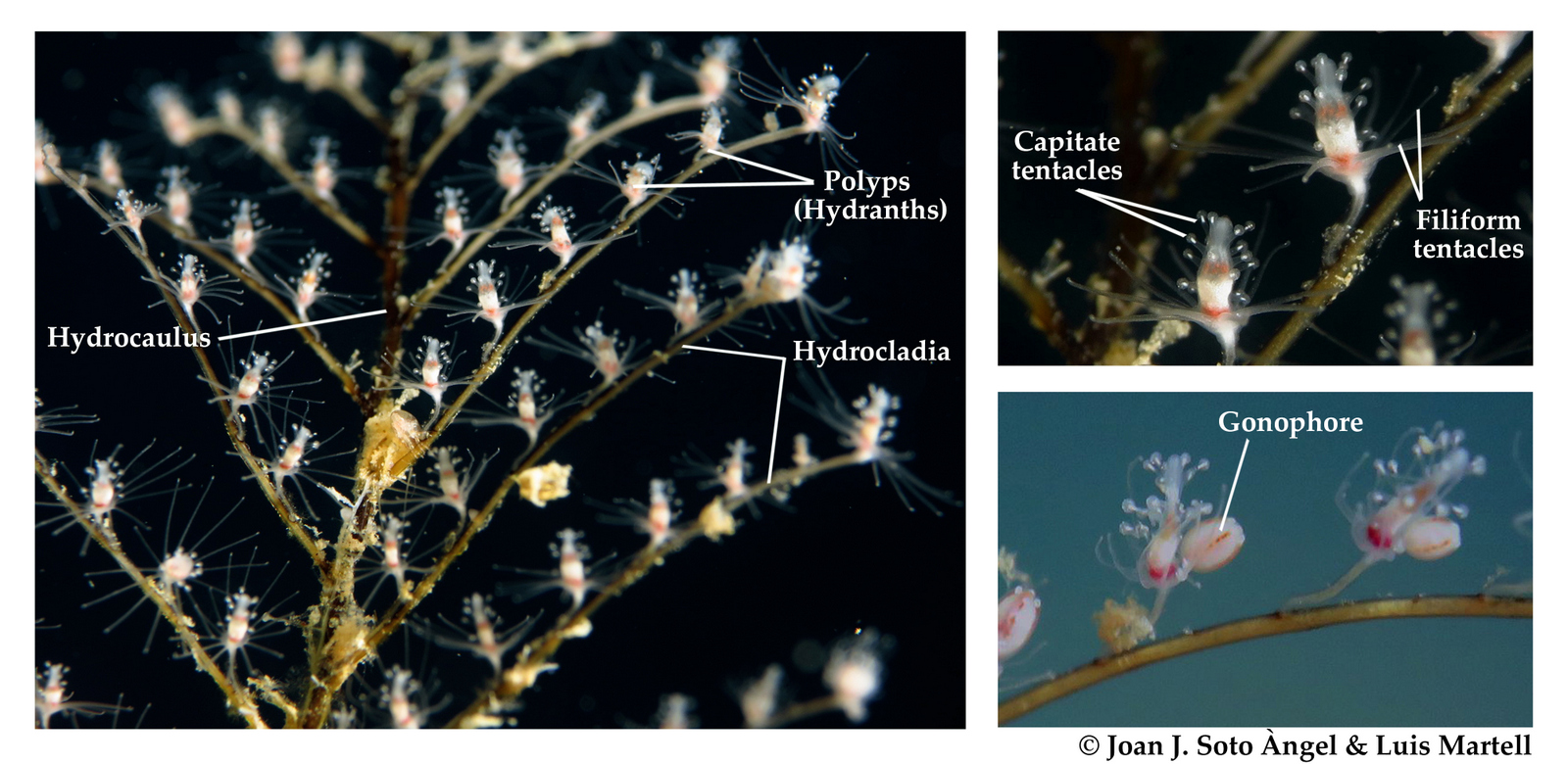
The study of molluscs (malacology) has a long tradition in Norway. Despite the nearly 50,000 species dwelling in the world oceans and seas, a number only barely supersede by the arthropods, new species continue to be discovered and our understanding of the relationships and systematics of molluscs to change.
