Follow us at @planetcopepod!
Tuesday may 19 was the first fieldwork of the new project called Hyperbenthic Copepoda (HYPCOP). You can read more about the field work and see some photos and videos from the field in the previous blog post.
 Copepoda are small crustaceans that are found all over the world in both marine and freshwater habitats. Species can be planktonic (drifting in the sea water) or can be parasitic and a large diverse group of them live on algae in the hyperbenthic (living near the bottom) zone. Copepoda are very important food source for many organisms like small fish, they are on the bottom of the food pyramid, together with other zooplankton. Without copepods, a lot of bigger animals would no exists. Despite being so important, not much is known about the biodiversity and taxonomy of these animals, especially that of the species that live near the bottom.
Copepoda are small crustaceans that are found all over the world in both marine and freshwater habitats. Species can be planktonic (drifting in the sea water) or can be parasitic and a large diverse group of them live on algae in the hyperbenthic (living near the bottom) zone. Copepoda are very important food source for many organisms like small fish, they are on the bottom of the food pyramid, together with other zooplankton. Without copepods, a lot of bigger animals would no exists. Despite being so important, not much is known about the biodiversity and taxonomy of these animals, especially that of the species that live near the bottom.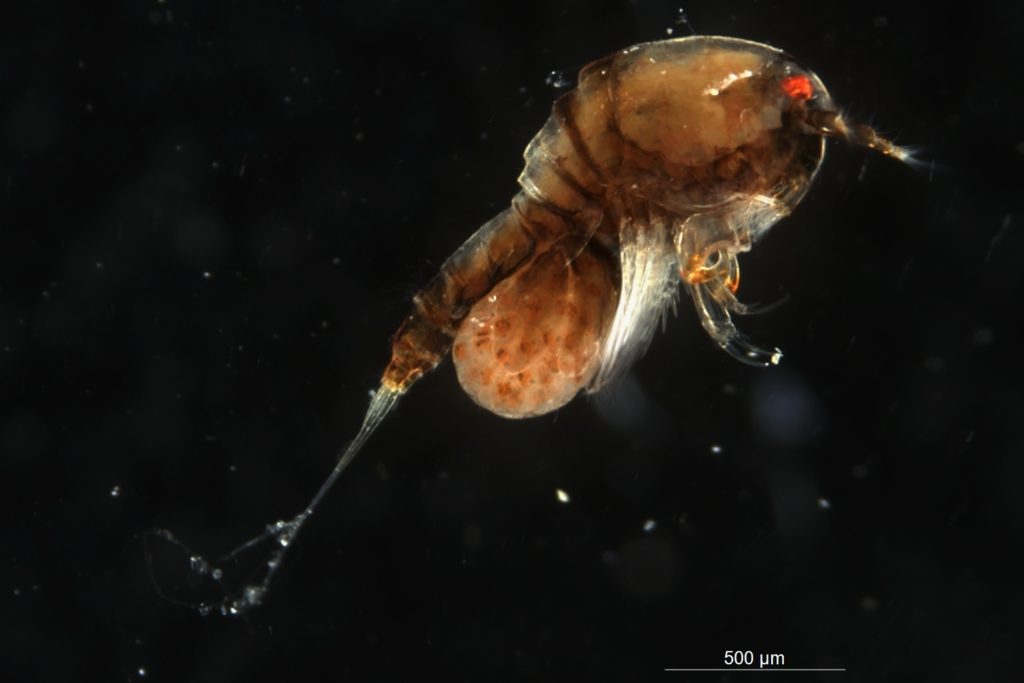 Some species like Calanus finmarchicus are the main nutritional basis for many fish species, and therefore of great importance for the Norwegian fish strains. Therefore Artsdatabanken is funding the new project HYPCOP in order to unravel the biodiversity and taxonomy of hyperbenthos copepods. With special focus on the species in the group Harpacticoida that live in the water masses just above or near the bottom. Copepods from shallow water will be collected in coastal areas, in deep fjords and on the continental shelf.
Some species like Calanus finmarchicus are the main nutritional basis for many fish species, and therefore of great importance for the Norwegian fish strains. Therefore Artsdatabanken is funding the new project HYPCOP in order to unravel the biodiversity and taxonomy of hyperbenthos copepods. With special focus on the species in the group Harpacticoida that live in the water masses just above or near the bottom. Copepods from shallow water will be collected in coastal areas, in deep fjords and on the continental shelf.
