During our field-trip to Disko-fjord we took samples from an area densely covered with so-called Lithothamnion-aggregations (rodoliths) – a very special habitat (see also Mette and Jenny’s entry on our “Trip to Disko Fjord”) !
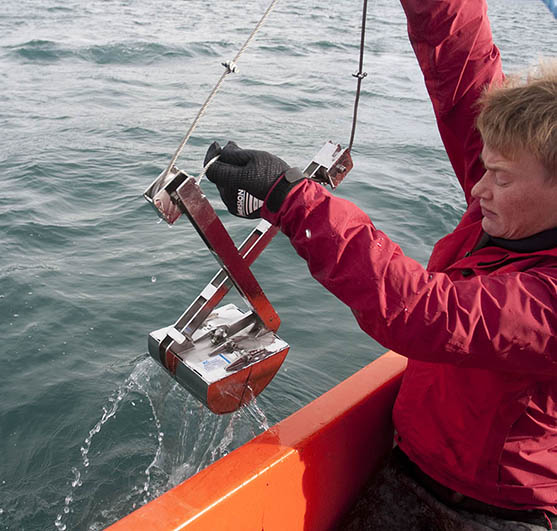
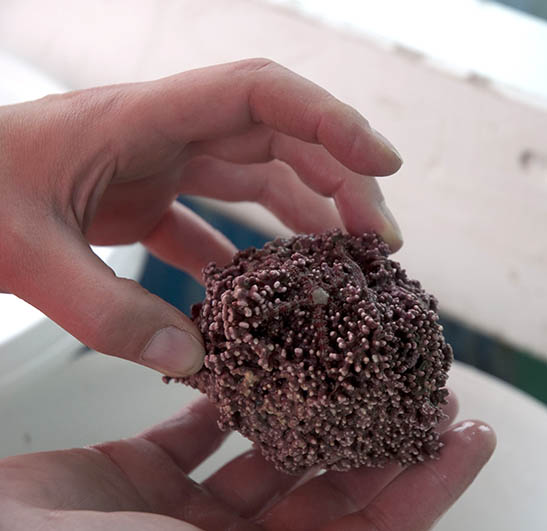
Mette taking a sample at the site. Christiane holding a gigantic Lithothamnion rodolith.
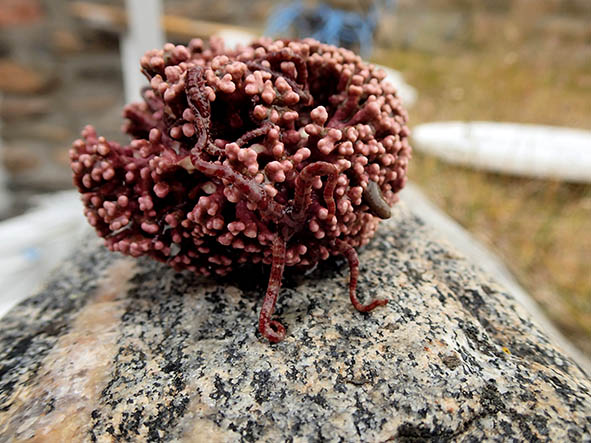
Lithothamnion species are calcareous red algae, that is, they have hard thalli due to calcium carbonate deposits. Most commonly they form a coating over hard substrates, but in Disko Fjord there is a species (Lithothamnion glaciale) that rather looks like a coral and forms so-called rodoliths. These aggregations grow to about fist sized “balls” that under stormy conditions may tumble on the muddy seafloor, much like tumble weed through old western movies, but usually they just lie there peacefully.

