Drøbak 6th till 15th of May 2018
The Norwegian Taxonomy Initiative funded project Sea slugs of Southern Norway had its official kick-off with its first expedition to Drøbak, a little village on the east side of the Oslofjord about 40 km south of Oslo. Main goal, start mapping the sea slug species diversity of that area which we will continue to do so along different carefully chosen locations along the Southern Norwegian coast. But besides finding sea slugs, we had another ambition; meeting up with our hard-working collaborators that would help us out during our stay.
Sea slugs of Norway, a love story
Sea slugs are often a diver’s favourite encounter underwater. They are colourful, have an overall attractive appearance, with their little rhinophores exploring their surroundings, gliding slowly through their habitat.

Caronella pellucida, photographed by Anders Schouw
They are exciting to photograph as, besides pretty, it can be technically very challenging to get a good shot of them since they are often just a few millimetres long. Despite being popular animals, relatively little is known about them. Just recently the attention from the scientific community started to grow, and manuscripts with new records and species for Norway become to be published. However, the target areas were often the Northern territories of Norway rather than the South, and this resulted in a huge gap lasting already for about 80 years within the scientific literature for this particular area. About time to do something about it!
The citizens that are scientists
Southern Norway alone has a coastline of about 8000km, which makes it a monstrous task to really get a proper picture of the sea slug biodiversity (let alone cryptic species variation, invasive species etc.). Therefore, we asked for help from the so-called citizen scientists. Citizen scientist are volunteers that help out scientists by providing them with data as a hobby in their spare time. Many of them are not to be considered amateurs though, due to their many years of experience and enthusiasm, they are professionals when it comes to their knowledge of species and their habitats. Such a tight community is also found here in Norway within the dive community, and during this project of our hunt for sea slug species, we heavily rely on their input and willingness in order to make the mission a success.
Back to Drøbak
It was not a blind pick on the map to go to Drøbak as our main starting point. Drøbak is strategically chosen as former literature describes it as a type locality for a variety of the Norwegian sea slug species. Besides, the University of Oslo has its Marine Biology field station, with sleeping facilities, located here. Near the field station, there is also the – all famous – dive centre called Gylte, were many dive enthusiasts rent their gear, fill up their pressure tanks and go diving in the centres’ backyard. Not surprisingly one of the workers of Gylte is big sea slug enthusiast; let me introduce you to Tine Kinn Kvamme

Manuel Malaquias with Tine Kinn Kvamme
There was great excitement from both parties to finally meet in person and she was able to help us get in touch with other citizen scientists and explain in detail about all the species she encountered in the last years. The list was impressive,and a valuable contribution to our project;

Tine’s sea slug species check list for the area
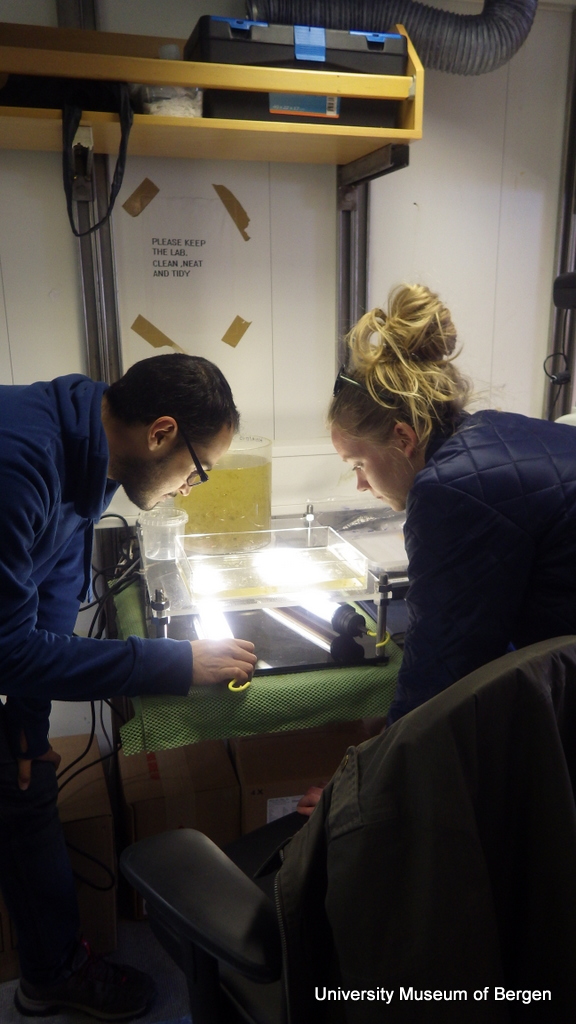
That week we managed to meet up with her several times, and she brought us more sea slugs. We introduced her to the laboratory facilities in the Marine field station, where she had the opportunity to look at her beloved Doto’s in detail with help of a microscope, while telling us more about other possible interesting locations and possibilities to collect different species! This is what it is all about, happy scientists and happy citizen scientists!
