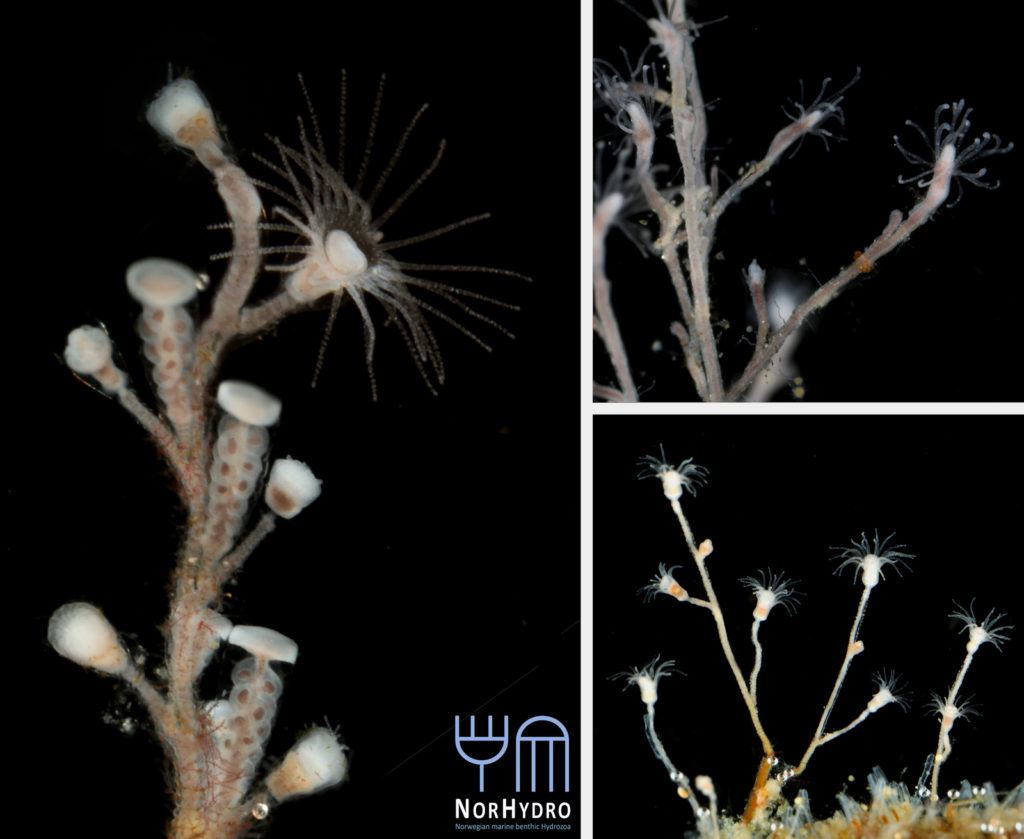
Professor Dr. Idzi Drzycimski was one of the few who studied copepods here in Bergen, and in particularly the order of Harpacticoida. Drzycimski was foremost an occupied oceanologist and ichthyologist (the study of fish), but during his career he also described several new species from the order Harpacticoida. A few of those records are from Norway and are currently an important resource for our study of hyberbenthic copepods (HYPCOP). Drzycimski stayed in Bergen for a few years during the sixties and build up an extensive collection of copepods.
Idzi Drzycimski
Idzi Drzycimski was born December 5th, 1933 in Klonowo; a very small village North of Bydgoszcz, Poland. He studied Biology with a specialization in Hydrobiology at the Odessa University of I.I. Miecznikow. In 1957 he graduated and started working at the Sea fisheries Institute in Gdynia at the Oceanography Department, led by Professor Kazimierz Demel. Later followed by a career at the Department of Oceanography and Marine Biology at the University of Agriculture in Olsztyn, Faculty of Fisheries. In 1963 he obtained the degree of Doctor in natural sciences and in 1969 he habilitated. In 1985 he received the academic title of associate professor and eventually became full professor in the same year.