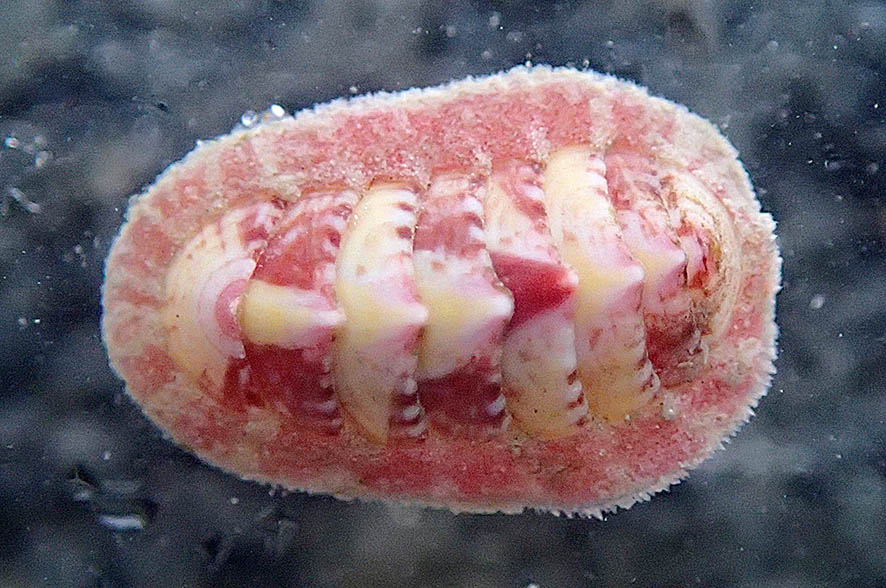
Broken up Lithothamnion aggregate with sipunculid worms (the muddy, sticky-out thing on the right is actually an animal!)
As they are the only hard substrate in an otherwise very “soft” environment, they act as oases attracting a wide range of animals otherwise not found on mud. Also, the rodoliths appear to act as a nursery habitat for diverse species (we found baby chitons, baby sea cucumbers and various baby snails).
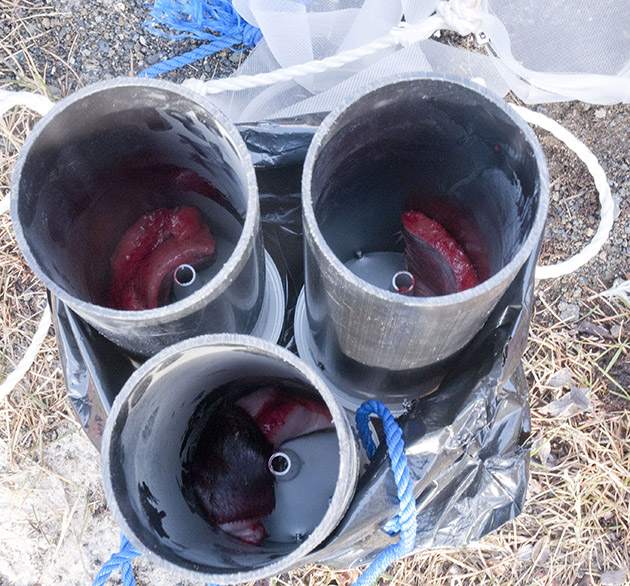
Some of the animals are big enough to be seen by naked eye and are sitting on the algae. Other organisms are very small and need to be persuaded to let go and come out of their holes. So after picking all animals that we could see by eye, like some tiny sponges of not more than a centimetre, beautiful pink chitons, brittlestars, small sea urchins and sipunculid worms, we smashed all the algae and submerged them in magnesium chloride.