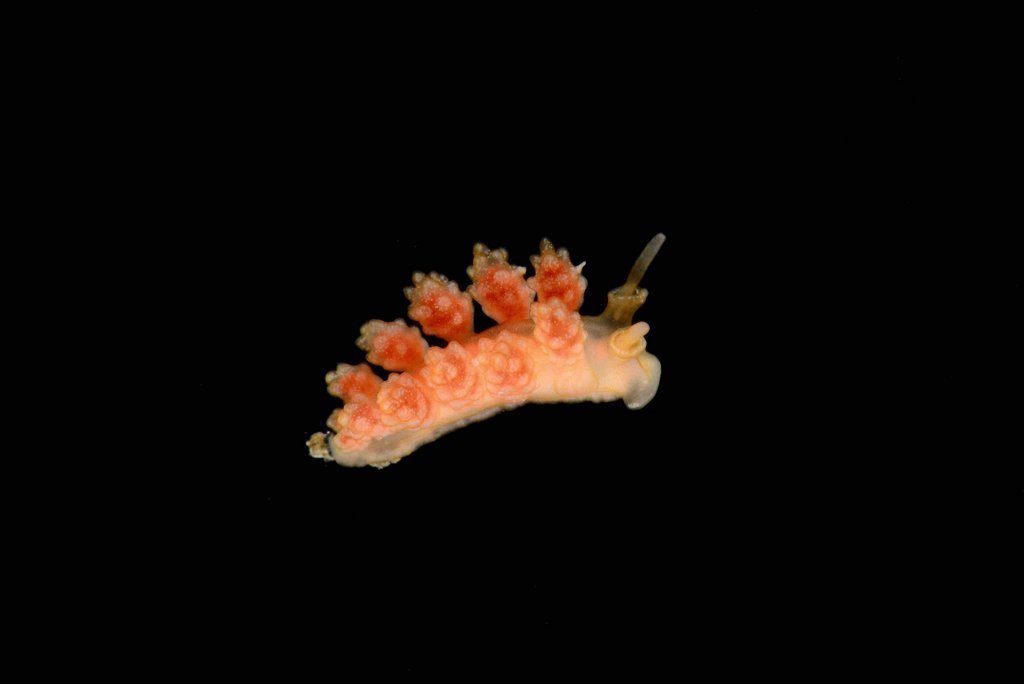
Doto fragilis
Two other members of our team that joined us during the length of our stay in Drøbak were the respected divers Anders Schouw (from Bergen) and famous underwater photographer Nils Aukan (from Kristiansund).