Throughout his career he completed several internships in Germany, Norway, Italy and participated in several research cruises in the South Baltic Sea, North Sea and the Norwegian Fjords. During these cruises he collected and described 11 species new to science and 3 new types of marine crustaceans that have entered into the international zoological systematics. He promoted 8 doctors and continued to be the head of the department of oceanography at the faculty of sea fisheries. All while he published hundreds of articles and finally in 2001 he was awarded the Medal of Professor Kazimierz Demel.
Sampling for copepods
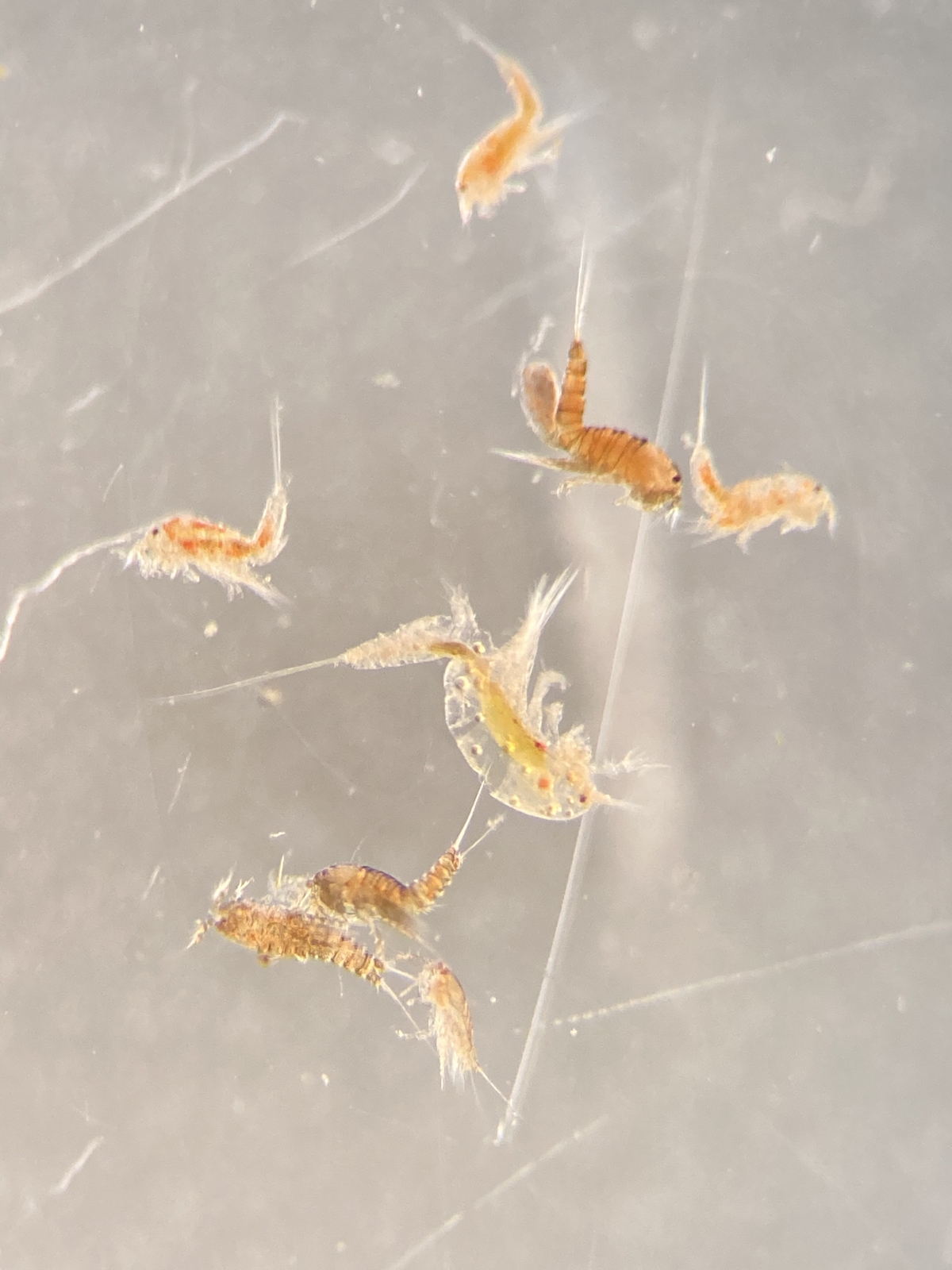
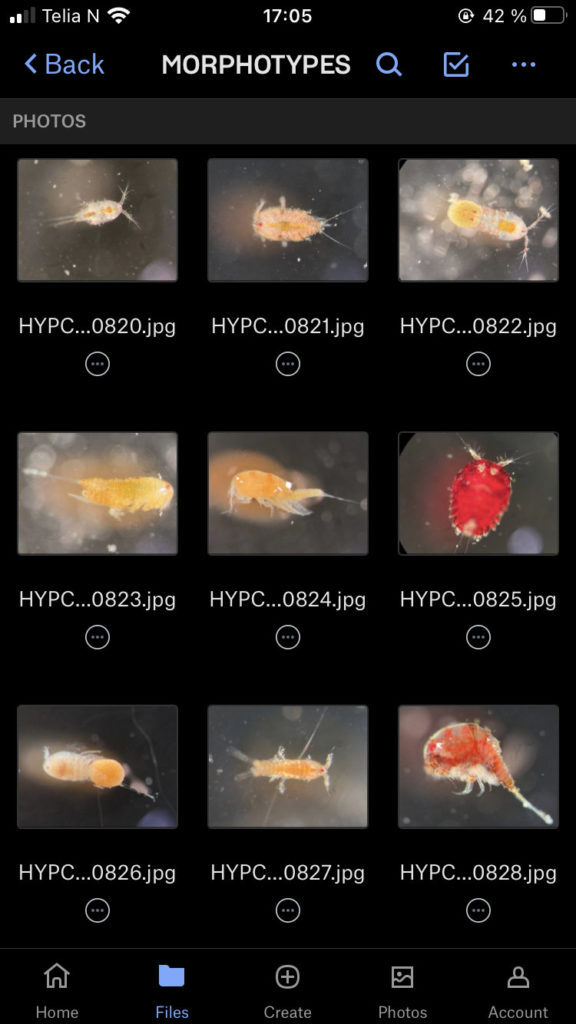
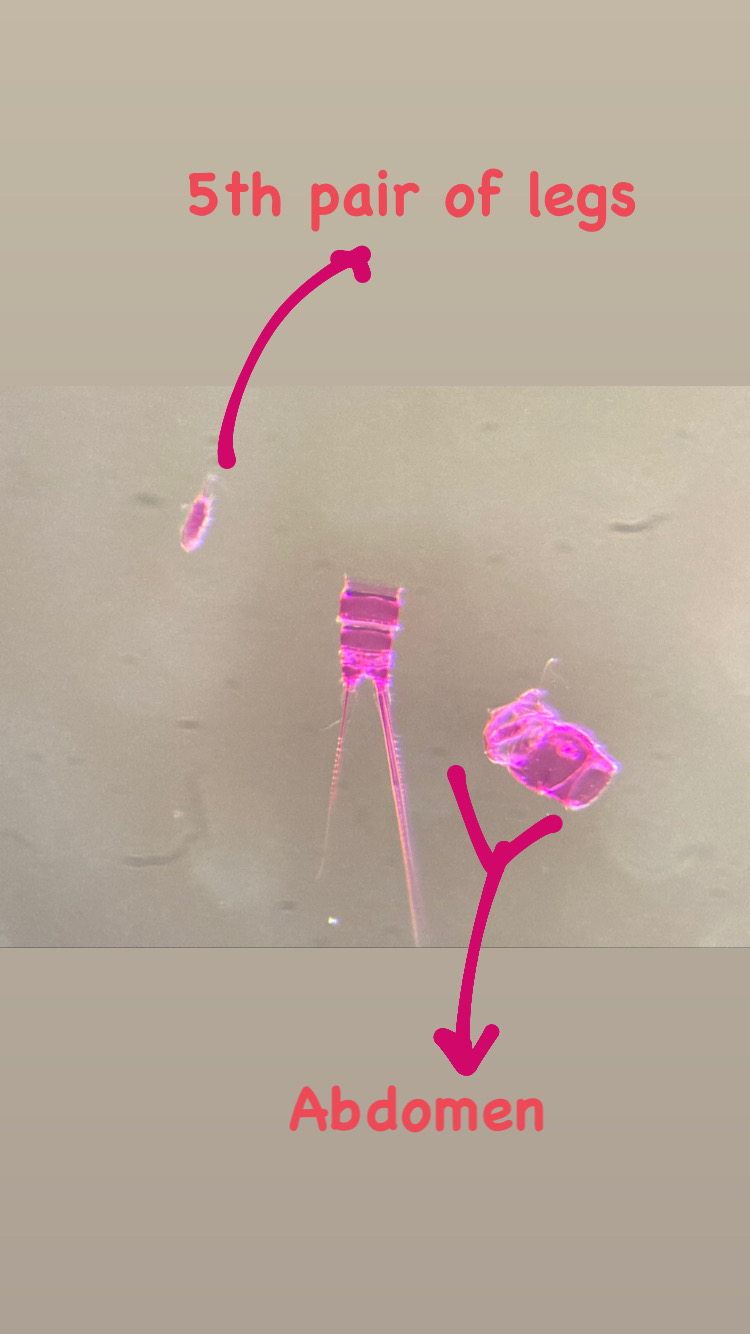
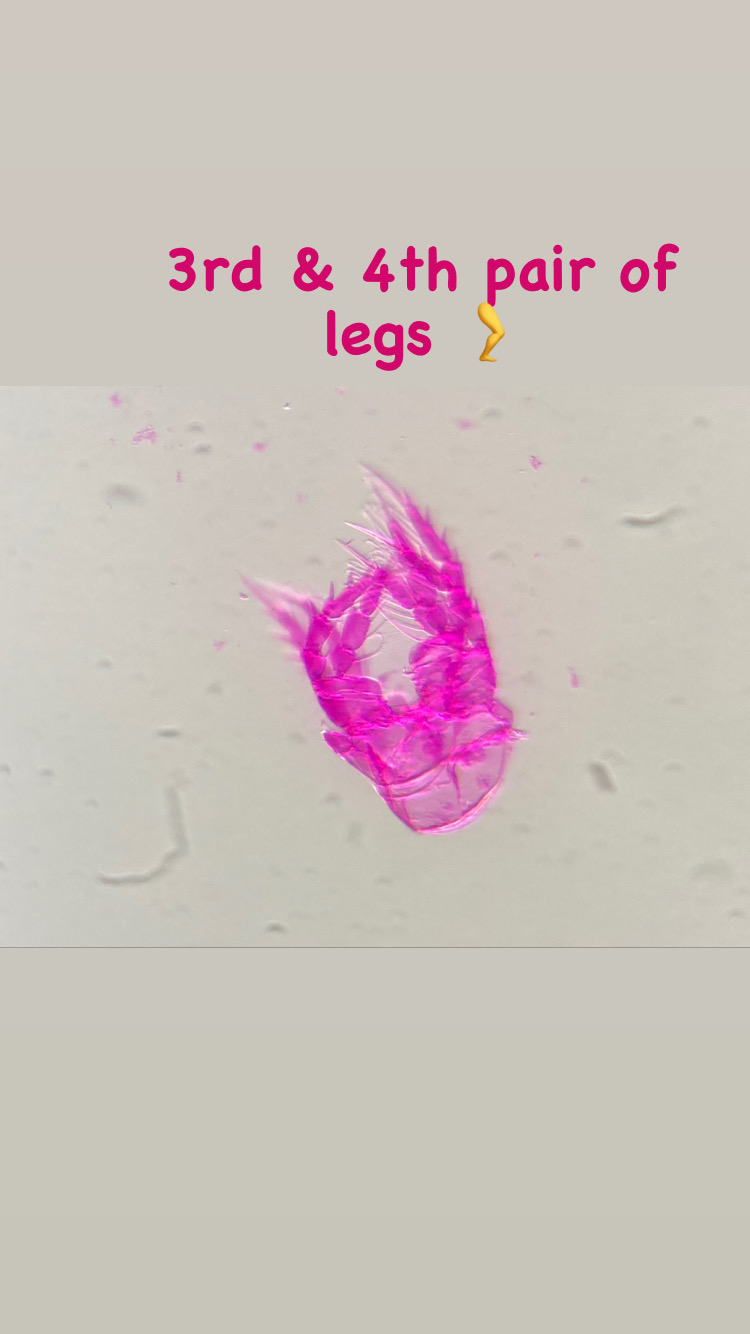
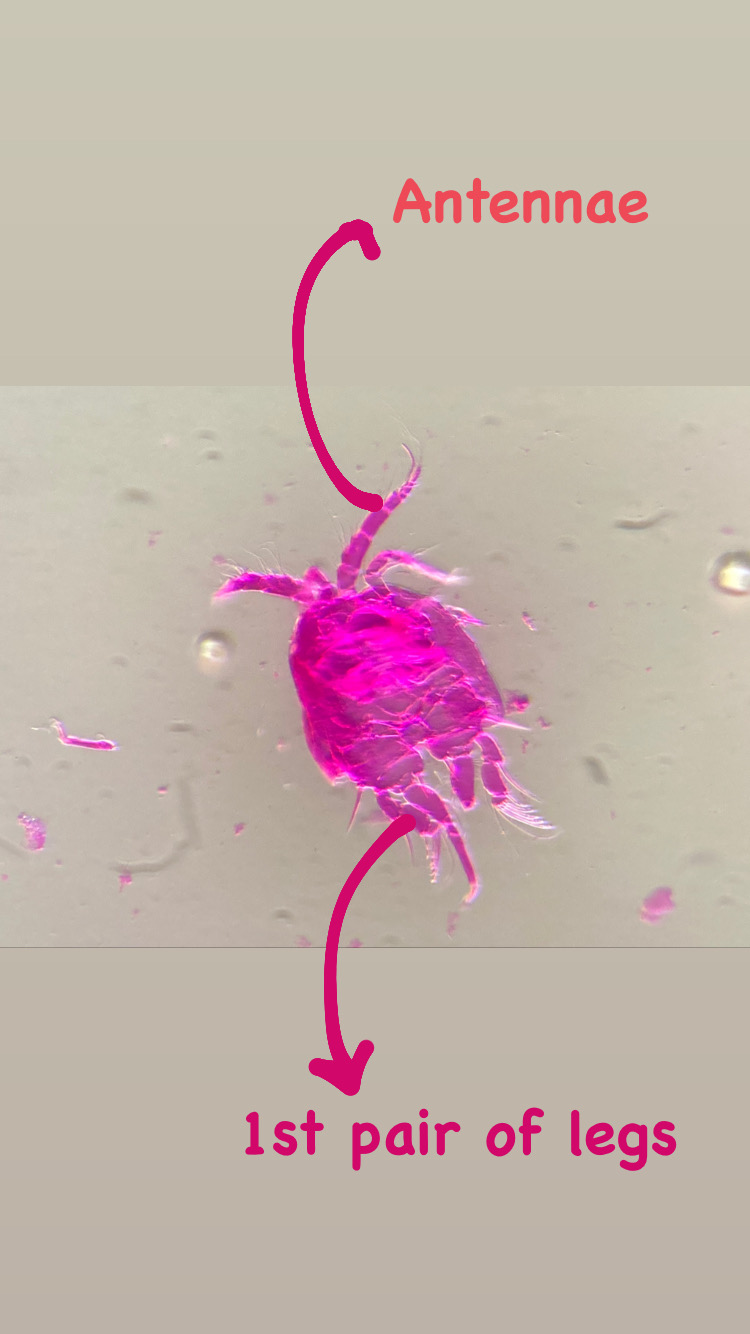
As noted earlier, HYPCOP uses Drzycimski works for the project; his database, collection and publications from his years in Bergen are good source of information. Drzycimski published two publications with Harpacticoida findings from 1967 and 1968. He described 5 new species of Harpactcoida from West Norway, with sampling locations close to Bergen. Now, half a century later, we wanted to revisit these sampling sites to see if we could find the same or different species. Some off the sampling locations were from the middle of the fjords near Bergen and would therefore be excellent to revisit. Drzycimski had sampled different spots from around the Krossfjorden, Bjørnefjorden and Raunefjorden. Most of these were deep sandy and muddy bottoms, from around 300-700m. Species that he had found there he described as Marsteinia typica, Pseudotachidius vikingus, Marsteinia similis, Leptopsyllus elongatus and Dorsiceratus octocornis. These all have the typical small body sizes of around 400-800 μm and are very inconspicuous and hard to find with the naked eye.
