Does that not sound appealing?
It was actually a lovely event!
The IPC2016 logo © National Museum Wales
The 12th International Polychaete Conference took place in Cardiff, Wales during the first week of August. These events have been taking place every third year since 1981, and the previous one was in Sydney, Australia in 2013.
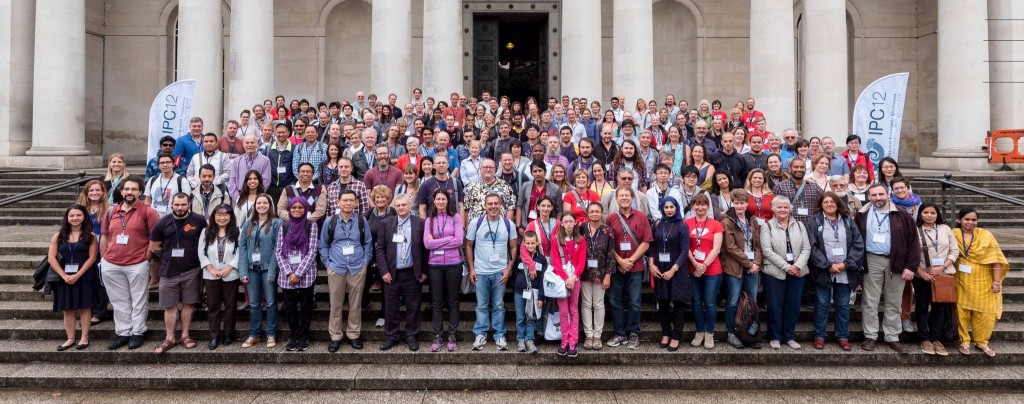

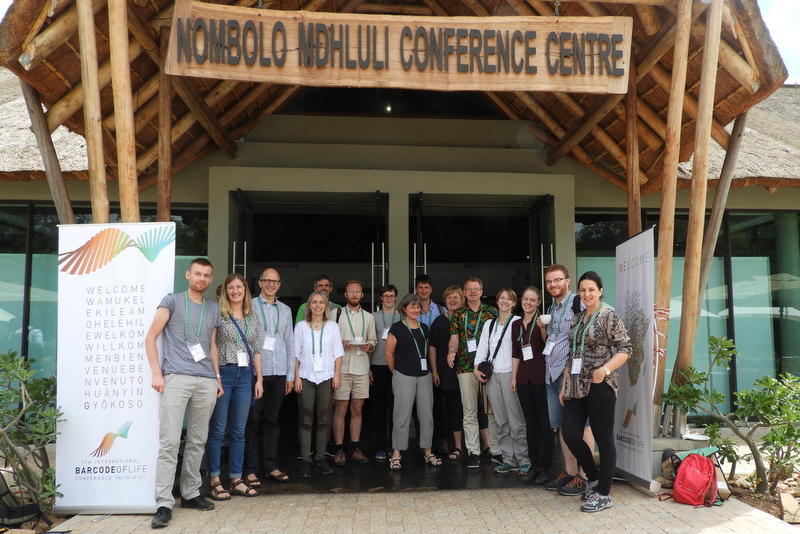
Polychaetologists anno 2016 assembled on the steps of the National Museum Cardiff © National Museum Wales
During an intensive week of presentations and posters spanning topics within Systematics, Phylogeny, Ecology, Methodologies, Biodiversity, Biodiversity and Ecology, Morphology, Reproduction & Larval Ecology, Development, and Polychaete studies, people had the chance to showcase their work, and learn more about what others are working on. The local organising committee invited us to “Have a happy conference, re-connecting with those already known, meeting correspondents for the first time, ans making new connections and new friends” – and I think we can safely say that the mission was accomplished!
Cardiff – and the National Museum Wales – was an excellent venue for “polychaetologists” from all over the globe.