Anders Schouw showing his photography skills in the laboratory
It was an honour to be able to work together with them, Anders proved his photography skills both underwater and above water to be of incredible valuable input and Nils great knowledge of Marine life and amazing photography skills made me and Manuel blush on our cheeks more than we would like to admit. They both dived every single day during our stay and brought sea slugs back to the laboratory where we together could identify, photograph, measure and prepare them for transport back to Bergen. Nils Aukan is a known sensation within the Norwegian diving community and ever since the project started we have received many samples from him. He is able to photograph the species in their natural habitat capturing the tiniest details, a valuable asset to later identify the species properly.
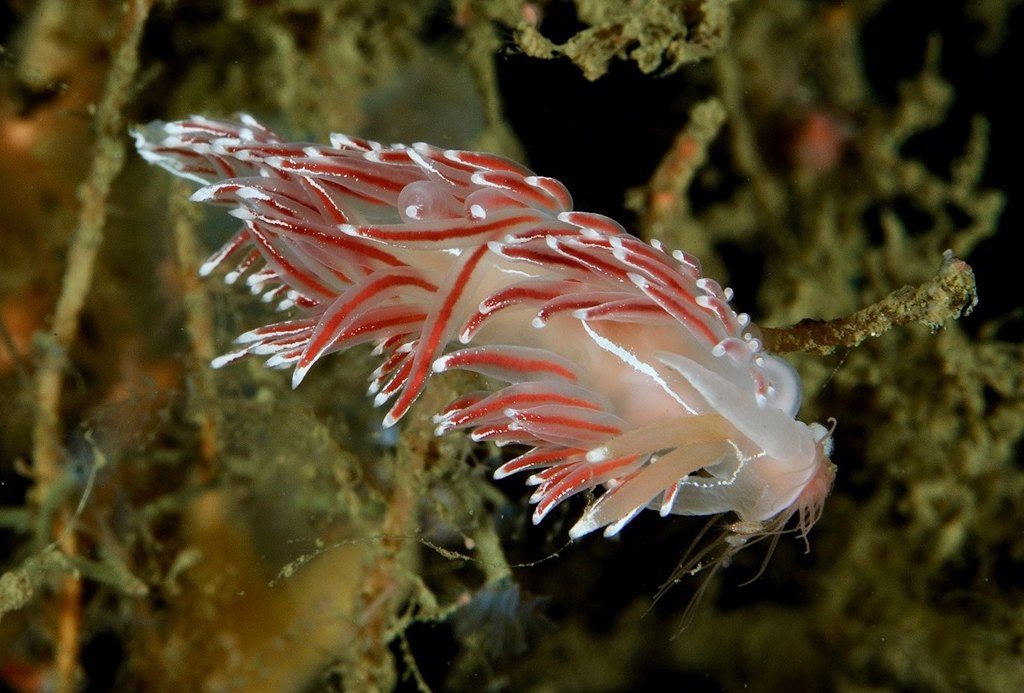

Fjordia lineata photographed by Nils Aukan
Anders is the guy every expedition need; he knows everyone, everywhere, and we’re very happy to announce his decision to join us in our next field work trip to Hagesund (in July, facilitated with a blog, obviously).