Brattström & Drzycimski
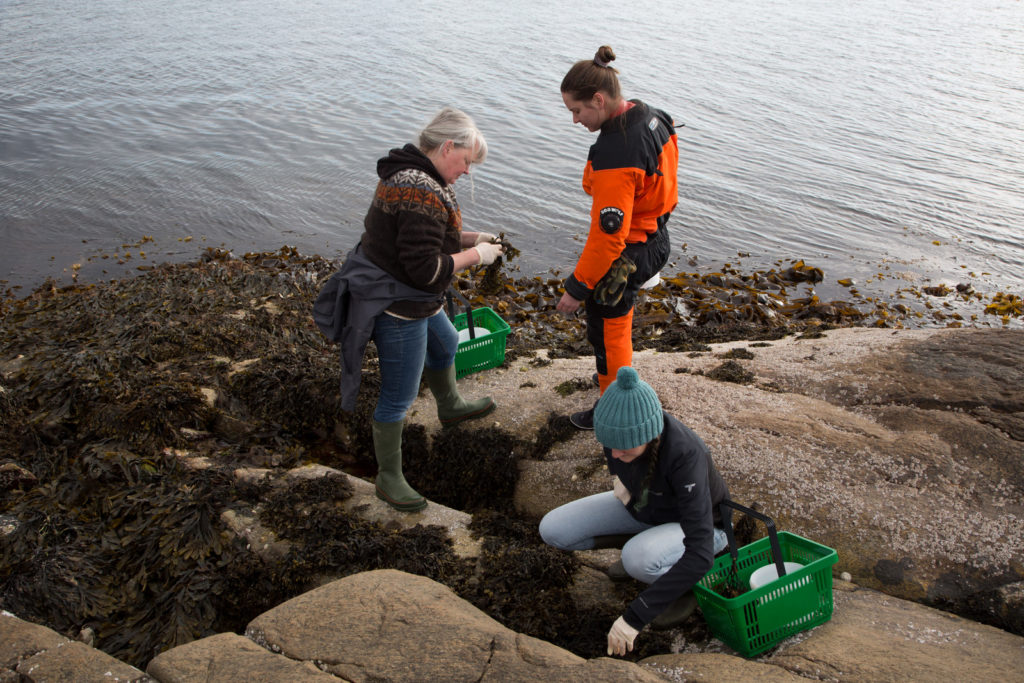
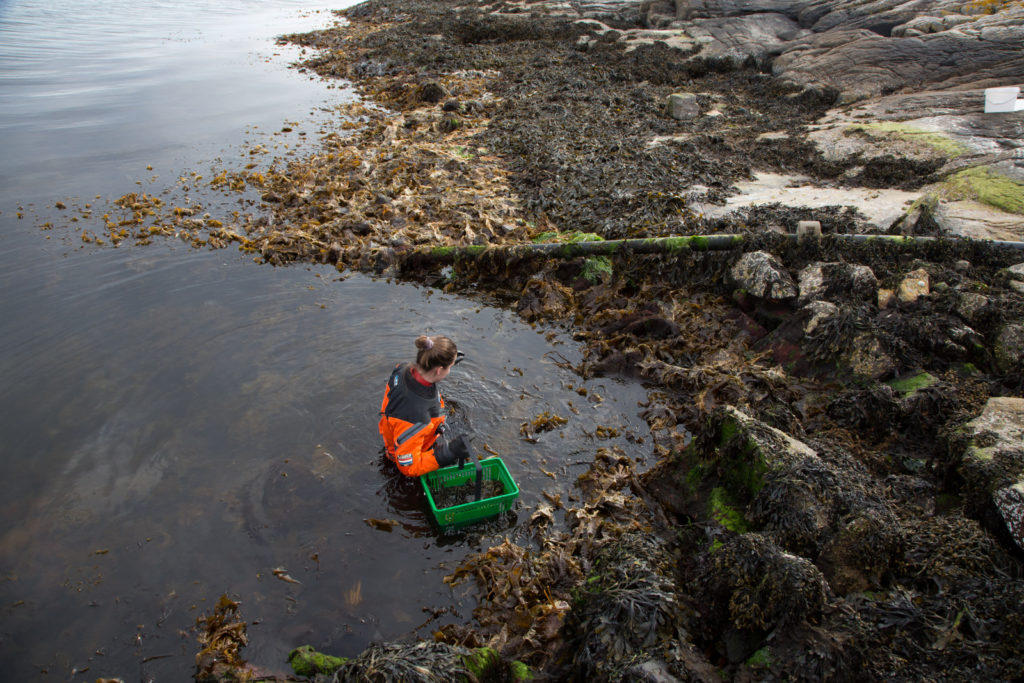
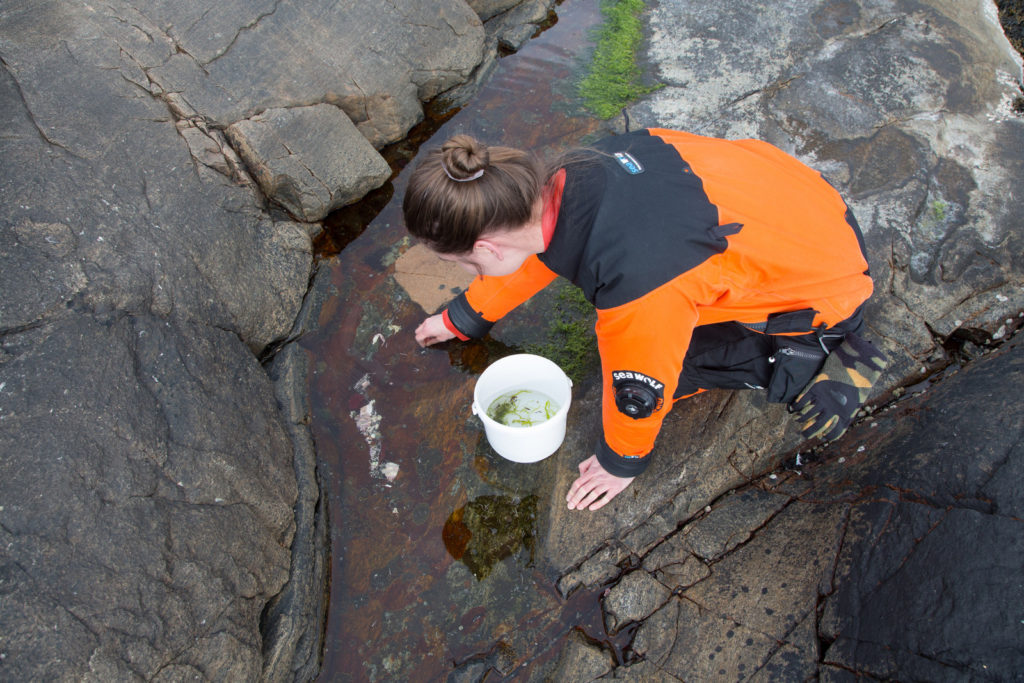
With help of research vessel Hand Brattström and researcher Anne Helene Tandberg, we managed to sample two locations in the Krossfjorden between 400-700m depth that were sampled before in the 60s by Drzycimski. Prior to the sampling day we made a hit list of 4 locations that we wanted to revisit, but two of those locations got inaccessible. In the span of 60 years a lot of things have changed, places that once where easy accessible for sampling are nowadays littered with e.g. fishing gear waste. Which would destroy our plankton nets when they get stuck in this. On top off that Drzycimski also did not describe in his papers how he managed to collect his copepod samples, but most likely this was done with a sled, and in this case we would be using the R.P. sled. The R.P. sled is an epibenthic sampler. That means that it samples the