-
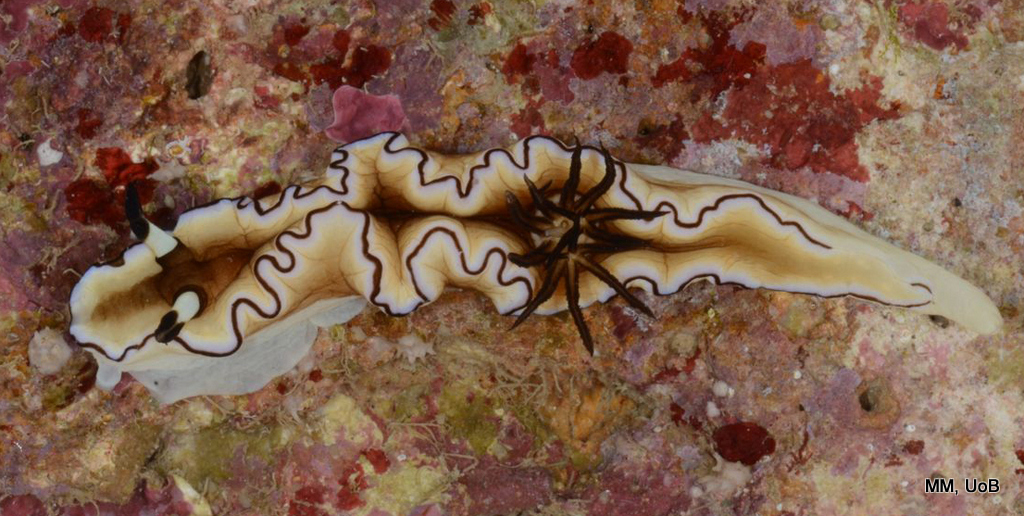

-
Glossodoris sp.
-
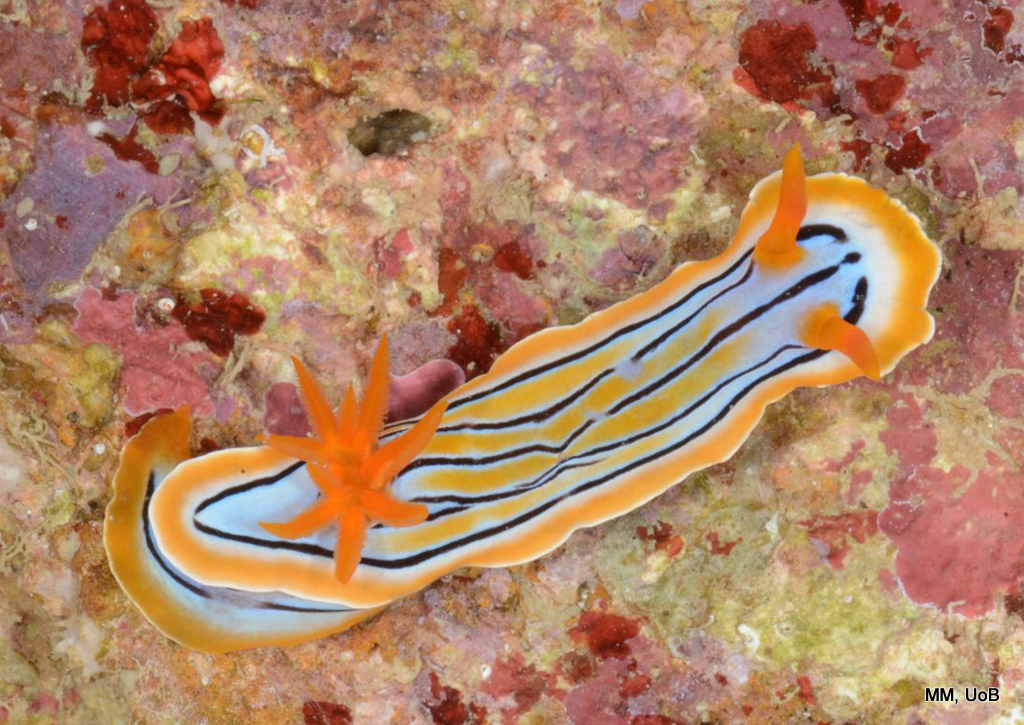

-
Chromodoris sp.
