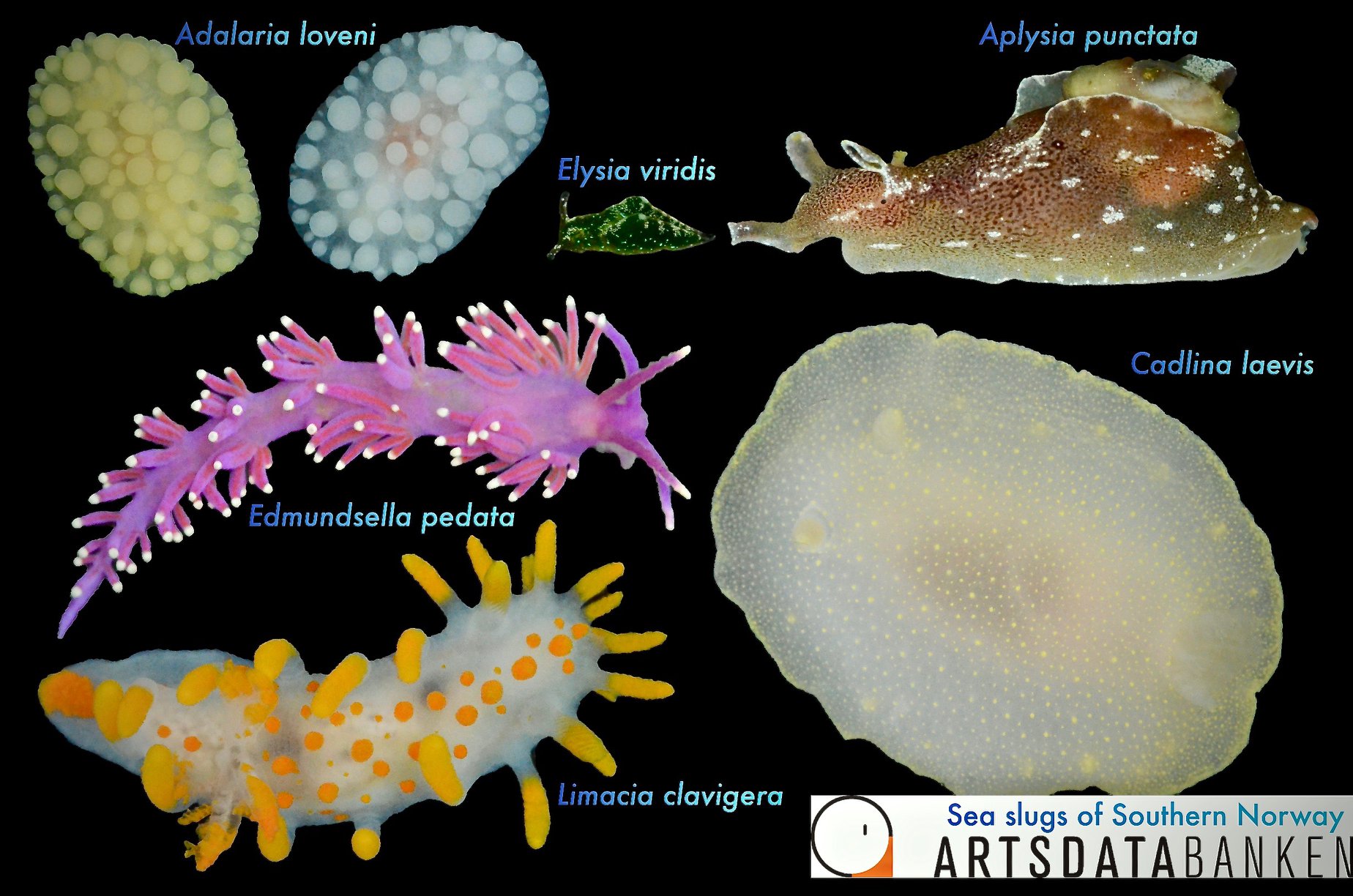
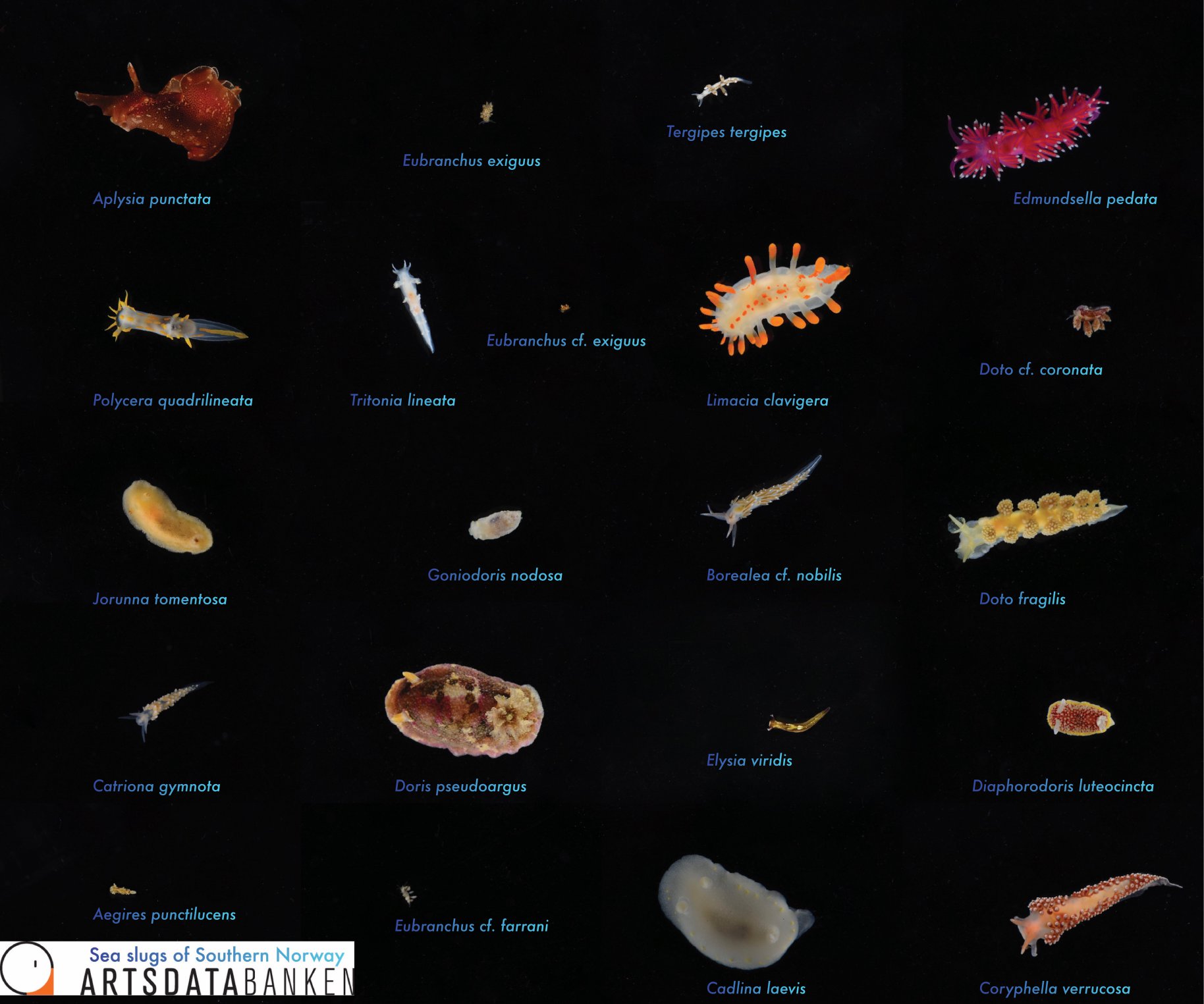
For a long time the different colours and patterns were regarded as natural variation within the species, consisting of shades of grey-white, cream-yellow, pale orange and either plain of blotched with light brown or chocolate brown spots of various sizes, distributed either irregularly or in lines, or combination of both!
But it was this variety that tossed up the question eventually whether we are dealing with a single species after all.
The nudibranch genus Jorunna consisted of eleven recognized species occurring in European waters. At that time, Jorunna tomentosa (Cuvier, 1804) was the only known species of this genus to be found along the Norwegian coastline. Prior to the study, the northernmost record of J. tomentosa was listed from Vestvågøy, Lofoten, Nordland. Today we know that the species is found at least 550 km further North in the Magerøysundet, Troms og Finnmark.
Jorunna tomentosa has an oval-elongate body shape with different colours varying from grey-white to cream-yellow and pale orange. They can reach a size up to 55 mm and occur at depths from a few meters down to more than 400m. They feed on sponges of the species Halichondria panicea, Haliclona oculata and Haliclona cinerea. J. tomentosa can be found from Finnmark in northern Norway, southwards along the European Atlantic coastline, the British Isles, the French coast, Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean Sea up to Turkey, and the Azores and Canary Islands. Besides the species has even been recorded from South Africa.
Jenny compared specimens from different parts of the world, including Norway, Ireland, Spain, France, Portugal including the Azores and South Africa. She took tissue samples for genetic studies and dissected them for their anatomy.
For the genetic studies we selected three different gene markers called COI, 16S and H3 to check how these morphotypes compare with each other and evaluate the meaning of genetic distances.
From the genetic distance analyses, it became clear that we were dealing with a “cryptic species complex”, as a clade of three specimens showed substantial genetic difference compared to J. tomentosa but seemed morphologically indistinguishable from another at first glance.
