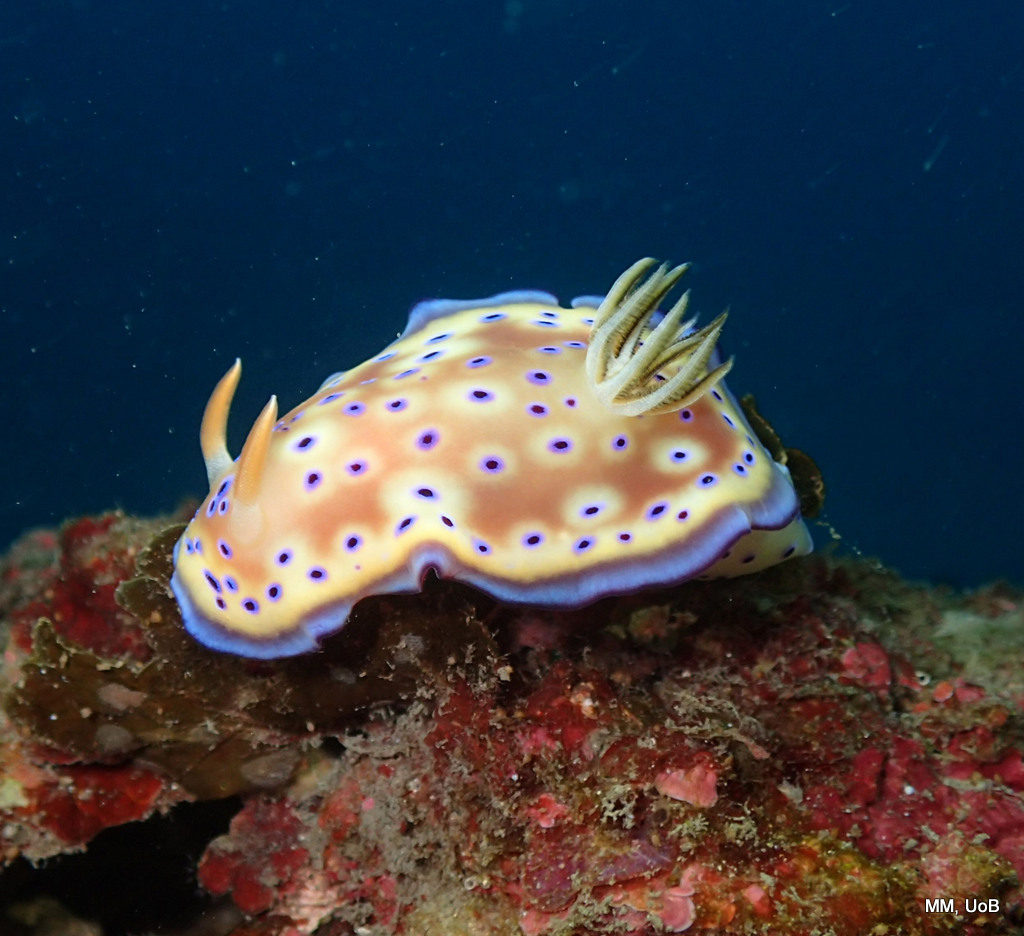
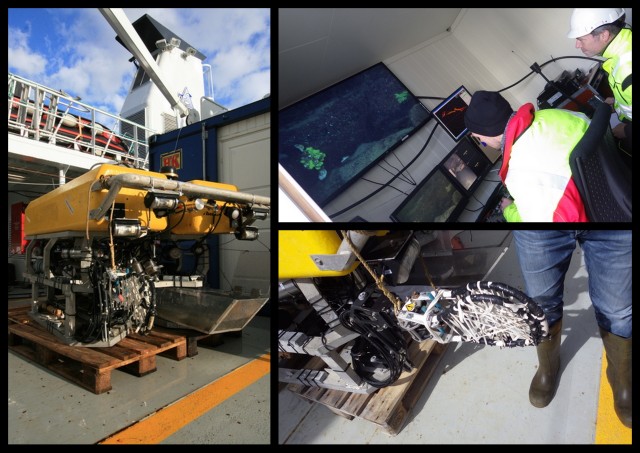
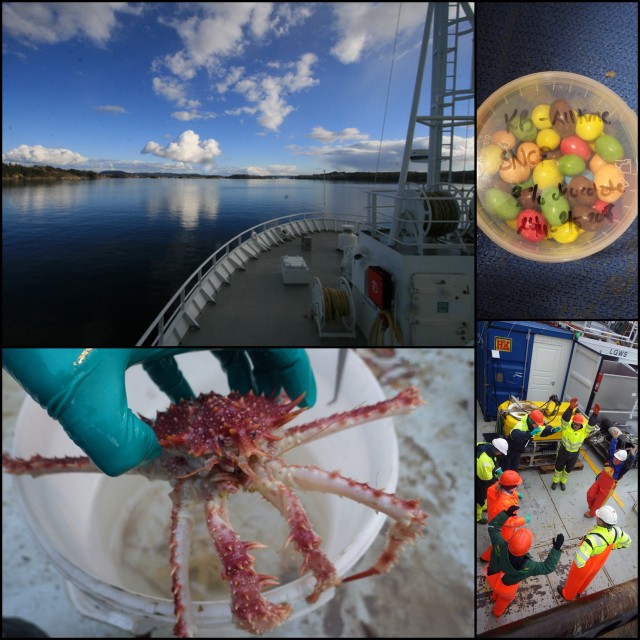
The blog has been quiet over summer – but we’ve been busy!
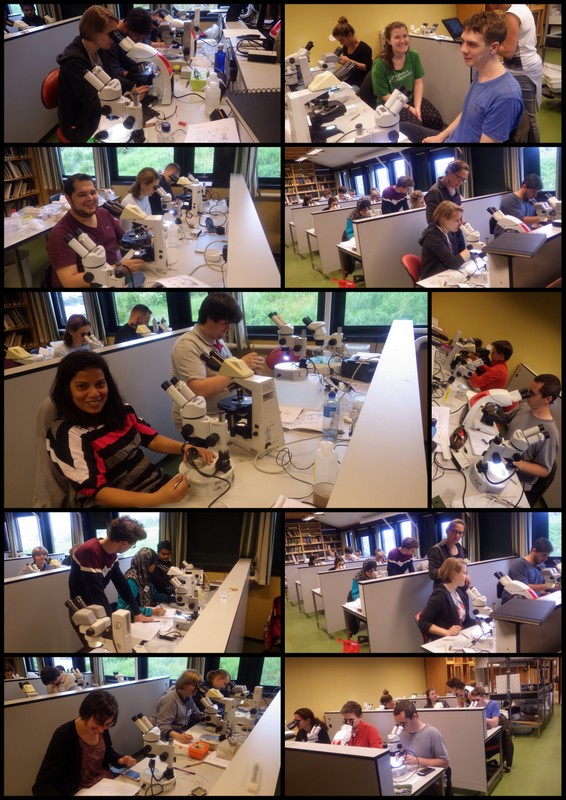
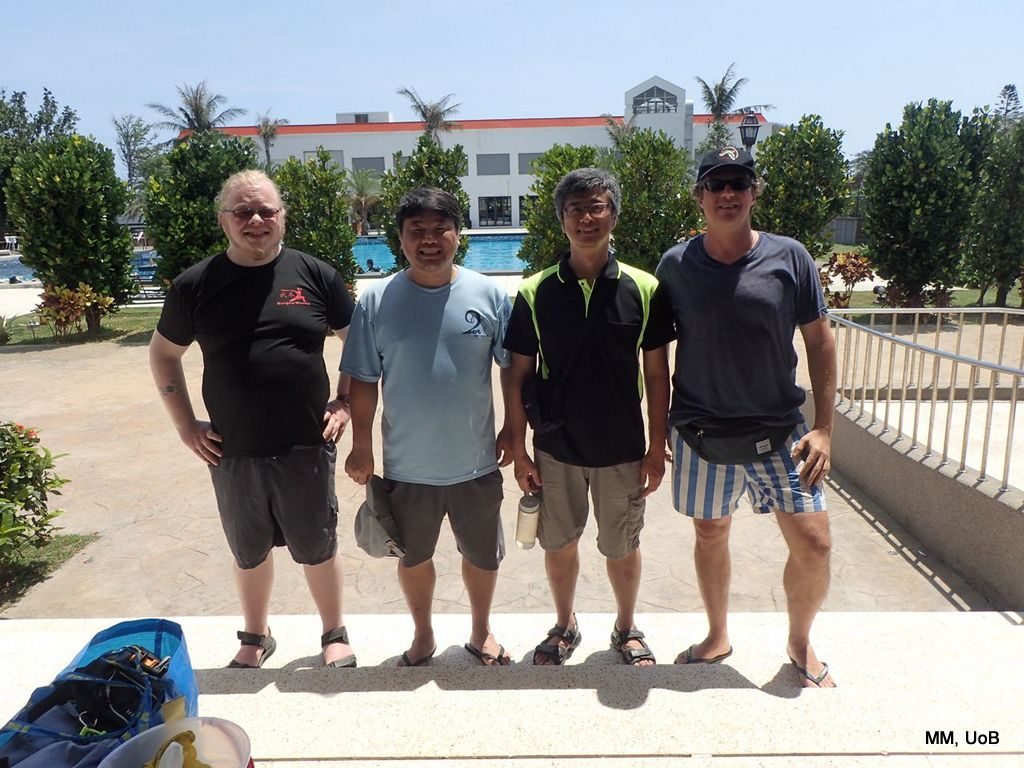
The #AnnelidaCourse2017 came to an end, and happy participants went back to their home institutions with a lot of new knowledge, a increased contact network, and many new friends.