-

-
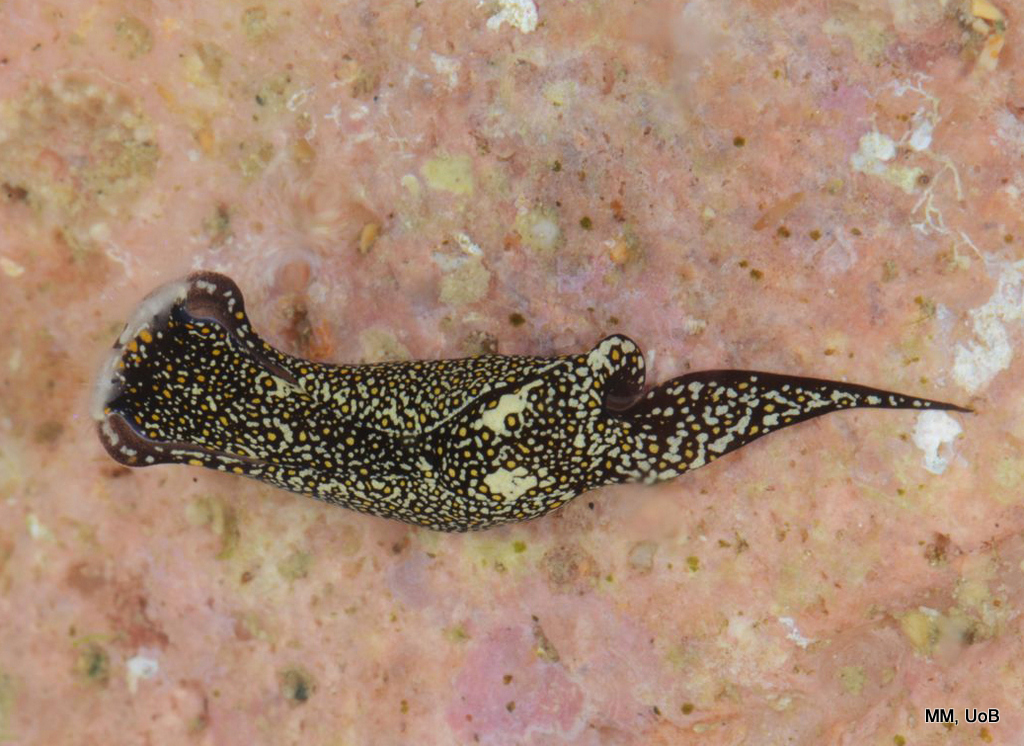
Chelidonura sandrana
At the Natural History Museum of Bergen, the study of molluscs is focal, and research is carried out on various aspects of their diversity, morphology, ecology, systematics, evolution, and biogeography, using state of the art methods like DNA barcoding, molecular phylogenetics, and electron microscopy. Understanding the patterns and processes that drive present diversity in the oceans is one of our main goals and our research foci are framed within several “big questions”: How many and how can we differentiate between species? How do species originate in the oceans? Why some regions in the oceans are more diverse than others? Are mechanisms responsible for the patterns of diversity in the deep-sea the same as in shallow ecosystems?
Our quest for answers necessitate the continuous collection of new specimens and the exploration of remote geographies. We conduct regular fieldwork around the world including Norway, through numerous projects and partnerships.