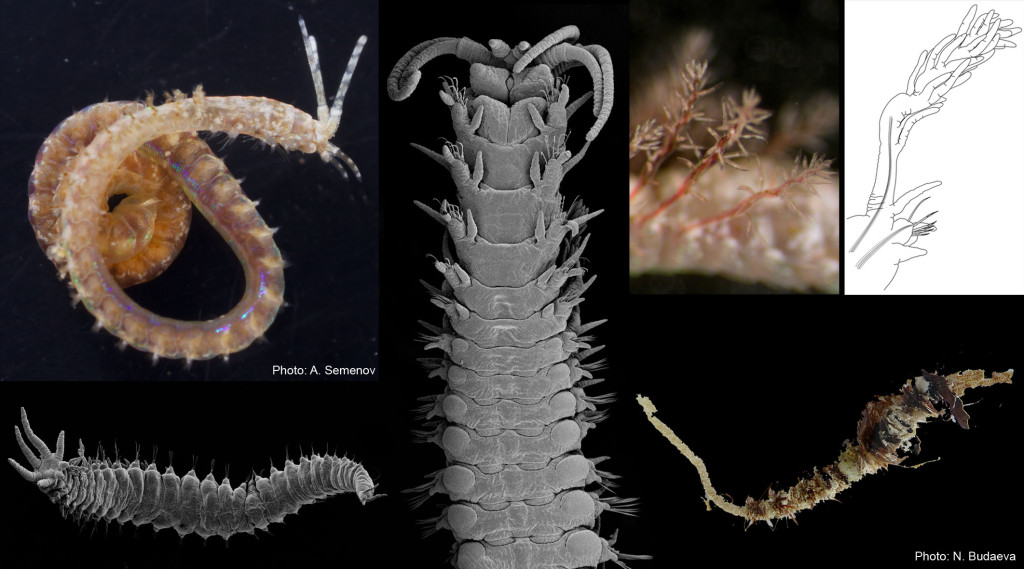
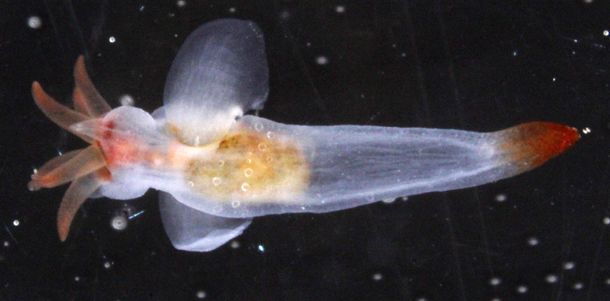
That is a rather sneaky method to get to the tiny hiding creatures that still hold on and/or escaped our attention. Magnesium chloride acts as an anaesthetic and the animals let go of the substrate and can be washed off into a fine-meshed sieve and then be transferred into our petri dishes for further examination. And this method revealed an even more stunning variety of animal life under 1 cm length: several possibly undescribed species of Acoela, microscopic worms that by some are thought to resemble the first bilaterian animals, but also different snails, flatworms, mites, polychaetes and crustaceans.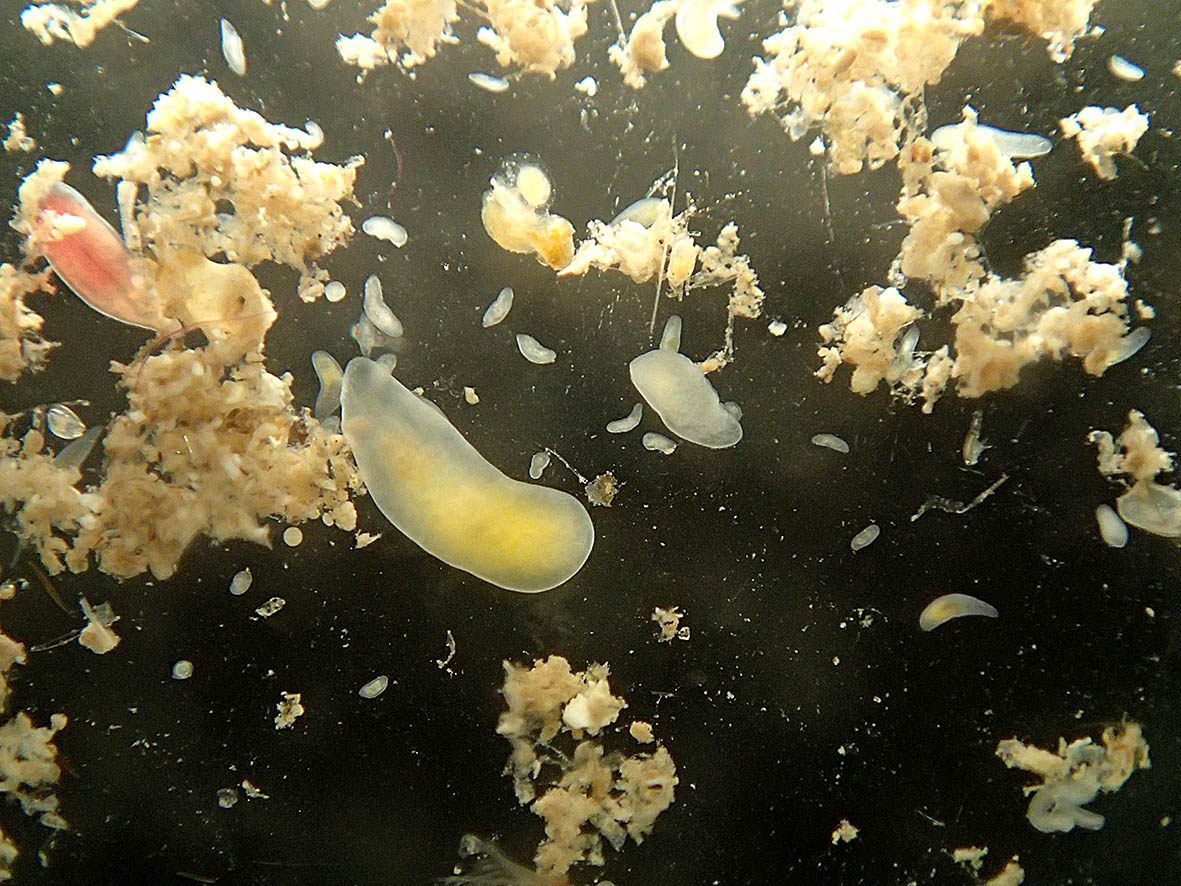 
