Today we celebrate Sea Slug Day! ✨
The day coincides with the birthday of Terry Gosliner, who has discovered one-third of all known sea slug species (more than a 1000!). Here’s a link to how October 29th became #SeaSlugDay.
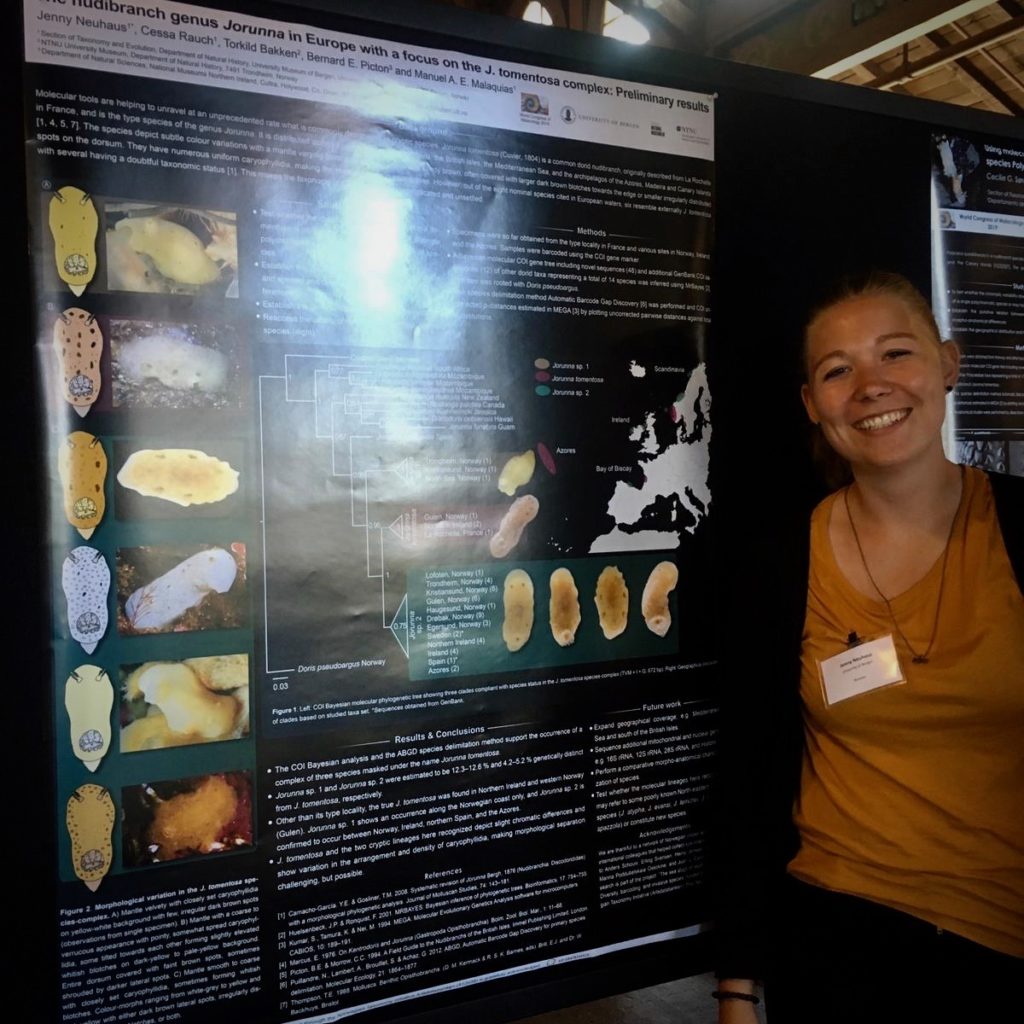
And what better way to celebrate it than introducing a new species to the world. Today it will all be about the Jorunna tomentosa species complex that our master student Jenny Neuhaus studied for the last two years.
Jorunna tomentosa is known to occur in a wide variety of colour patterns, which tossed up the question whether we are actually looking at a single species at all, or maybe dealing with cryptic lineages.