Here are some snapshots from recent fieldwork from Manuel & team:
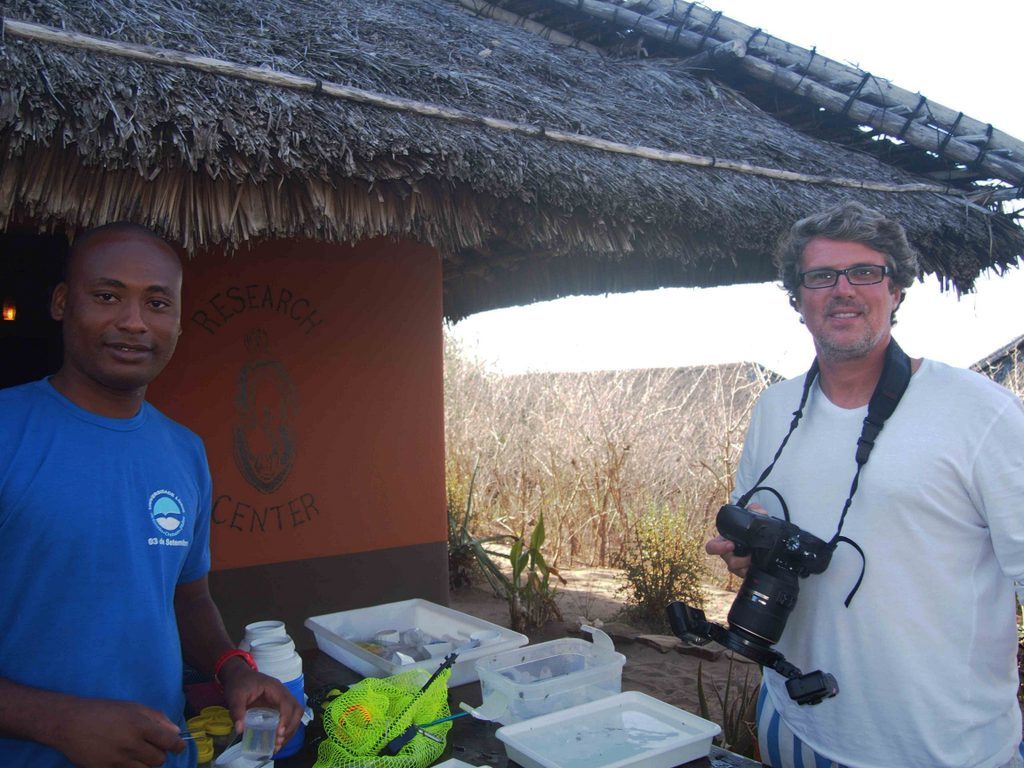

Working during October 2017 together with Professor João Macuio from the University Lurio (Pemba, Mozambique) in Nangata Bay (Nuarro, Mozambique) on a survey of the sea slug diversity inhabiting this pristine coral reef area and on an assessment of the structure and conservation status of the population of the threatened giant clam species (Tridacna maxima). Left image: Manuel Malaquias and João Macuio photographing sea slugs at the Nuarro Research Center.