Snapshots of Cardiff (photos: K.Kongshavn)
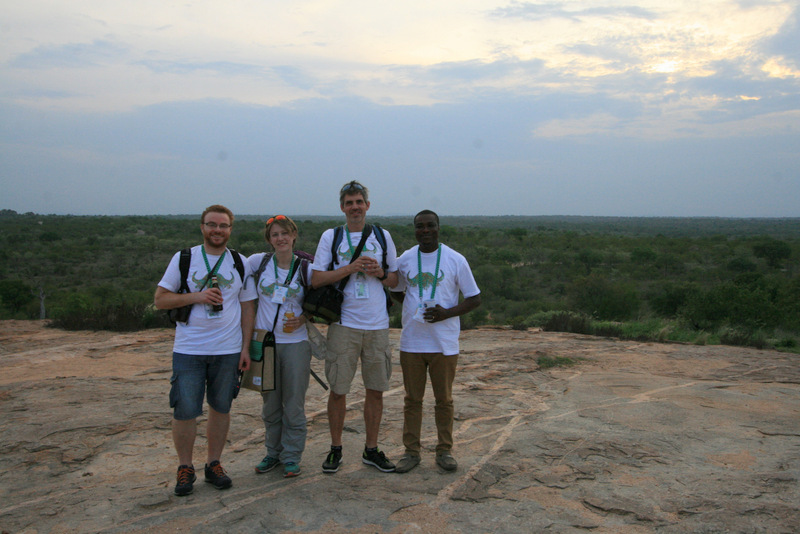
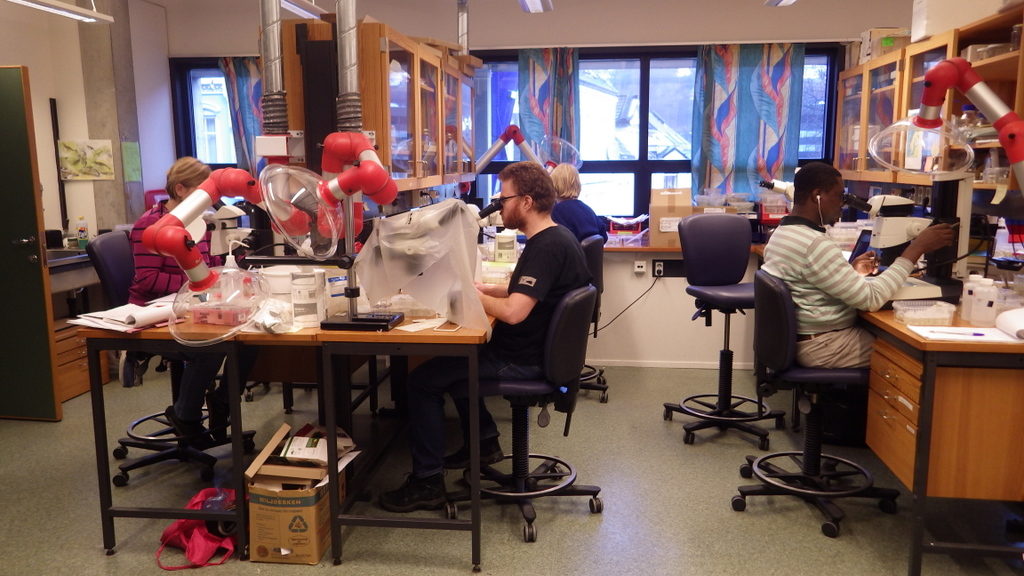
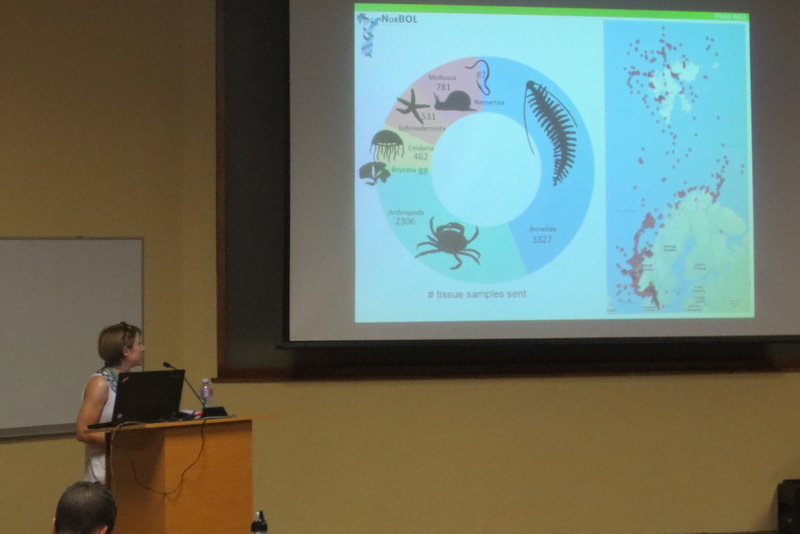
In all we were 190 attendees from about 30 countries present – including a sizeable Norwegian group! Some of us (below) gave talks, and most were also involved in posters. Results and material from large projects and surveys such as PolyNor (Polychaete diversity in Nordic Seas), MAREANO (Marine AREA database for NOrwegian waters), NorBOL (The Norwegian Barcode of Life), and MIWA (Marine Invertebrates of West Africa) were all well incorporated in the Norwegian contributions.