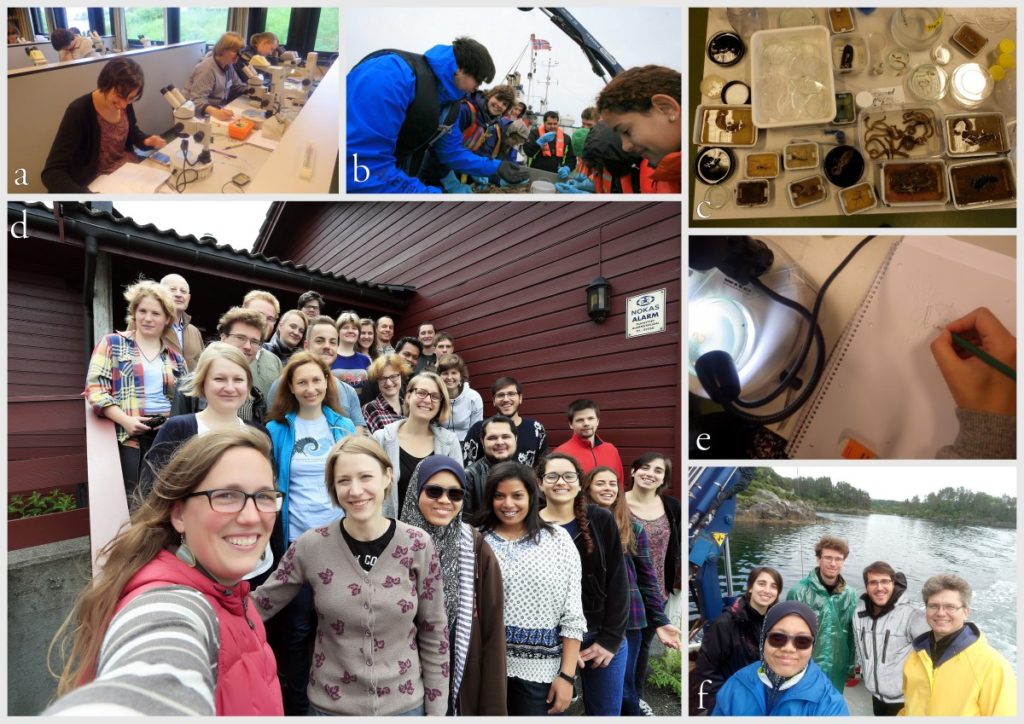

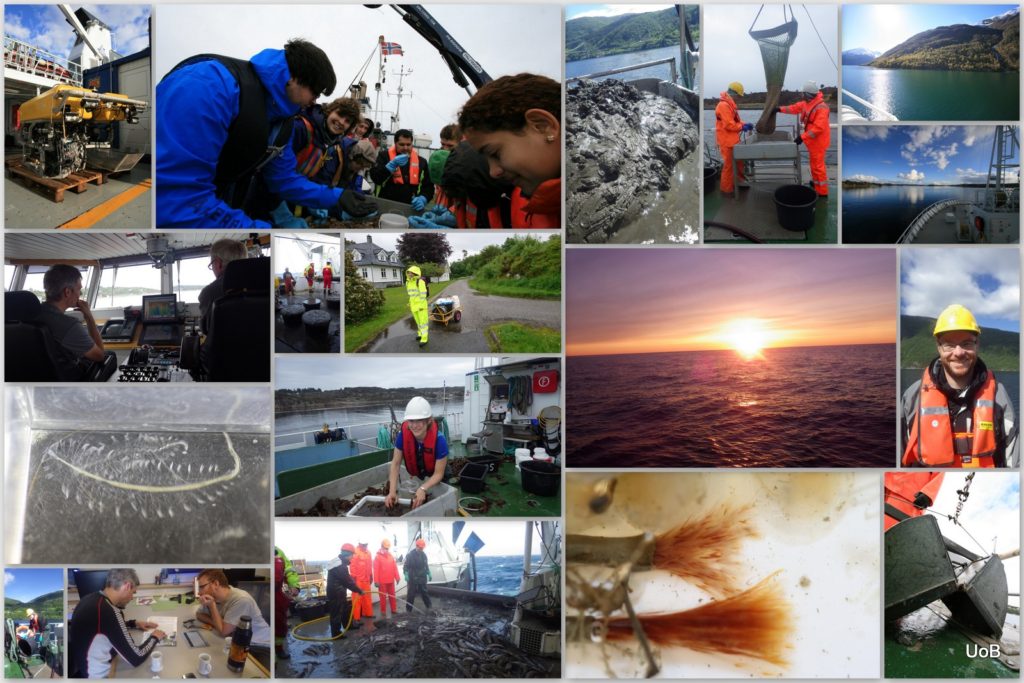
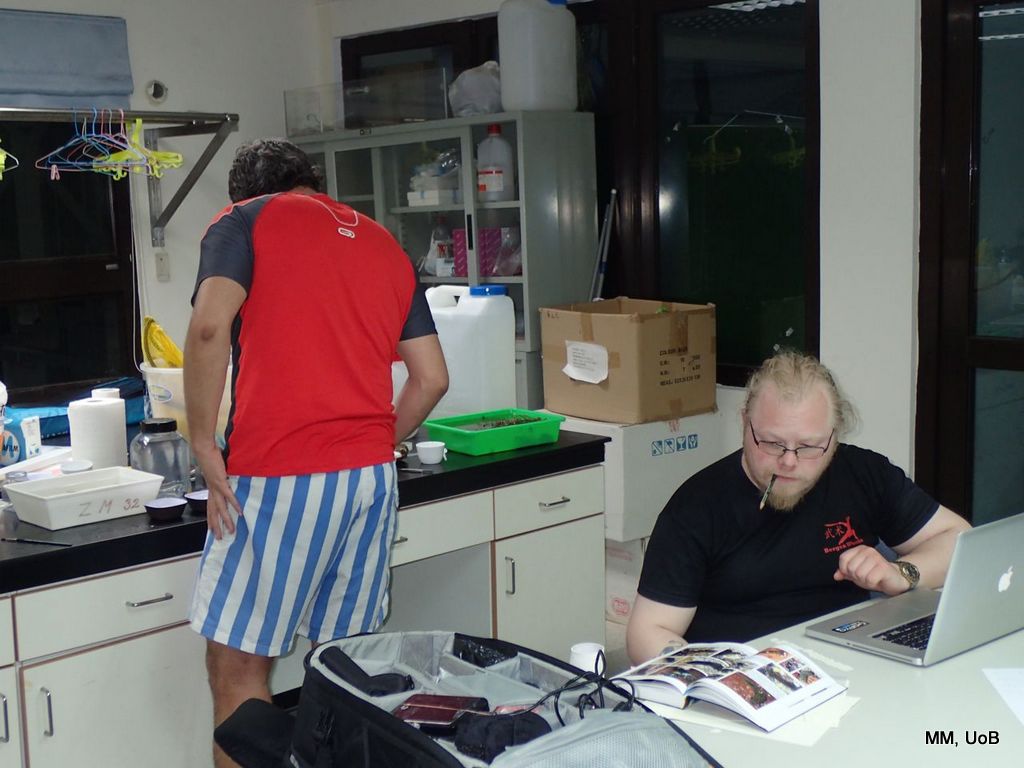
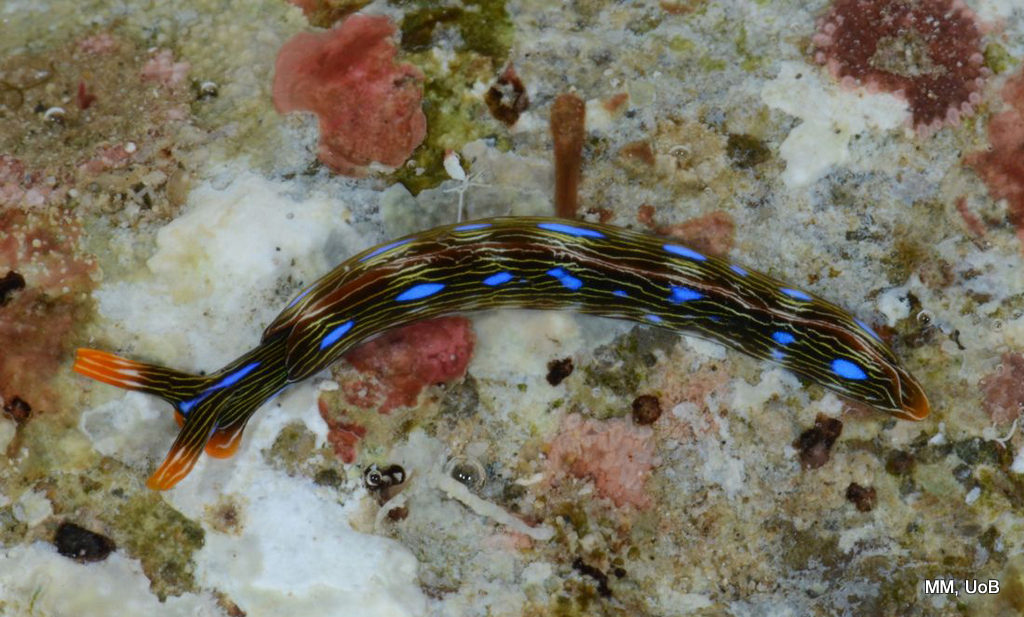
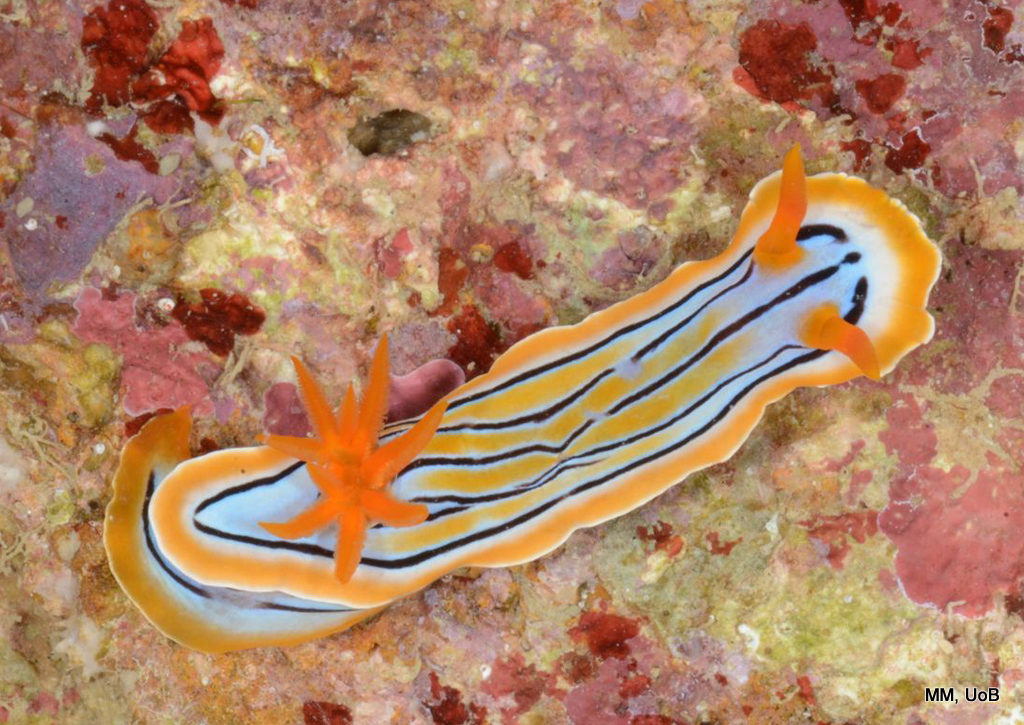
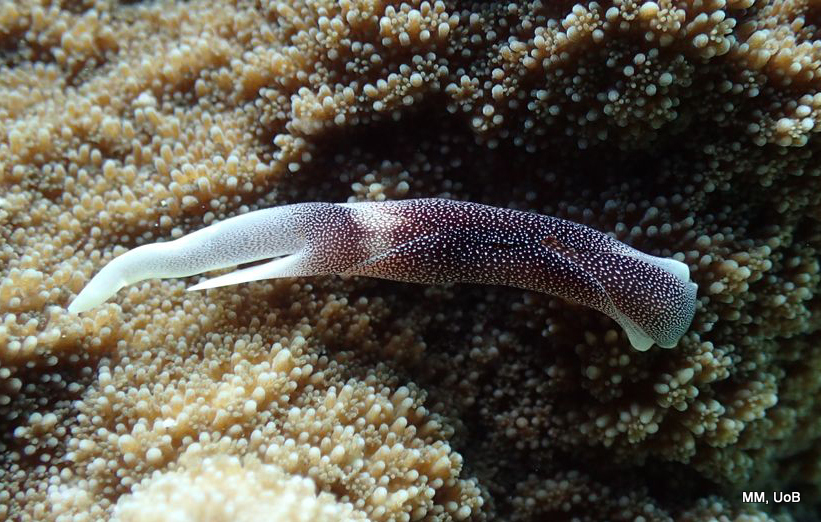
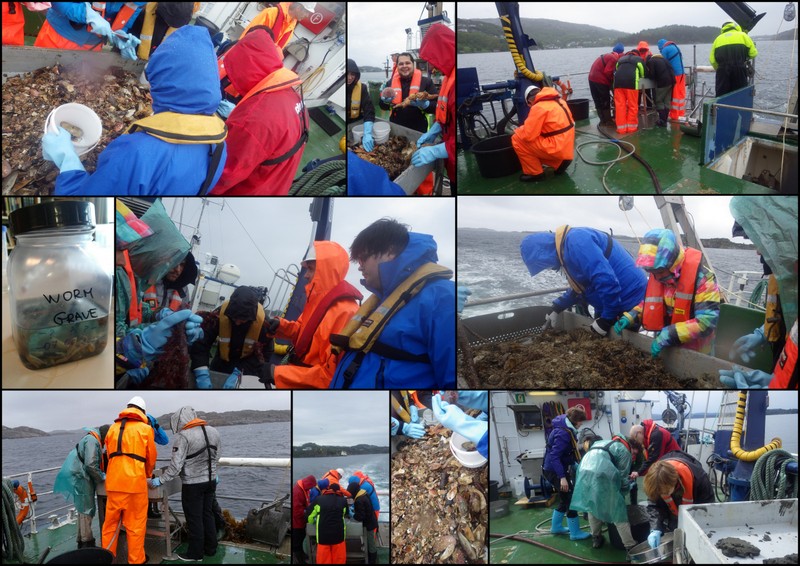
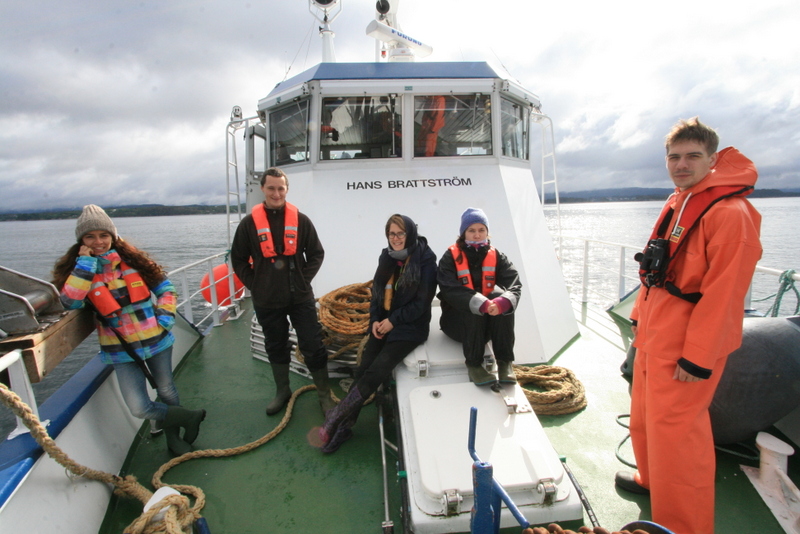