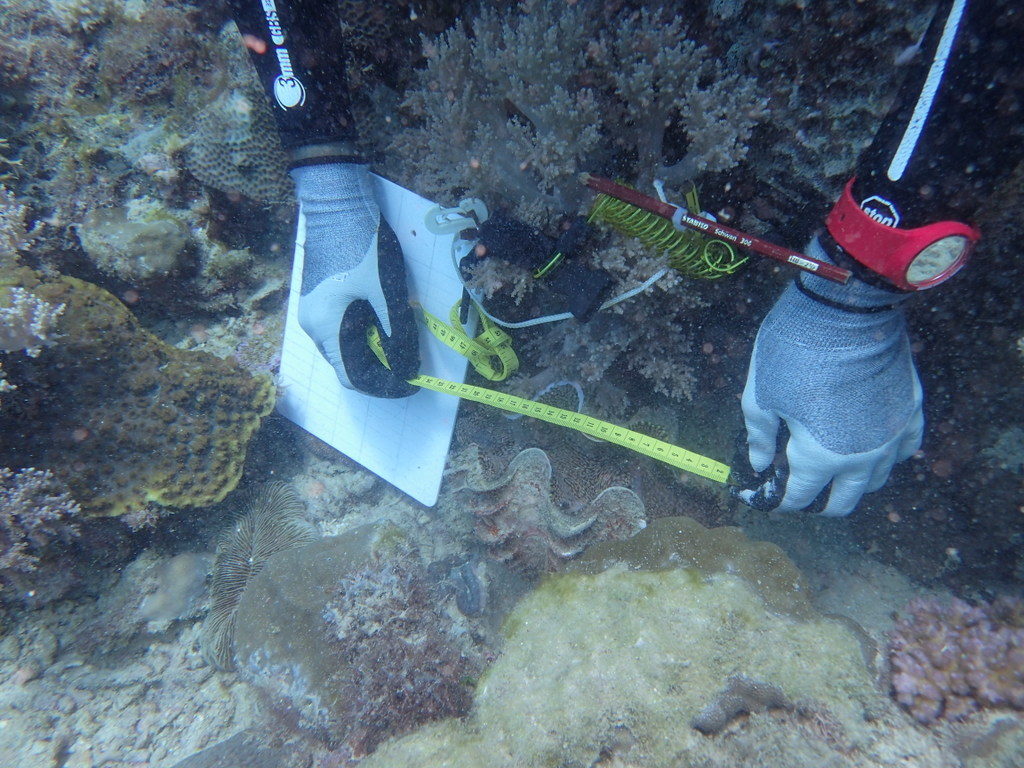

João Macuio measuring underwater the total length of a specimen of the giant clam Tridacna maxima
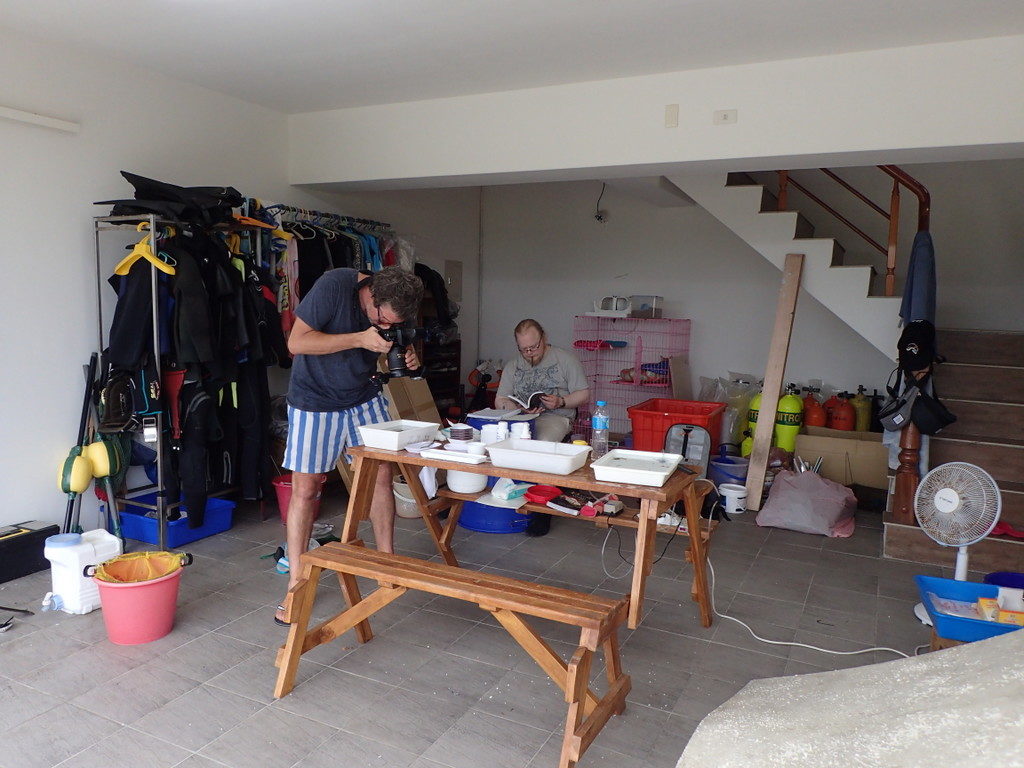

Working in remote places requires often some capacity to improvise and during a fieldtrip to Taiwan while in the Penghu islands we had to convince the manager of our hostel to let us set up a field-lab in the garage among his gear and pet-cage!