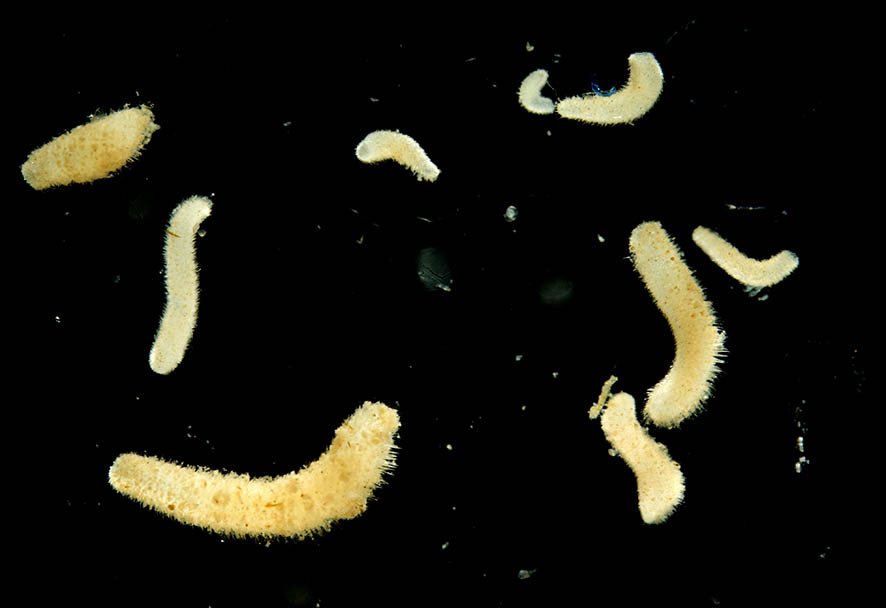
- Meiofauna extracted from the rodoliths (with several acoel flatworms)
Also, Christiane found several individuals of a certain species of solenogasters (worm-shaped, shell-less, spiny mollusks) hitherto only known as the “Greenland neomeniomorph”. She desperately had been looking for some additional specimens to get an official taxonomic description completed. – Juhuuu!
Rodoliths! – These beautiful algae turned out to hold an astounding variety of animal groups.
Written by Inga (Stockholm University) and Christiane (University of Bergen)