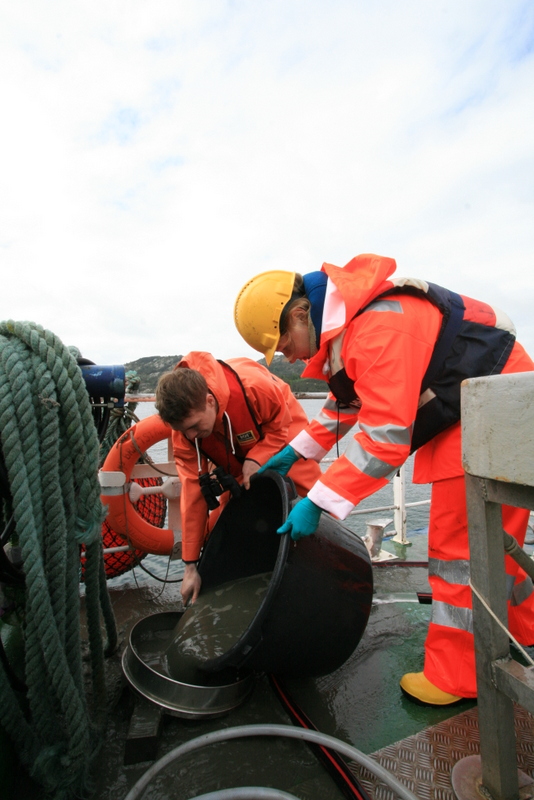
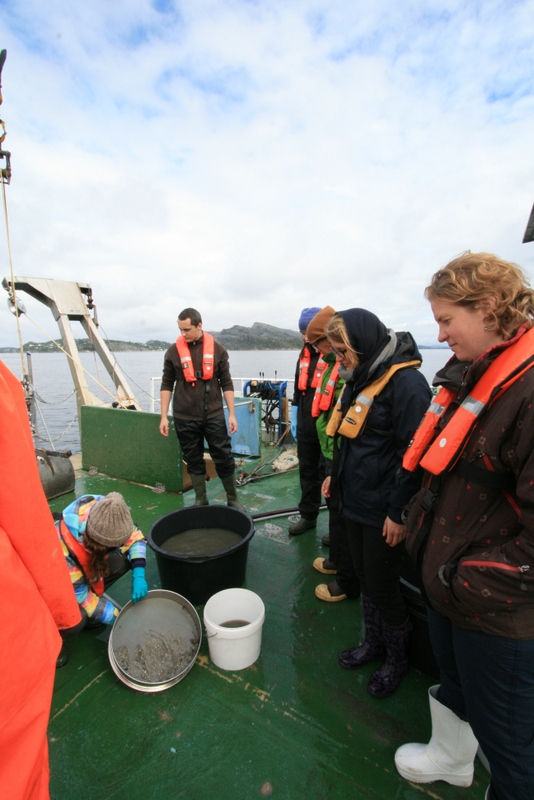
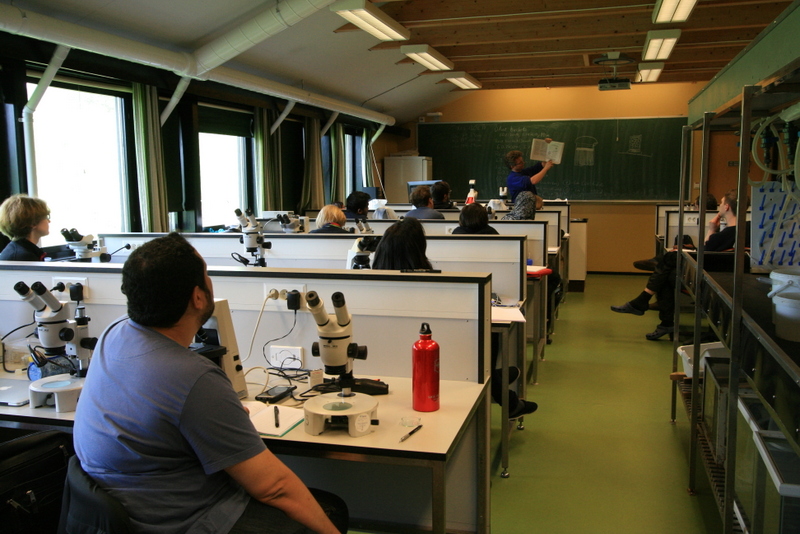
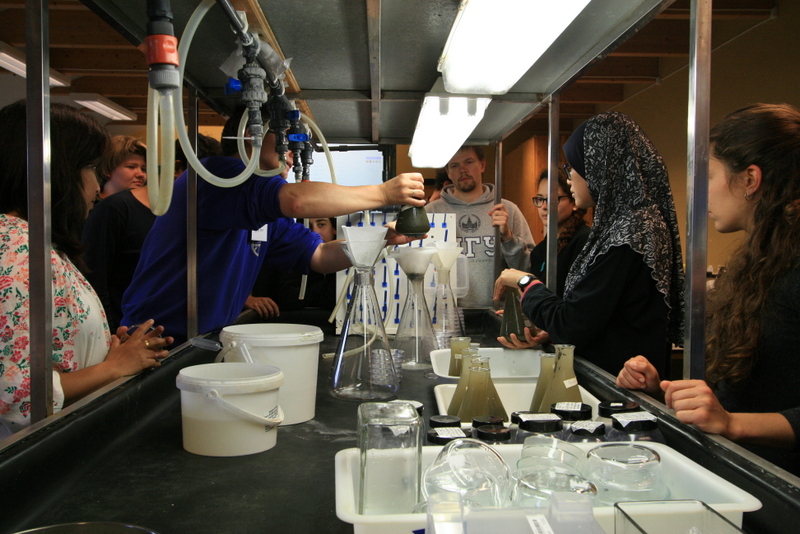
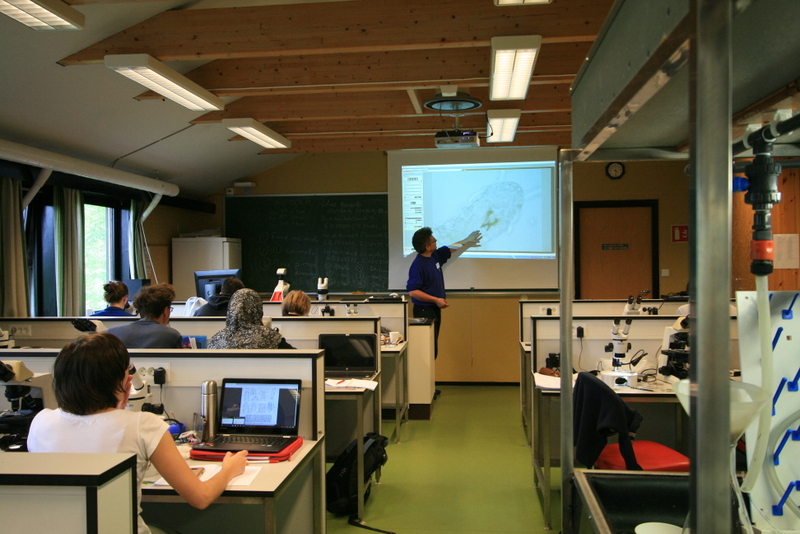
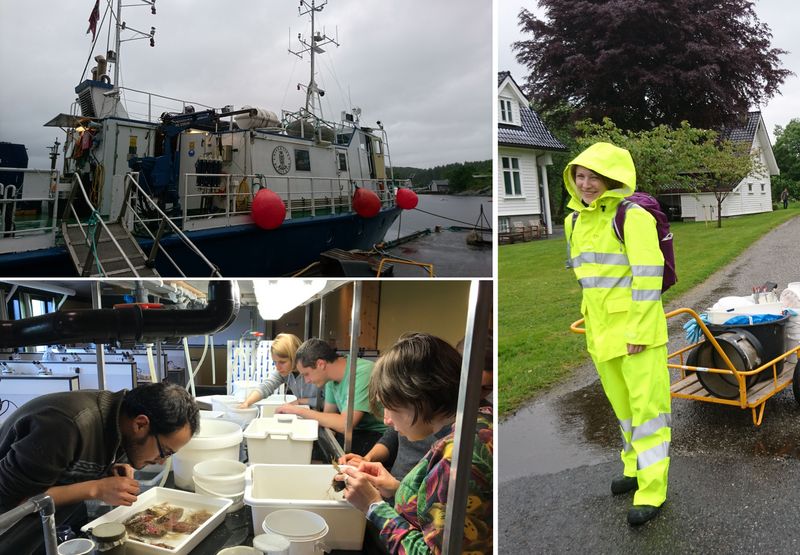
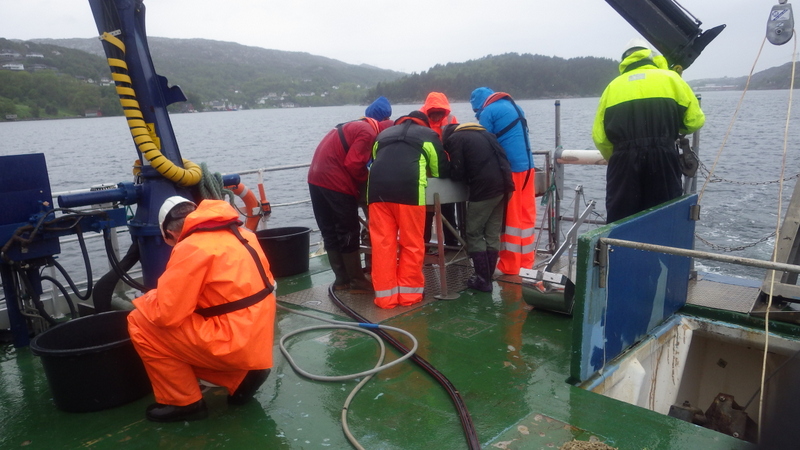
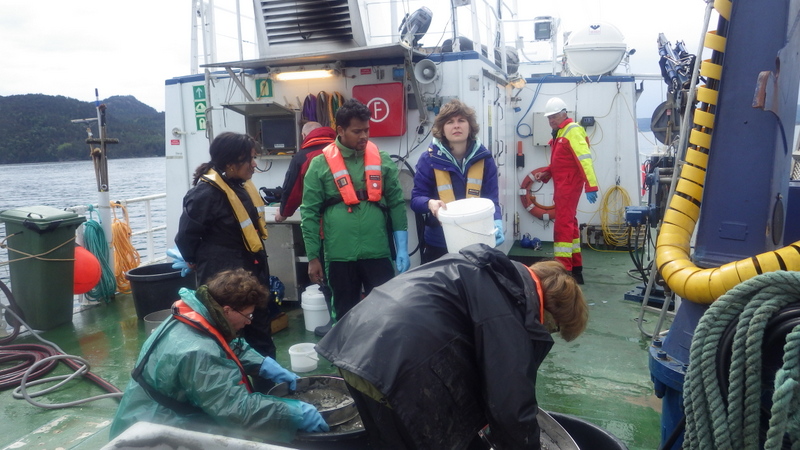