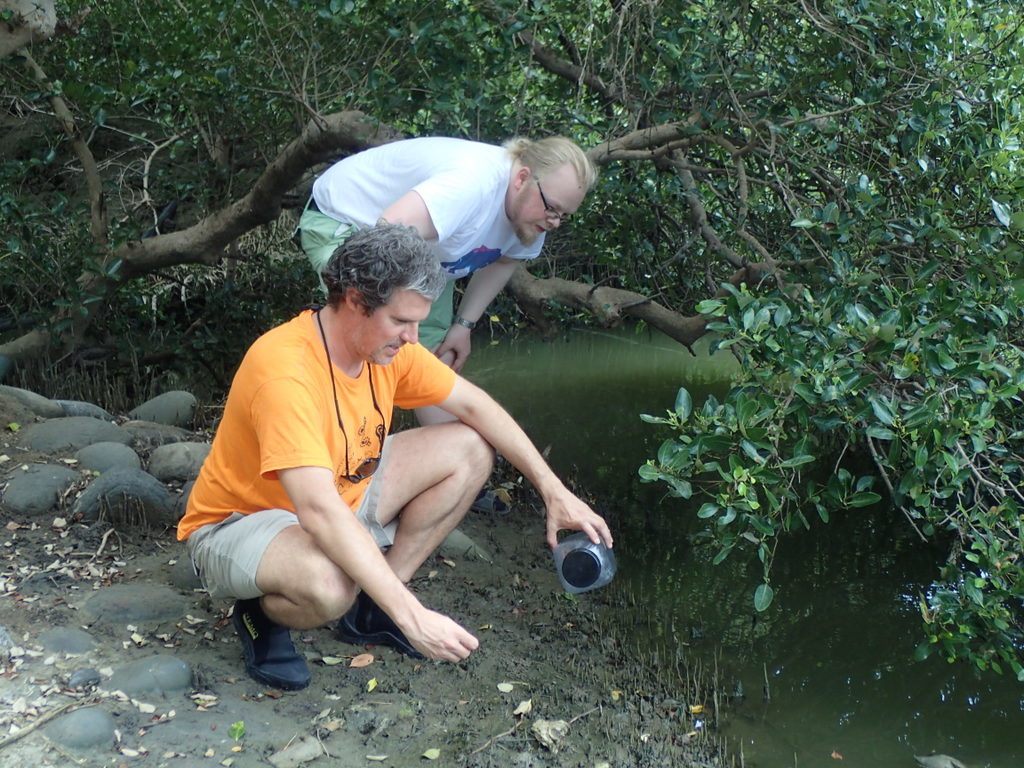

Manuel and Trond Oskars, PhD candidate at the Museum, searching for molluscs during May 2017 at mangrove systems near the city of Kaohsiung, Taiwan
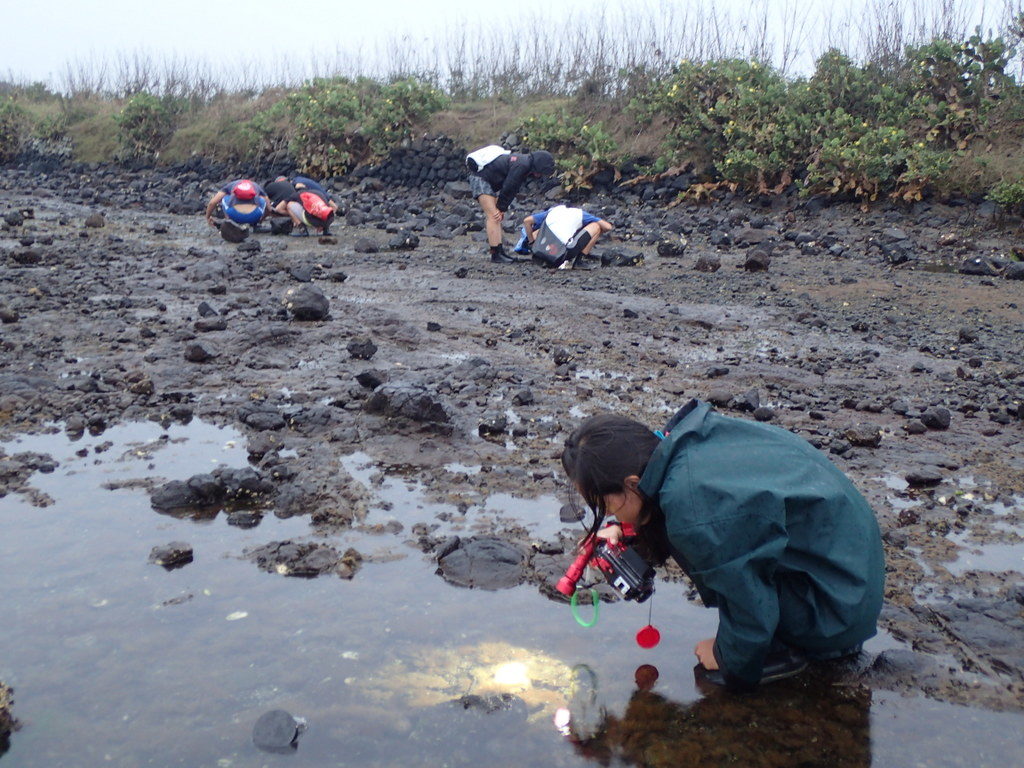

In the Penghu islands we had the opportunity to work in the field together with students from the National Penghu University of Science and Technology, here depicted in the right image helping collecting sea slugs along a water stream lined by few mangrove bushes.