-

-
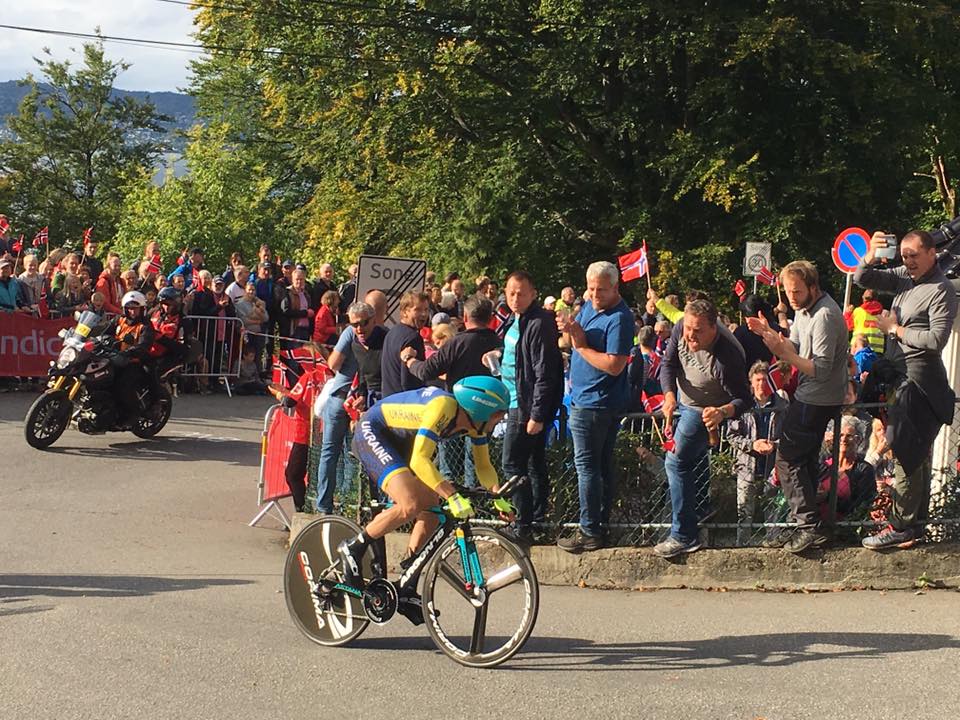
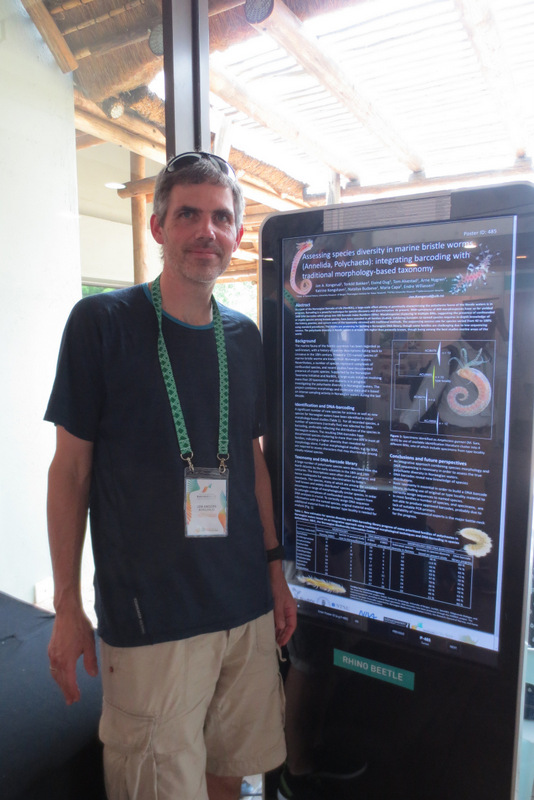
Torkild
-
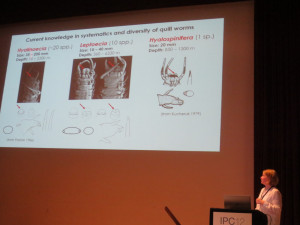
-
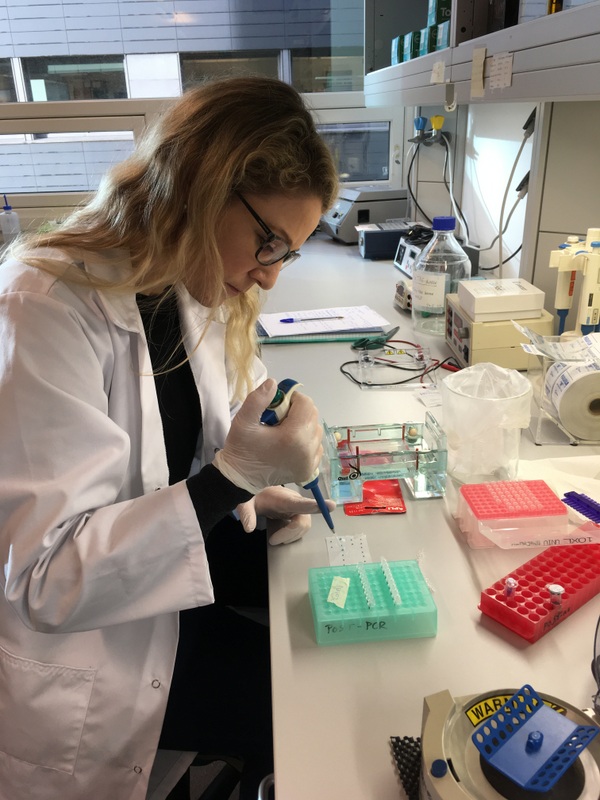
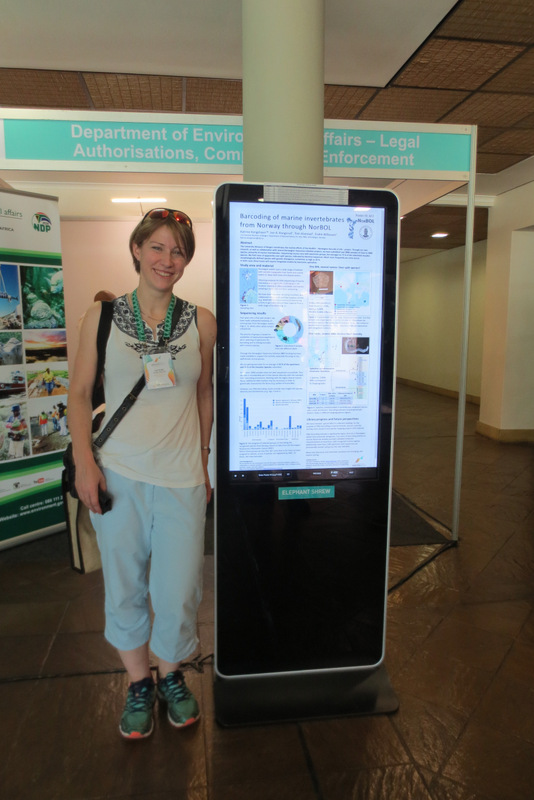
Nataliya
-

-
Martin
-

-
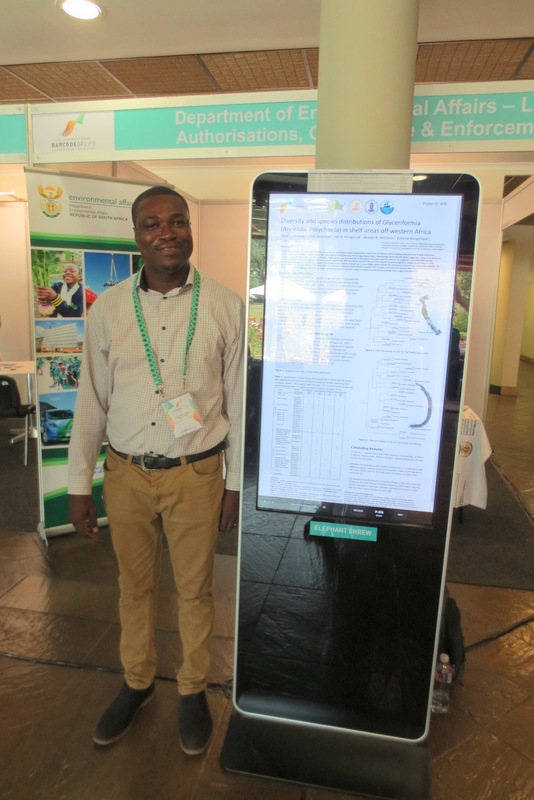
Katrine
There were in fact a lot of contributions involving one or more collaborators from a Norwegian institution (UM, NTNU, NIVA, The SARS center, NHM Oslo, Akvaplan-NIVA ++) being presented during the conference. It is really nice to see that the community is growing through recruitment of both students and international researchers.