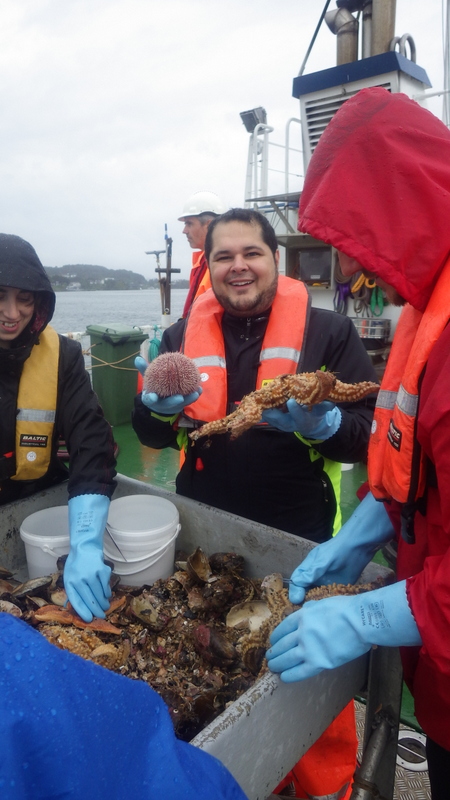
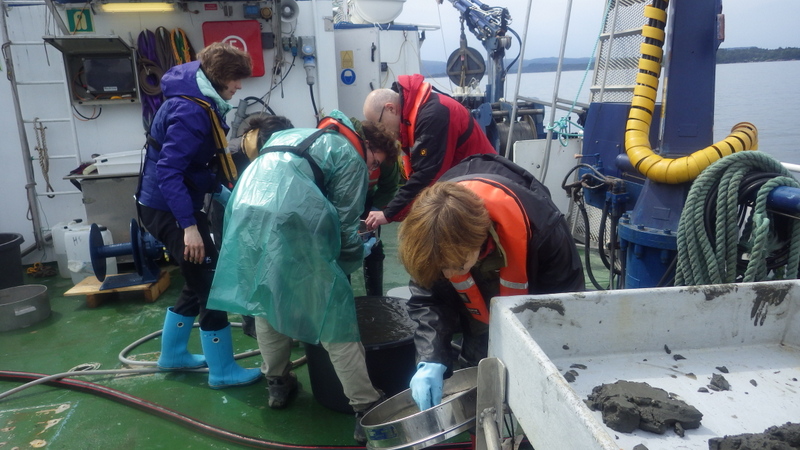
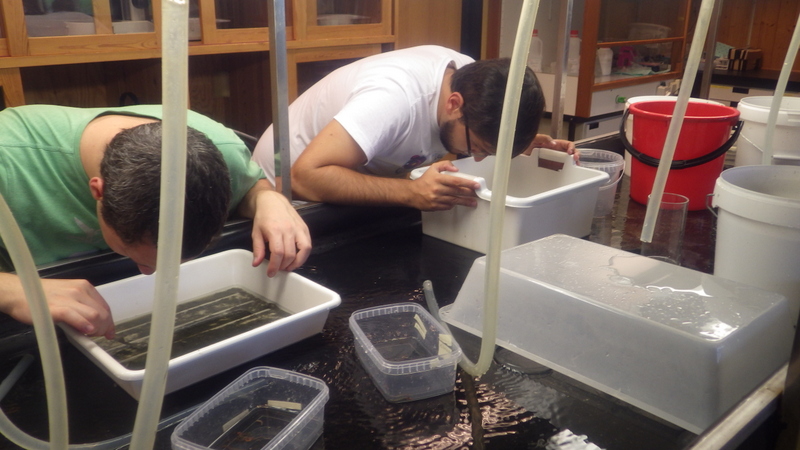
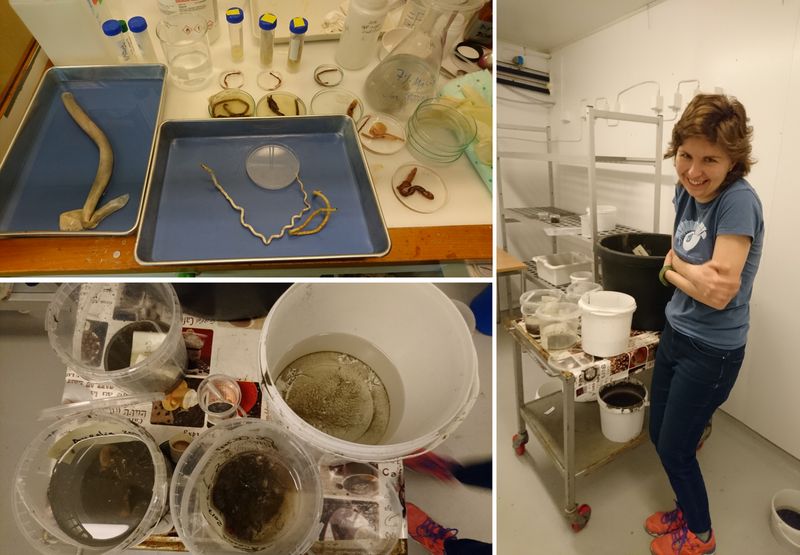
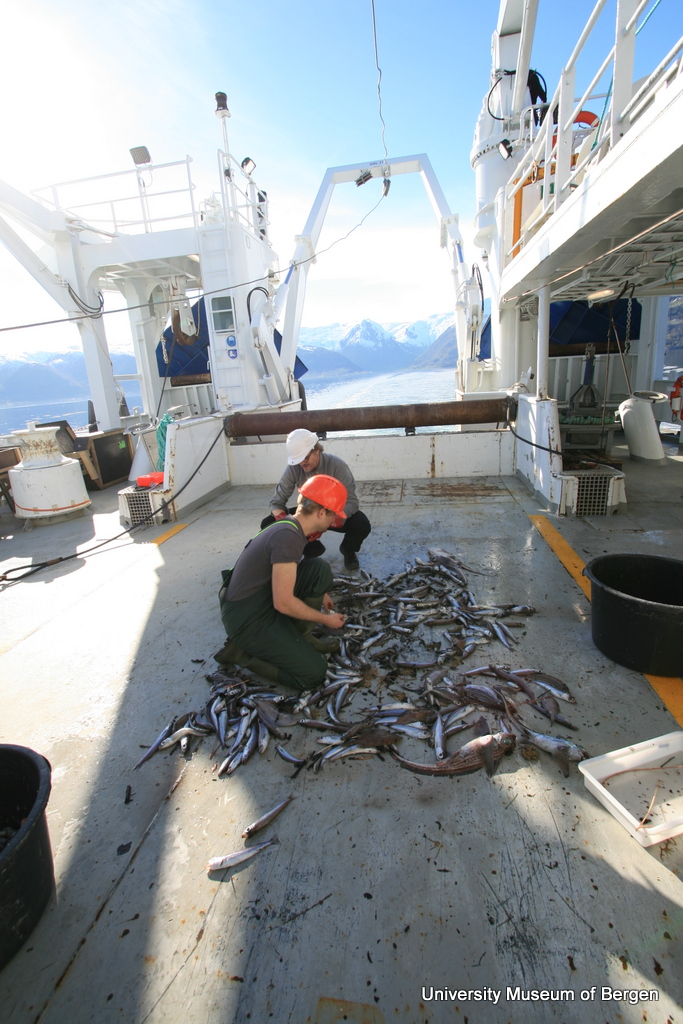
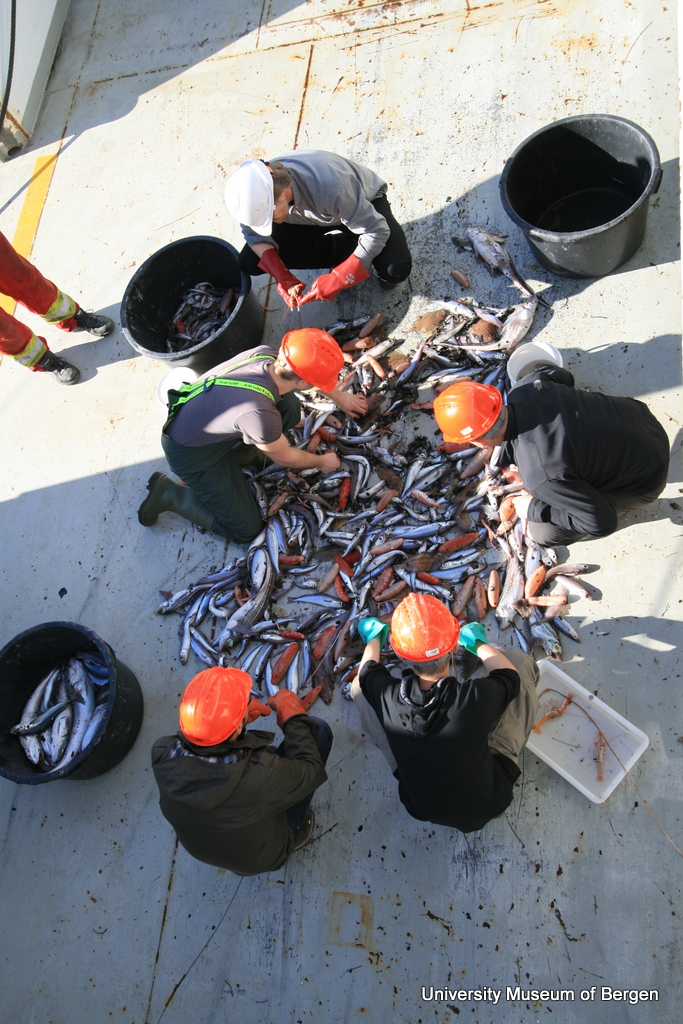
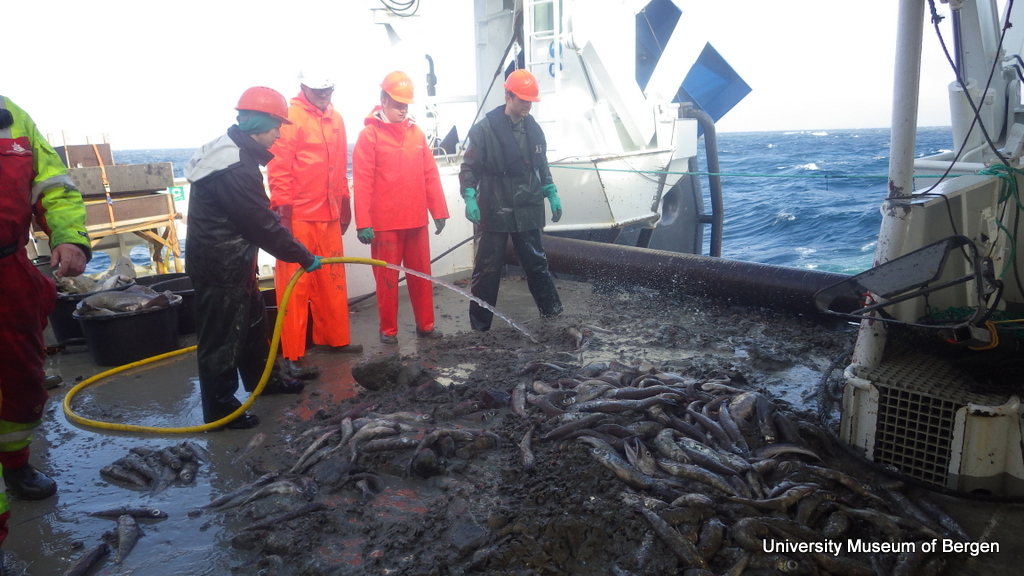