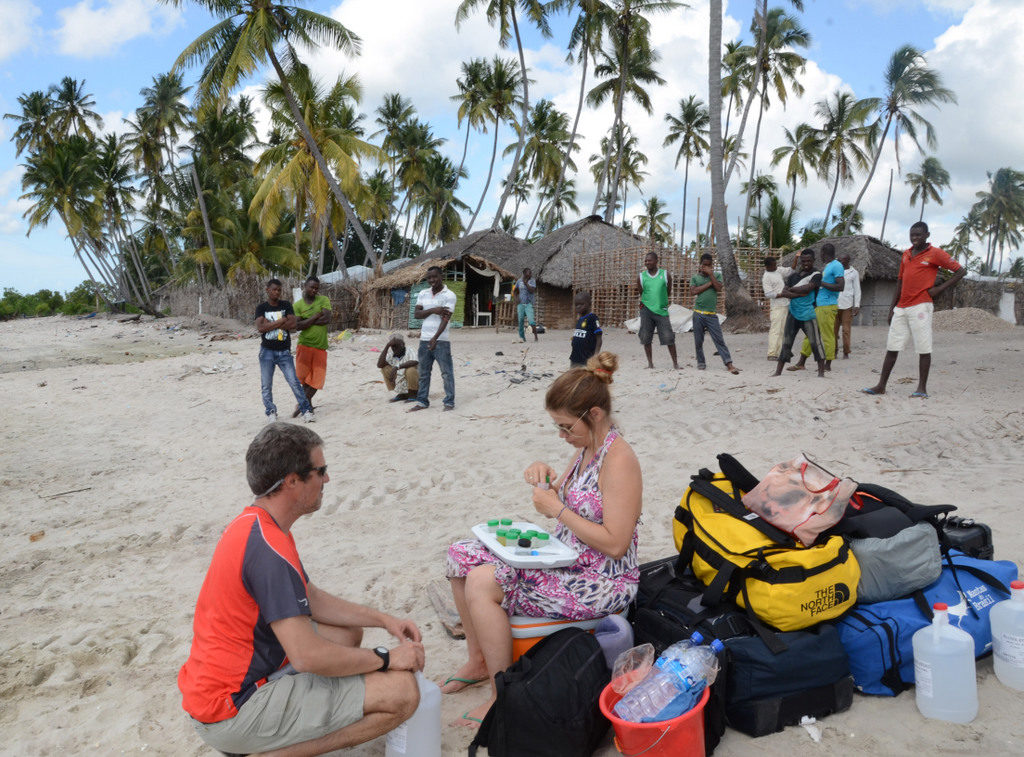

After a three weeks fieldtrip to Vamizi island in the Quirimbas archipelago, north of Mozambique during May 2015, we were finally brought to shore at Palma village near the border with Tanzania where we had to do some final sorting and organization of samples under the curious eyes of the local villagers (Manuel Malaquias and Yara Tibiriça from the Zavora Marine Lab in Mozambique).