The gate to grass
At the spot we also met with the citizen scientist Roy Dahl, his son and Heine Jensen
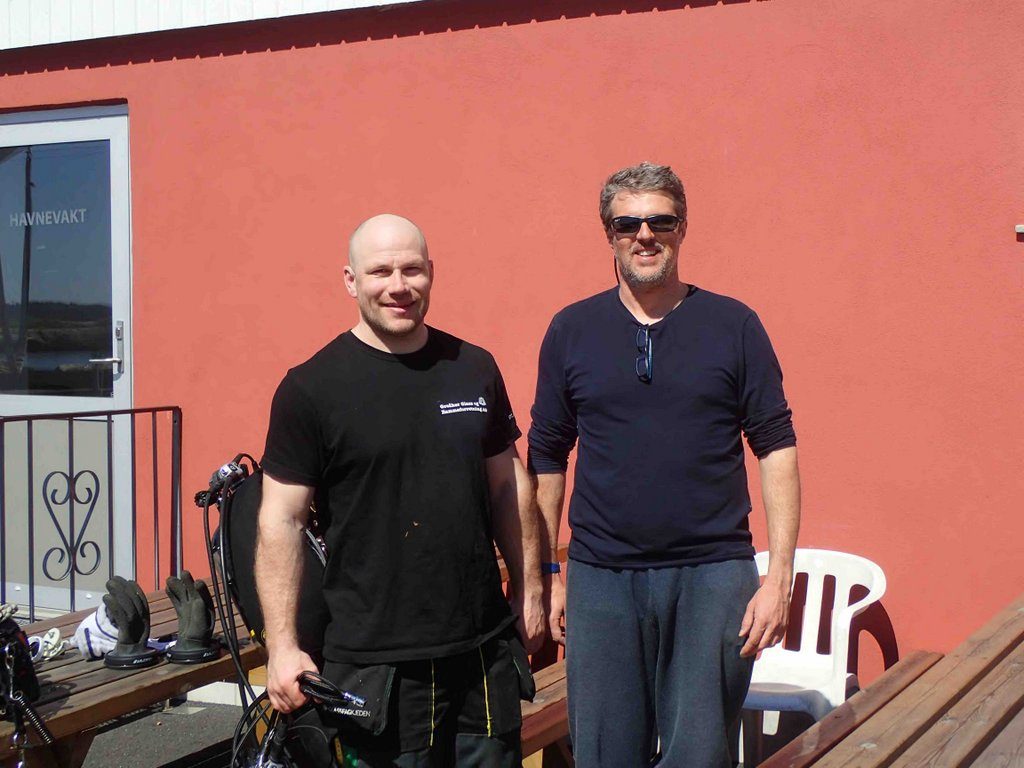

Heine Jensen with Manuel Malaquias
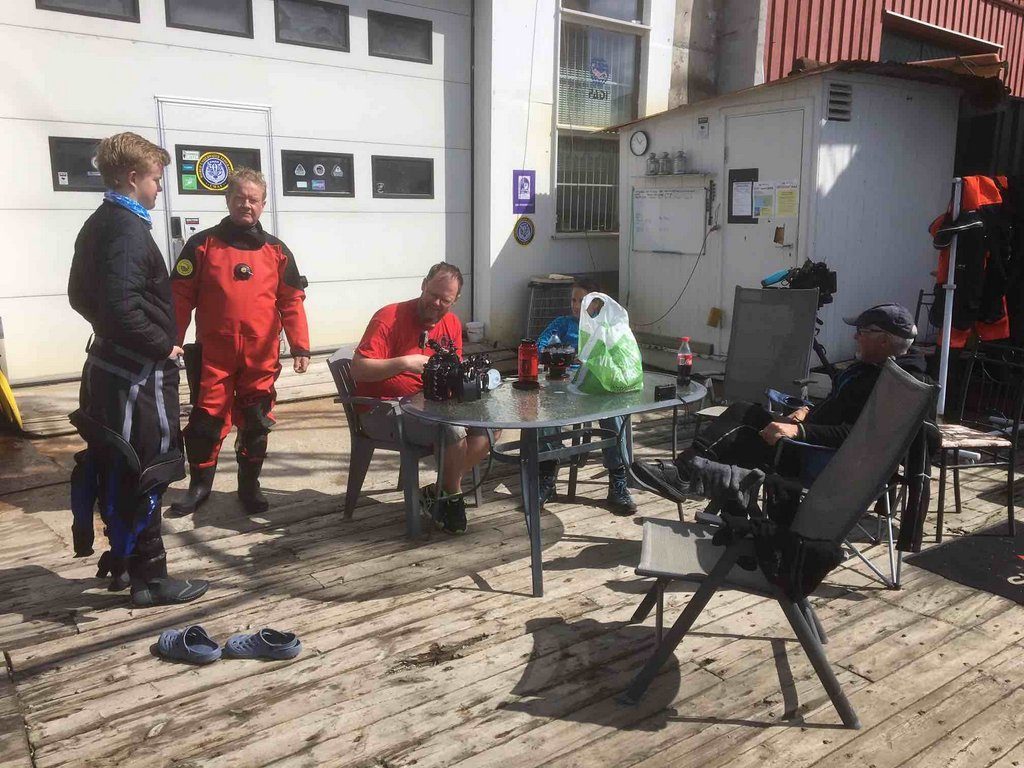

A snapshot of the group, from left to right; A snapshot of the group, from left to right; Roy Dahl’s son, Roy Dahl, Anders Schouw, Cessa Rauch and Nils Aukan
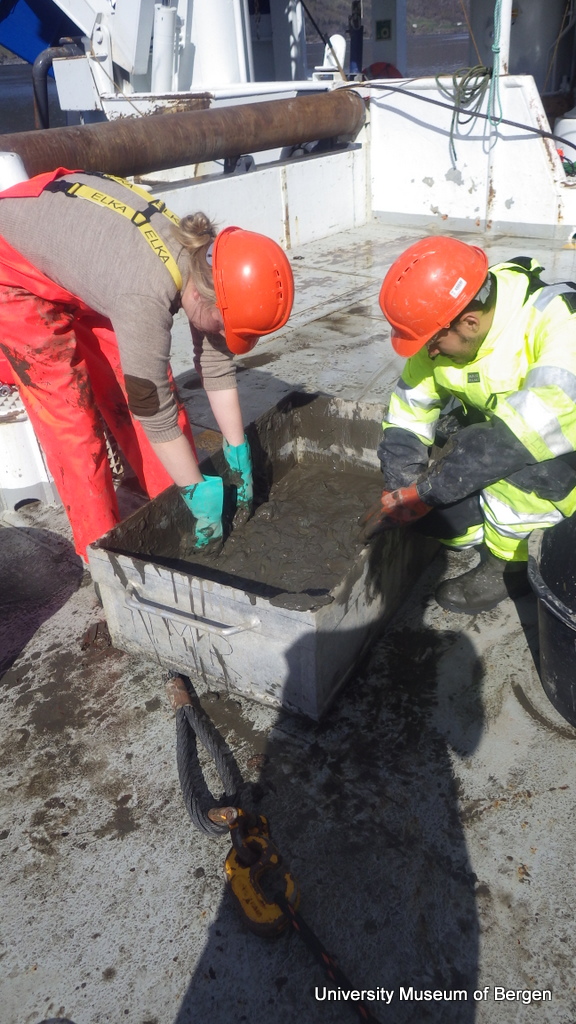
Roy and Heine have been collaborating and sampling for us in the Oslofjord area. They know their favourite diving spots on the back of their hands and shared with us all the details one needs to know about the sea slugs’ habitat. They knew about species diversity, where to find but also when to find them. There is some change in sea slugs’ diversity when it comes to different times of the year, some species thrive just before spring starts, others are more regularly seen throughout the summer. All interesting and valuable information for us in order to see the bigger picture. Most diving spots were easy accessible and well facilitated, but sometimes the hunt for different habitats does not always favour you in a laidback access to the water. Manuel and I were a little obsessed with probing for sea slugs within the seagrass meadows of the Oslofjord. You never know what you can find there! Healthy seagrass meadows are the nursery, hiding, and hunting ground of many marine organisms, and we would not let the opportunity to study this habitat pass by!