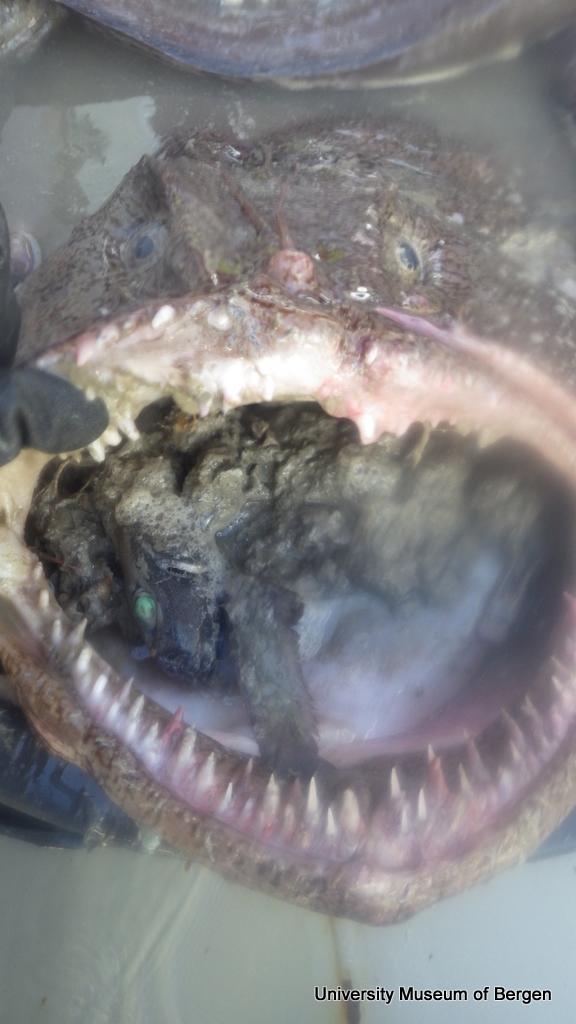
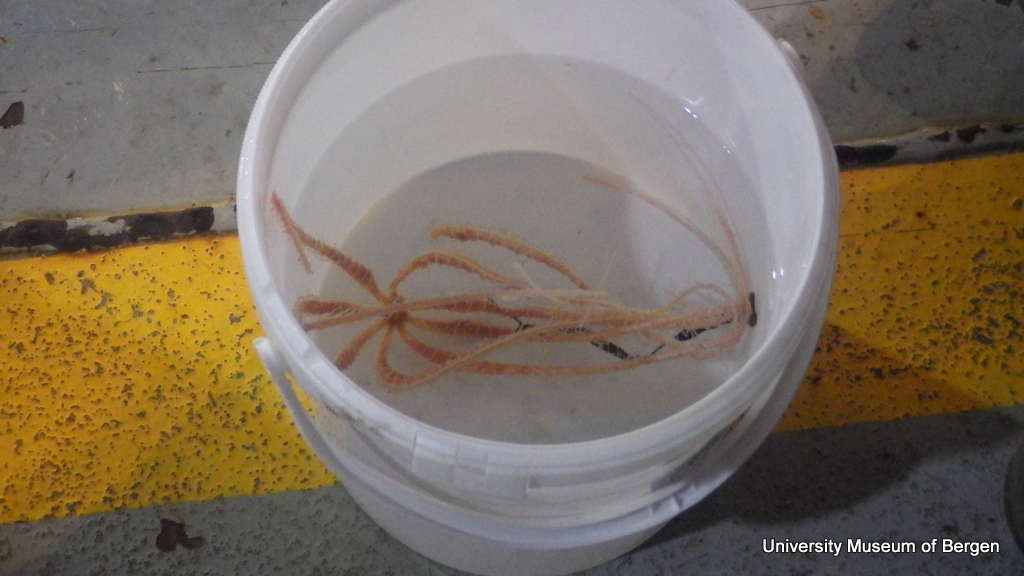
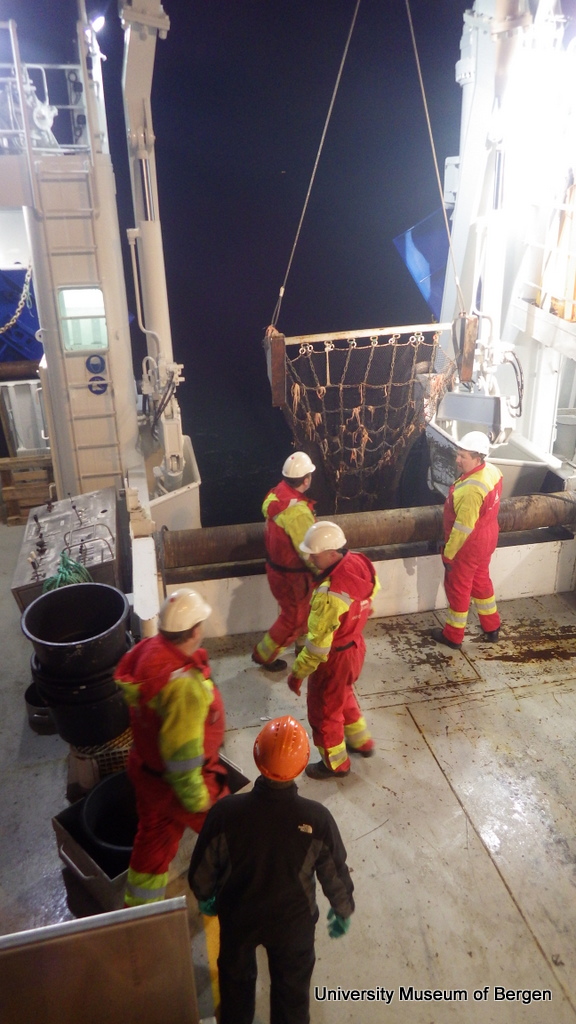
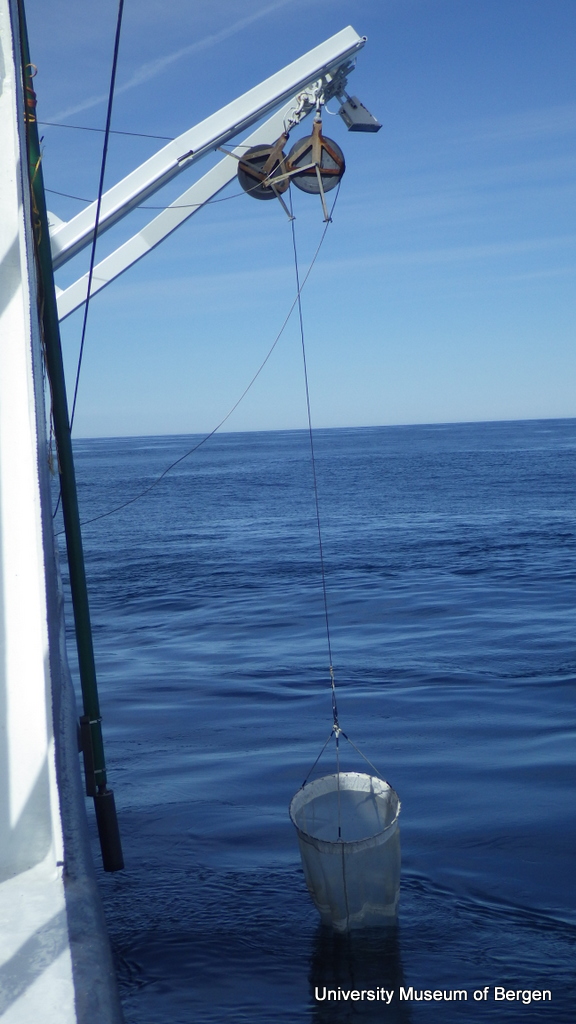
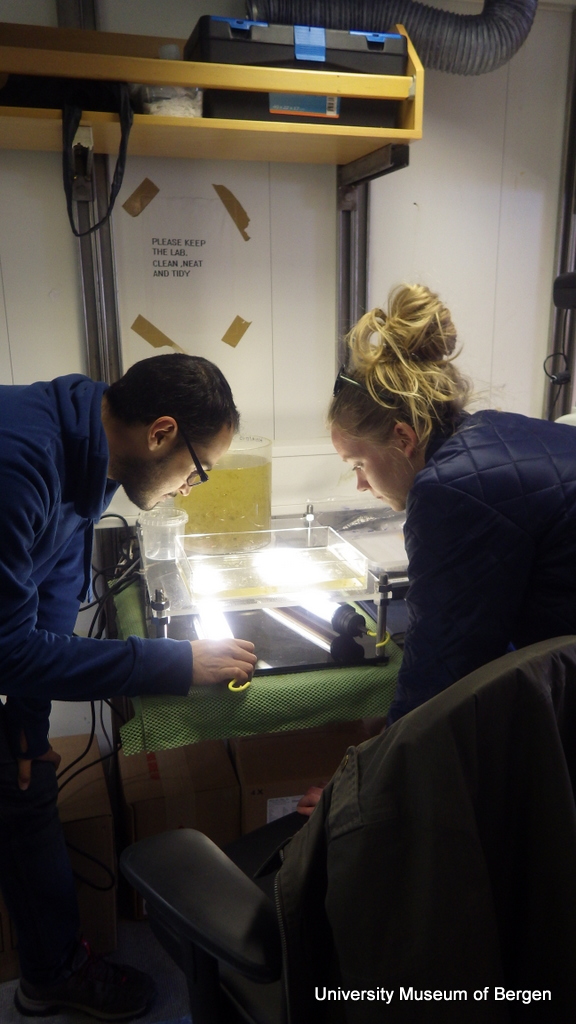
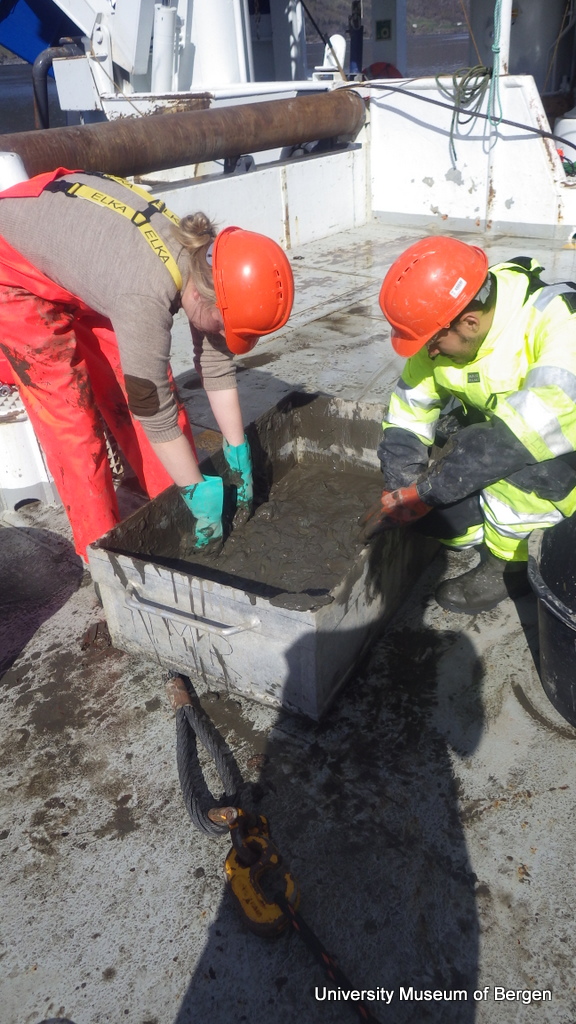
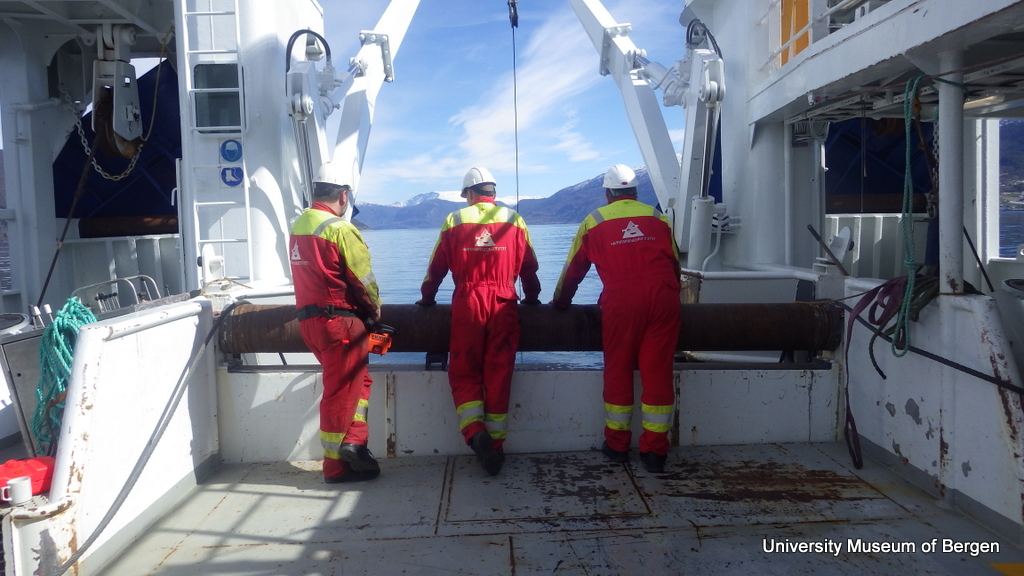
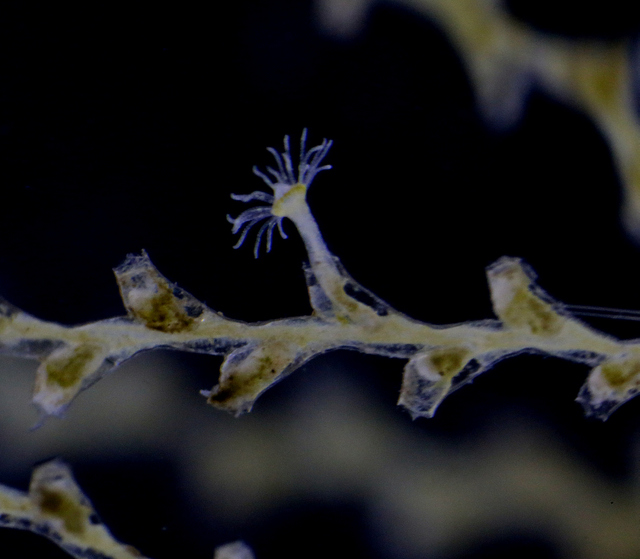