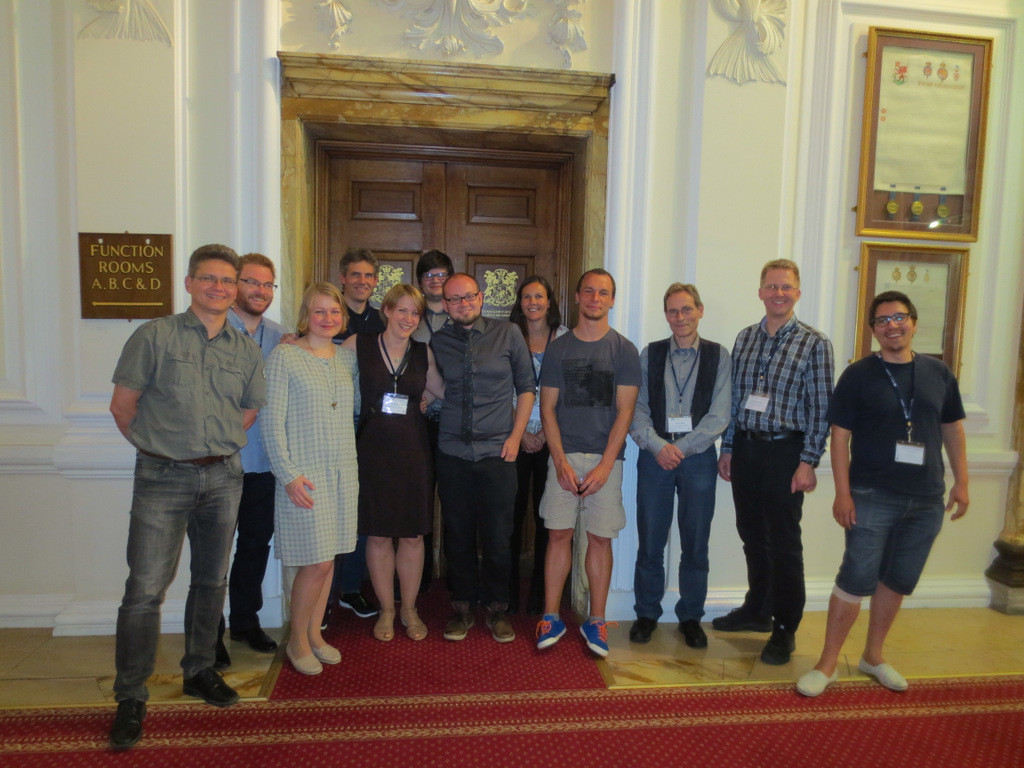

Norwegian delegates lining up in the City Hall before the start of the banquet
As Torkild said in his excellent blog post (in Norwegian, translation by me):
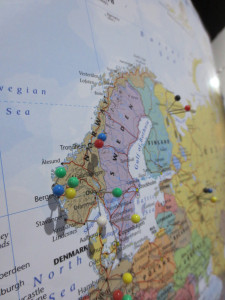
Pins marking where participants come from – this was not quite completed when the photo was taken, but none the less..well represented!
With so many active participants in the field, a lot of exciting research is being carried out in Norway. Not only do we have many projects – large and small – running at our institutions involving our “regular” Norwegian collaborators; there is also a significant proportion of international participation in these projects.
Furthermore, our activities enable researchers from all over the world to visit or loan from our scientific collections, and study the substantial (new) material that the projects are generating. It is nice to see that our efforts are being recognized in the international community! The recent flurry of activities has been well aided by the Norwegian Species Initiative (Artsprosjektet) (and the MIWA-project at UM).
The majority of our research is based on, or incorporates, museum material from our collections. The collections have been built over years, decades and even centuries, and continue to increase in scientific value as new science is added.
It is gratifying to see the material being used, and we hope it will gain even more attention in the aftermath of the conference.