The Institute of Marine Research (IMR), Natural history museum of Bergen (UiB), Norwegian Institute for water research (NIVA) and the Norwegian Barcode of Life (NorBoL) are working together to survey the diversity of marine copepods in Norwegian waters and expect to find and describe species that are new to science and new for Norway! Currently some of the taxonomic competence in Norway is lacking, but through collaboration with foreign experts this knowledge will increase among Norwegian researchers and students!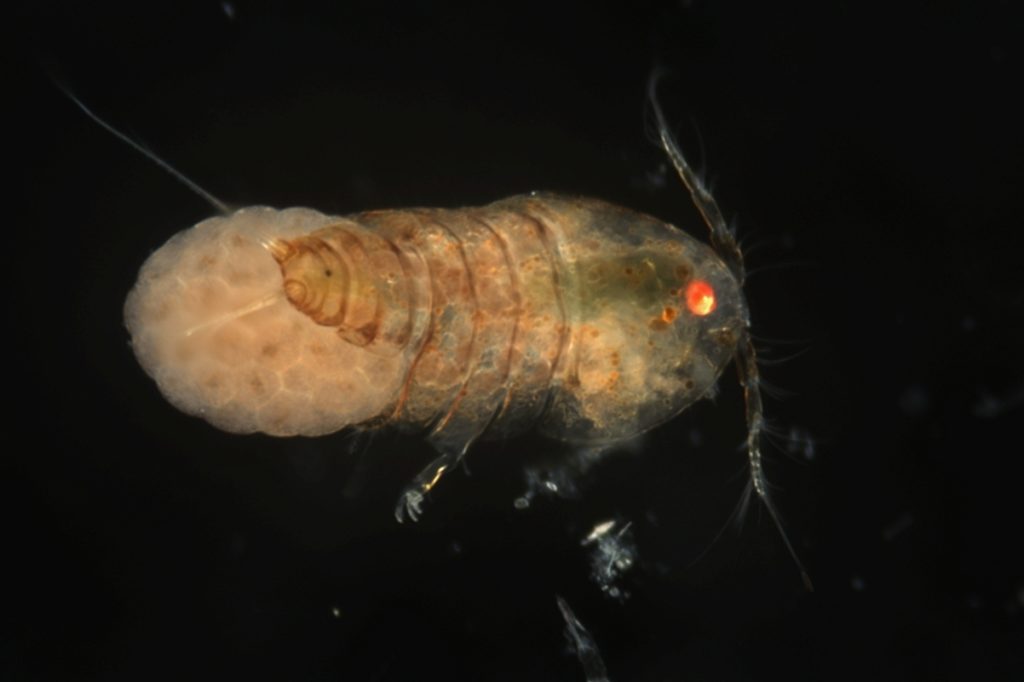
The projects duration will run from 2020 until 2023 and last week was the official kickoff with some fieldwork to get fresh material to work with! Together with the project Hardbunnsfauna we drove to a local favorite collection site of us; Biskopshavn; very close to Bergen city center. Around the hard substrate we found lots of freshly grown algae that contained many small animals for us to collect! In order to get good quality samples we needed to be in the water and snorkel. With plankton nets we collected algae and sieved the water column catching the smallest of the animals; copepods!
And even though this was just a first test of equipment and collection methods, it was not without success. Back in the lab the microscope revealed the beautiful and diverse world one drop of seawater contains. A lot off small crustaceans and of course the copepods were omnipresent.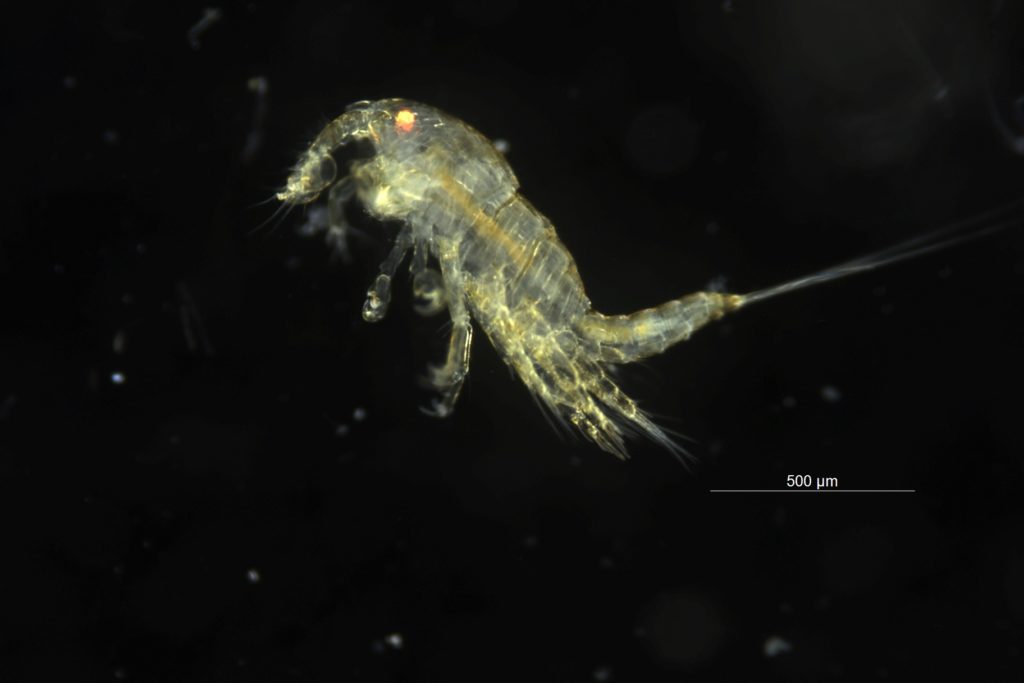
Our findings had to be shared and especially for #InternationalDayForBiologicalDiversity the copepods cannot be left out as they from such an important group! See for yourself the beauty of our copepod planet!
-Cessa