a) Students working in the lab; b) Picking interesting animals from the samples onboard R/V Hans Brattström;
c) Animals to be studied; d) Group photo of most of the participants; e) Detailed study and drawing of a specimen; f) Field work onboard R/V Aurelia Fotos: K.Kongshavn (a,b,e), G. Kolbasova (c), G.Jolly (d), S. Rosli (f)
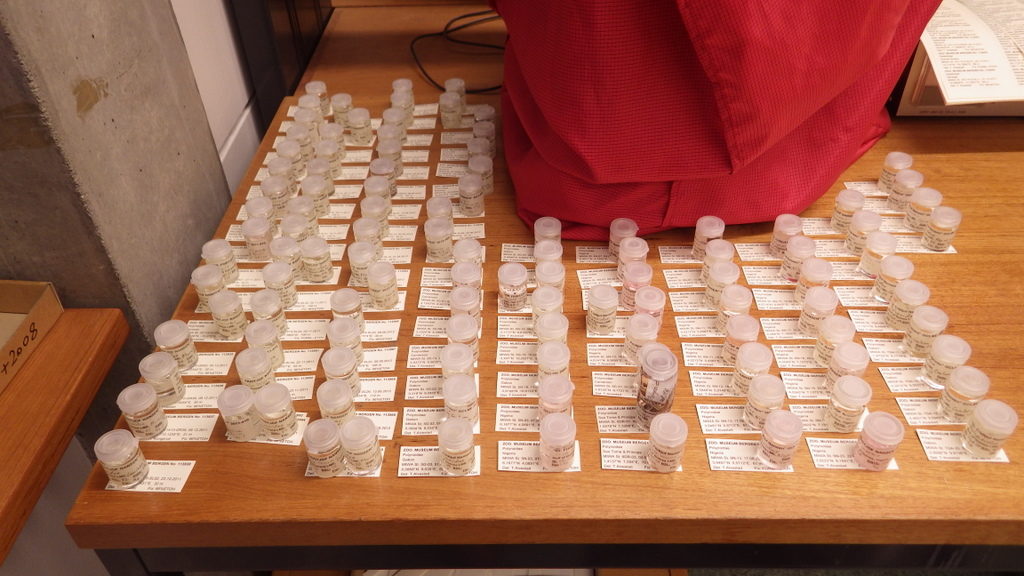
Heaps (HEAPS!) of samples have been cataloged and labeled, DNA-sequencing has completed on the shipment we sent in June and we’re working on analyzing the results, and samples from the cruises we particpated on have and are being sorted.
- Labels need to be..
- ..matched to samples..