From the poster session – these are some (!) of the posters we were involved in (photos: K.Kongshavn)
The University Museum was well represented, both in attendance, and in contributions. Below is a list of what we (co-)authored, presenting author is in bold, and University Museum people are in italics. We plan on posting some of the posters here, so stay tuned for that!
Presentations:
- Giants vs pygmies: two strategies in the evolution of deep-sea quill worms (Onuphidae, Annelida)
Nataliya Budaeva, Hannelore Paxton, Pedro Ribeiro, Pilar Haye, Dmitry Schepetov, Javier Sellanes, Endre Willassen
- DNA barcoding contributing to new knowledge on diversity and distribution of Polychaeta (Annelida) in Norwegian and adjacent waters
Torkild Bakken, Jon A. Kongsrud, Katrine Kongshavn, Eivind Oug, Tom Alvestad, Nataliya Budaeva, Arne Nygren, Endre Willassen
- Diversity and phylogeny of Diopatra bristle worms (Onuphidae, Annelida) from West Africa
Martin Hektoen, Nataliya Budaeva
- Experiences after three years of automated DNA barcoding of Polychaeta
Katrine Kongshavn, Jon Anders Kongsrud, Torkild Bakken, Tom Alvestad, Eivind Oug, Arne Nygren, Nataliya Budaeva, Endre Willassen
Posters
- Diversity and species distributions of Glyceriformia in shelf areas off western Africa
Lloyd Allotey, Akanbi Bamikole Williams, Jon Anders Kongsrud, Tom Alvestad, Katrine Kongshavn, Endre Willassen
- Eclysippe Eliason, 1955 (Annelida, Ampharetidae) from the North Atlantic with the description of a new species from Norwegian waters
Tom Alvestad, Jon Anders Kongsrud, Katrine Kongshavn
- Phylogeny of Ampharetidae
Mari Heggernes Eilertsen, Tom Alvestad, Hans Tore Rapp, Jon Anders Kongsrud
- Ophelina (Polychaeta, Opheliidae) in Norwegian waters and adjacent areas – taxonomy, identification and species distributions
Jon Anders Kongsrud, Eivind Oug, Torkild Bakken, Arne Nygren, Katrine Kongshavn
- Pista Malmgren, 1866 (Terebellidae) from Norway and adjacent areas
Mario H. Londoño-Mesa, Arne Nygren, Jon Anders Kongsrud
- Lumbrineridae (Annelida, Polychaeta) from Norwegian and adjacent waters with the description of a new deep-water species of Abyssoninoe
Eivind Oug, Katrine Kongshavn, Jon Anders Kongsrud
- Nephtyidae (Polychaeta, Phyllodocida) of West African shelf areas
Ascensão Ravara, Jon Anders Kongsrud, Tom Alvestad
- Phylogeny of the family Maldanidae based on molecular data
Morten Stokkan, Jon Anders Kongsrud, Endre Willassen
We had a mid-week excursion where we got to see a bit more of our hosting country; namely the impressive Caerphilly Castle constructed in the 13th century and still looking magnificent today, and a lovely lunch at the Llanerch wineyard with time for informal mingling and catching up.

Caerphilly Castle (photo: K.Kongshavn)
Note the red dragon in the Castle wall; this is the dragon of the Welsh flag. The story goes something like this (according to Wikipedia, at least!): From the Historia Brittonum,[2] written around 830 a text describes a struggle between two serpents deep underground, which prevents King Vortigern from building a stronghold. This story was later adapted into a prophecy made by the wizard Myrddin (or Merlin) of a long fight between a red dragon and a white dragon. According to the prophecy, the white dragon, representing the Saxons, would at first dominate but eventually the red dragon, symbolising the Britons, would be victorious.
Being museum people (er..? People employed at a museum, I mean!) ourselves, we made sure to visit the exhibitions as well, and especially the new “Wriggle!” exhibition, which is all about..worms! Lots of fun, and a*a lot* of information packed in. Make sure to visit it, if you get the chance!

Visiting the “Wriggle!” exhibition during the Ice Breaker event
The attendants have also been busy on Twitter, visit @IPC2016 or check #IPC12Cardiff for loads of photos and on-the-spot-commentaries
Finally, we would like to extend our heartfelt thanks to the arranging committee – DIOLCH!
Cheers, Katrine
ps: Dw i’n hoffi mwydod!