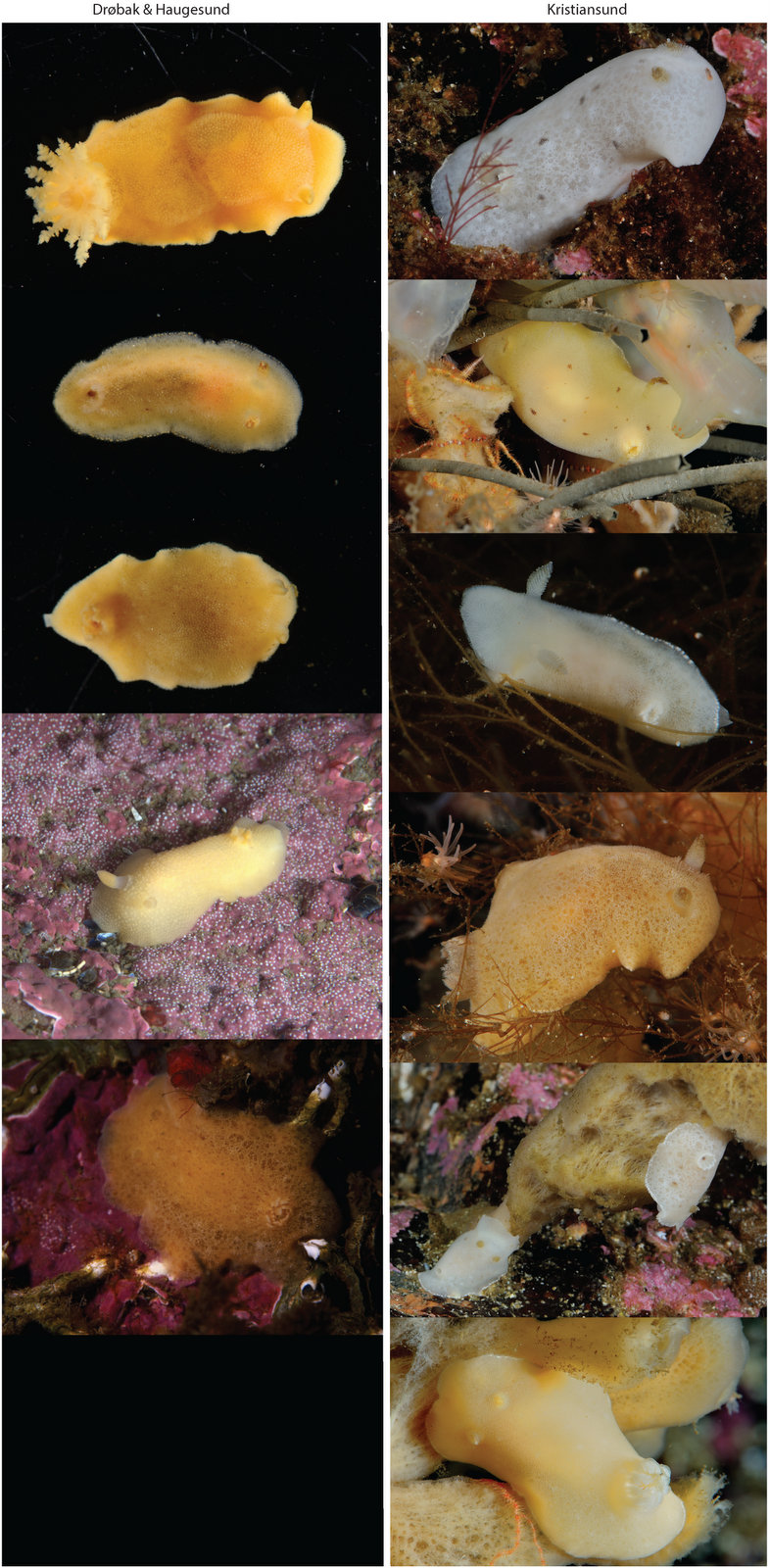

The colour diversity of Jorunna tomentosa, picture by Anders Schouw, Nils Aukan, Cessa Rauch, Manuel A. E. Malaquias
Jenny compared specimens from Norway, Ireland, Spain, Azores and South Africa, both genetically as well as anatomically. She used different gene markers like COI, 16S & H3 to check how these morphotypes compare with each other and evaluate the meaning of genetic distances. But she also did an elaborate morpho-anatomical study to look for differences between these colour patterns. Together with Dr. Marta Pola in Madrid, they dissected the different J. tomentosa specimens and looked at parts of the digestive (radula & labial cuticles) and the reproductive systems. These are all key to help unraveling putative different species and characterize them.
About Jorunna tomentosa
Jorunna tomentosa has an oval-elongate body shape with different colours varying from grey-white to cream-yellow and pale orange. They can reach a size up to 55 mm and occur at depths from a few meters down to more than 400m. they feed on sponges of the species Halichondria panicea, Haliclona oculata and Haliclona cinerea. J. tomentosa can be found from Finnmark in northern Norway, southwards along the European Atlantic coastline, the British Isles, the French coast, Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean Sea up to Turkey, and the Azores and Canary Islands,. Besides the species has even been recorded from South Africa.
Before Jenny studied J. tomentosa, the various colour morphs were regarded as part of the natural variation of the species. By combining molecular phylogenetics with morpho-anatomical characters Jenny investigated the taxonomic status of the different colour morphs of J. tomentosa.
Jorunna sp. nov.?
Jenny sequenced 78 specimens of which 60 where successful for using in the final phylogenetic analyses. Her results supported a new Jorunna species, and a possible case of incipient speciation in J. tomentosa with two genetic lineages morphologically undistinguishable.

From left to right Jorunna spec. nov. Jorunna tomentosa lineage A and down Jorunna tomentosa lineage B
The new Jorunna species was based on material collected from Norway (Kristiansund, Frøya & the North Sea). Jorunna spec. nov. has a distinct colour pattern of cream-yellow with dark small dots (plus, as important; major differences in the radula and reproductive system).
It has been our pleasure to have Jenny here as a student, and she has done excellent work. Last year she won best student poster award last year with her work on Jorunna tomentosa at the World Congress of Malacology in California, USA. Most recently, Jenny defended her thesis on October 26 and passed with an A for her great work – congratulations from all of us at the Museum!
-Cessa Rauch
Sea slugs of Norway Instagram: @seaslugsofnorway
Sea slugs of Norway Facebook: www.facebook.com/seaslugsofnorway