- ..and samples stored securely
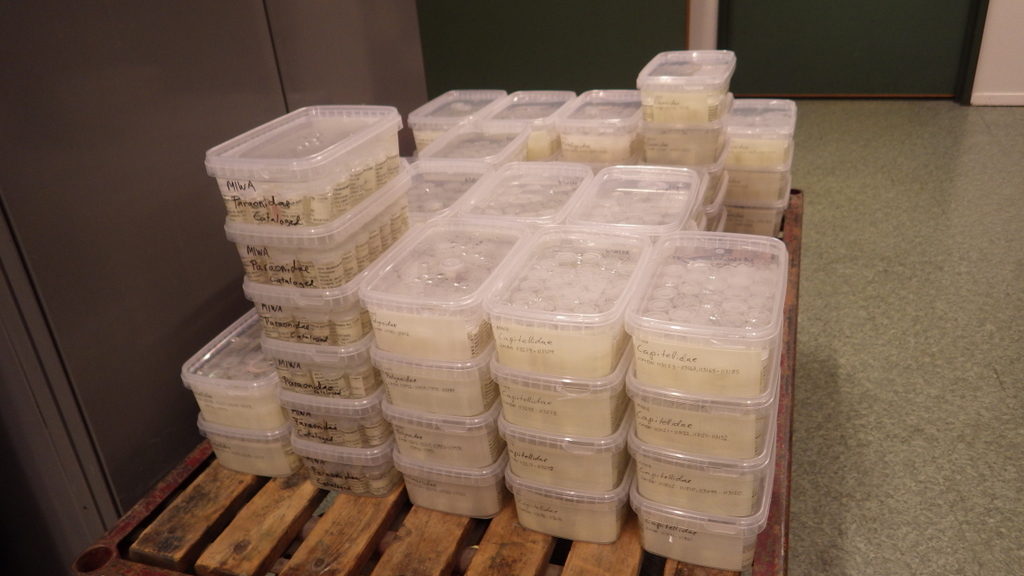
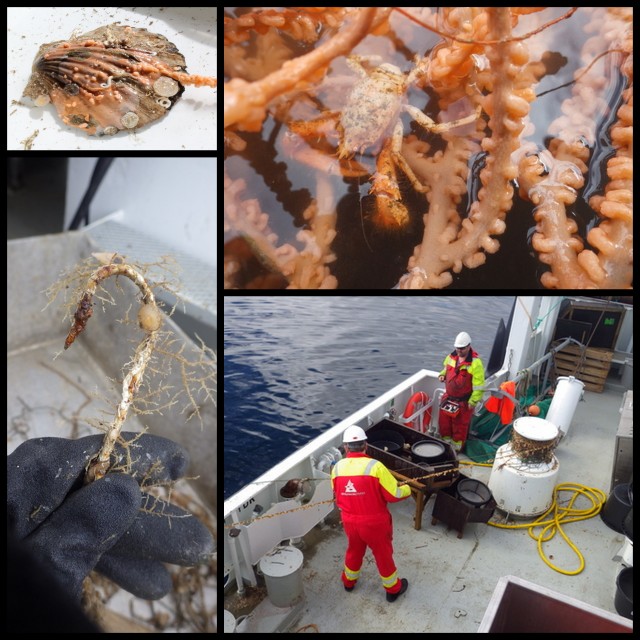
The next shipment of animals to be barcoded through NorBOL is being assembled – of marine invertebrates from our collections, one plate of polychaetes and one plate of isopods have been prepared, and we plan on completing a few more plates before shipping in October.
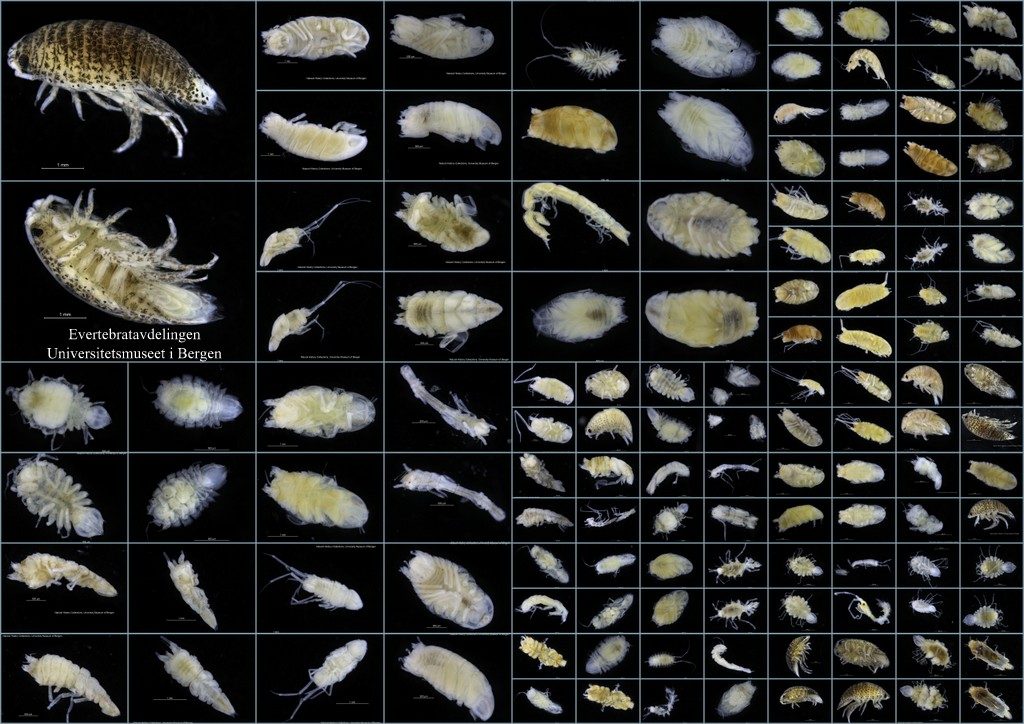
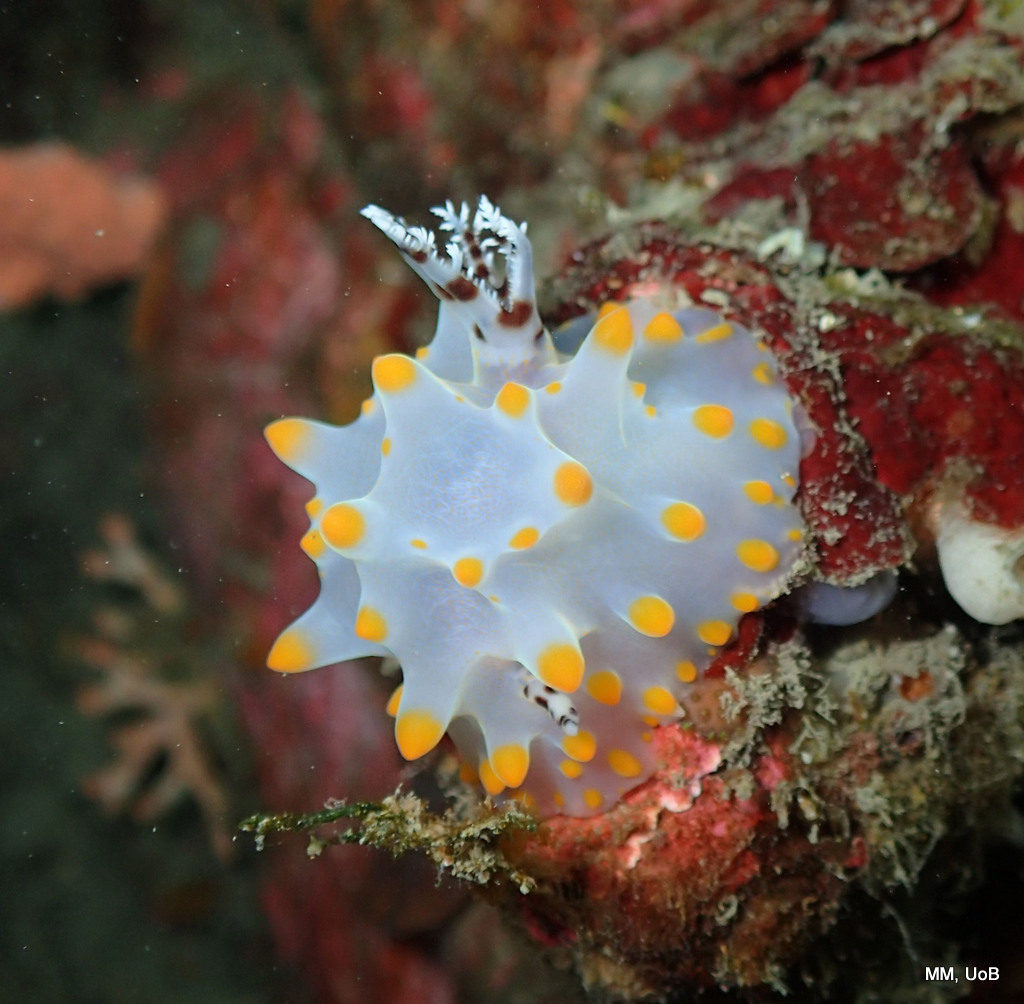
Isopods for barcoding – these have all been collected and identified by the MAREANO project. Photo: K.Kongshavn
We will also get contributions from several of the Norwegian Taxonomy Initiative projects (Artsprosjekt) that are running, and a plate with insect samples made by the students of BIO233 (I was down there today giving them an introduction to barcoding, NorBOL and the BOLD database) – hopefully we’ll get good results on all of it.
-Katrine