animals that live just at the top of the (soft) seafloor with a fine plankton net, if you want to read more details about the R.P. sled you can read that here. Once again our sled expert Anne Helene would join us on this trip to help HYPCOP with sampling and also to be on the lookout for sampling for amphipods. After the sled collected the benthic animals, we needed to filter the sled sample by a process which is called decanting (See the YouTube movie in this blog). With decanting you separate the mixture of the animal soup from the liquid by washing them in a big bucket, throw the liquid through a filter and collect the animals carefully to avoid damaging them.
Drzycimskis visit at the museum was during the years of Hans Brattströms Professorship at the University of Bergen in marine biology (1962-1978). During those years Brattström started the scientific journal Sarsia, where Drzycimski published his copepod species description’s. There is not much about whether the two professors knew each other well, but it is very likely. And so it was special that few generations later, Hans Brattström once again facilitates research for Drzycimski, although this time as a research vessel and a new generation of scientists working on marine benthos.

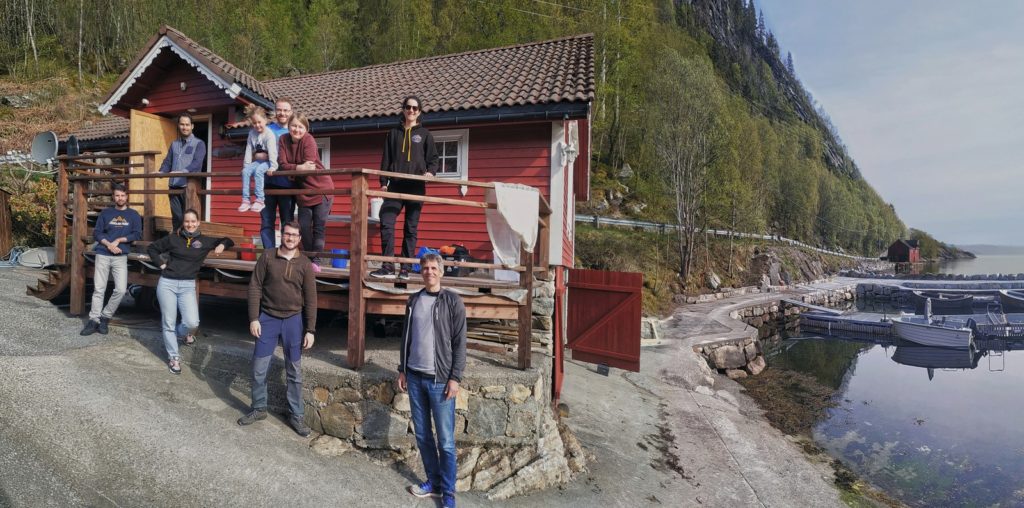
New generation of scientists working on marine benthos. from the left: Anne Helene Tandberg, Francisca Carvalho, Cessa Rauch, Ellen Viste and Justine Siegwald
Cessa & Anne Helene
Literature:
Drzycimski, I. “Zvvei neue Harpacticoida (Copepoda) aus dem Westnorwegischen Kdstengebiet.” Sarsia 30.1 (1967): 75-82.
Drzycimski, I. “Drei neue Harpacticoida aus westnorwegen.” Sarsia 36.1 (1968): 55-64.