As sea slug anatomy is a matter of complexity, especially since each animal possesses both male and female reproductive organs (hermaphrodite), the expertise of Prof. Marta Pola from the University of Madrid was essential to conduct detailed morpho-anatomical studies. We were able to detect structural differences in the rasping tongue (radula) and parts of the reproductive apparatus.
Meet Jorunna artsdatabankia!
Jenny sequenced the DNA of 78 specimens of which 60 where successful for using in the final phylogenetic analyses. Her results supported the presence of a new Jorunna species, and in addition a possible case of incipient speciation in J. tomentosa with two genetic lineages morphologically undistinguishable. The new Jorunna species was based on material collected from Norway (Kristiansund, Frøya & the North Sea).
J. artsdatabankia has a plain white to yellow background colour accompanied by small brownish spots irregularly placed on the body surface. Its distributional range is so far restricted to Norway, being recorded from Skogsøya, Frøya (Trøndelag), Brattøya, Kristiansund (Møre og Romsdal), and a North Sea plateau (60.726944 0.505371) with a depth range from 27 to 350 meters, suggesting a sympatric occurrence with J. tomentosa.
The name attributed to this new species was chosen to recognize the work of the Norwegian Biodiversity Information Centre (Artsdatabanken) for their instrumental role promoting and supporting biodiversity research in Norway.
– Cessa Rauch, Jenny Neuhaus, Manuel Malaquias
Sea slugs of Norway Instagram: @seaslugsofnorway
Sea slugs of Norway Facebook: www.facebook.com/seaslugsofnorway
The paper can be found here:
The genus Jorunna (Nudibranchia: Discodorididae) in Europe: a new species and a possible case of incipient speciation. Jenny Neuhaus, Cessa Rauch, Torkild Bakken, Bernard Picton, Marta Pola, Manuel António E Malaquias (2021), Journal of Molluscan Studies, Volume 87, Issue 4, December 2021, eyab028, https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/eyab028