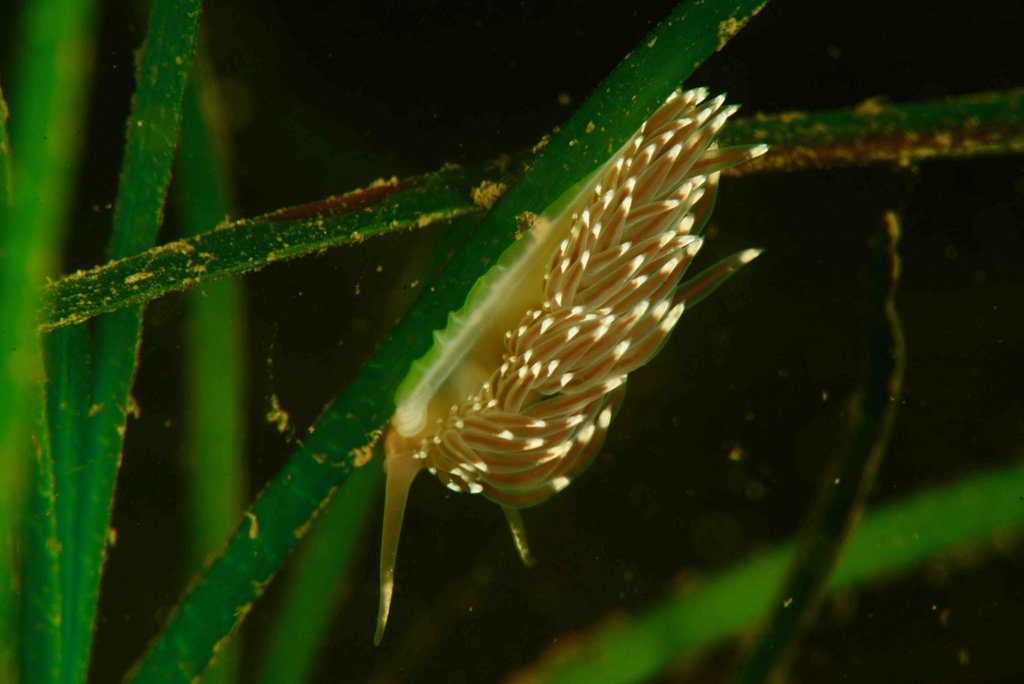

Facelina bostoniensis on sea grass photographed by Anders Schouw
Anders was able to find an area of seagrass that seemed to be accessible from the Google maps point of view. But was it in real life though? After driving around, back and forwards for almost an hour we sadly realized that the only land access was through a private condo, closed by a gate and inaccessible to us. Whilst driving around a little unsure about what the next plan of action would be, Anders decided to use his communication skills to find out if there was another way. By a matter of luck, chance, sign – you name it – Anders asked the way to a person that happen to live there and to have a remote device that could open the gate giving us access to the park. All together it took us a whole afternoon to figure out how to get to the seagrass meadow and I think we can vote for Heine Jensen as our most patient citizen scientist! As we were driving in many circles to find the sea grass meadows, Heine jokingly mentioned, ‘look, there is grass just next to the road, why don’t we look for our slugs there’. We definitely own him one for his stamina!
You reap what you sow
After 10 days the sea slug teller was on approximately 39 species, and this without the species collected by the citizen scientists before our fieldtrip. All together we have so far assembled 43 species from areas in the Oslofjord. The work has just begun, and as a consequence of our successful actions in Drøbak, we now have to face the mountain of work waiting; structuring our harvest and make some sense of it all in the light of evolution.
For frequent updates, awesome images, and much more information about sea slugs in Norway than you ever imagined encountering, join the projects Facebook group
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our collaborators during this project; Torkild Bakken from Trondheim University who was also part of the Drøbak team for a few days, and our dedicated citizen scientists; Anders Schouw, Nils Aukan, Tine Kinn Kvamme, Roy Dahl and Heine Jensen. We hope that during the two years of this project we will have many more chances to meet and that our teamwork continues to be fruitfully!