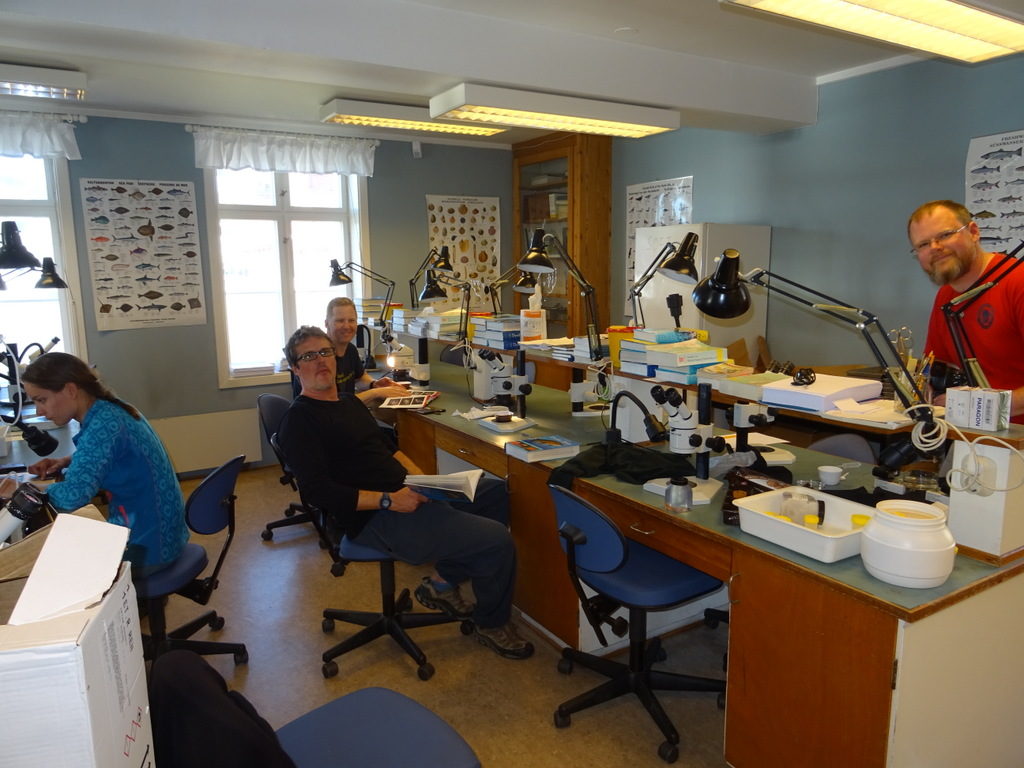

Fieldwork during May 2018 in the Oslo fjord as part of the project “Sea slugs of southern Norway” funded by Artsdatabanken. Left image: part of the team working through the catch of the day at the Tolboden Course Center in Drøbak, University of Oslo (left to right: Cessa Rauch, Manuel Malaquias, Torkild Bakken, Anders Schouw)
You can read more about some of these expeditions by exploring the posts found here (workshops) and here (fieldwork).
–Manuel
 For door #4 we are helping spread word about the 8th International Barcode of Life Conference, which will take place in Trondheim, Norway on June 17-20th next year.
For door #4 we are helping spread word about the 8th International Barcode of Life Conference, which will take place in Trondheim, Norway on June 17-20th next year.