By Cessa Rauch and Manuel Malaquias
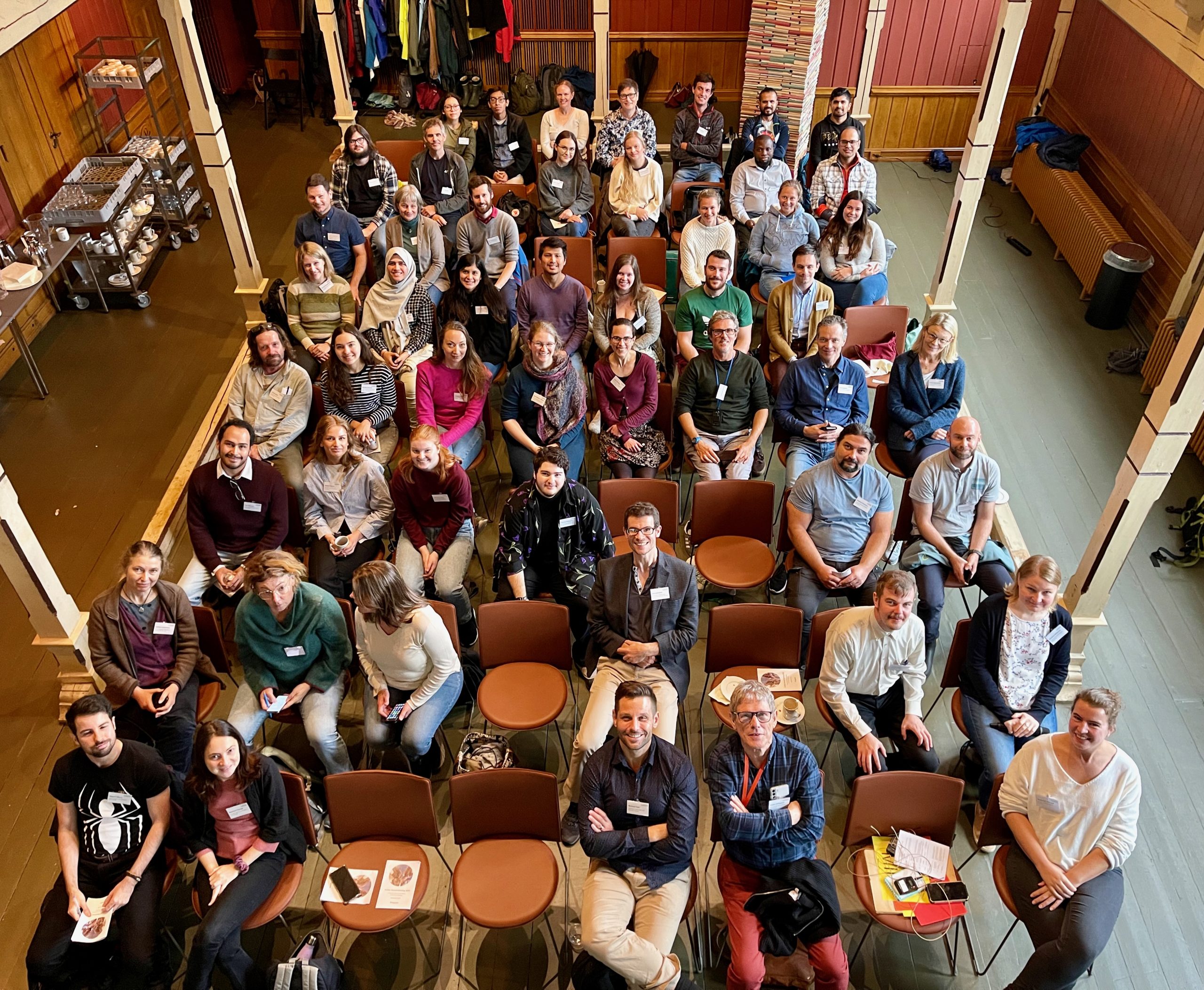
 Sixty participants from Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Czech Republic, Poland, Germany and Peru presented their research results in various fields of biosystematics.
Sixty participants from Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Czech Republic, Poland, Germany and Peru presented their research results in various fields of biosystematics.