In the last part of 2019 Francesco Golin collaborated with us as an intern in project NorHydro. Francesco is a student at the University of Algarve, where he is enrolled in the International Master of Science in Marine Biological Resources (IMBRSea). We asked him about his internship and this is what he told us:
During the 2019 autumn semester I joined Luis Martell and Aino Hosia in project NorHydro as a research intern. My research contribution was aimed at finding how many species of the hydrozoan genus Euphysa are present in Norwegian waters, and how to define them morphologically and genetically. Euphysa is a common genus with 22 accepted species, but many of them are not easy to tell apart from each other, which is why we decided to implement an integrative approach for species delimitation including morphological and molecular analyses.
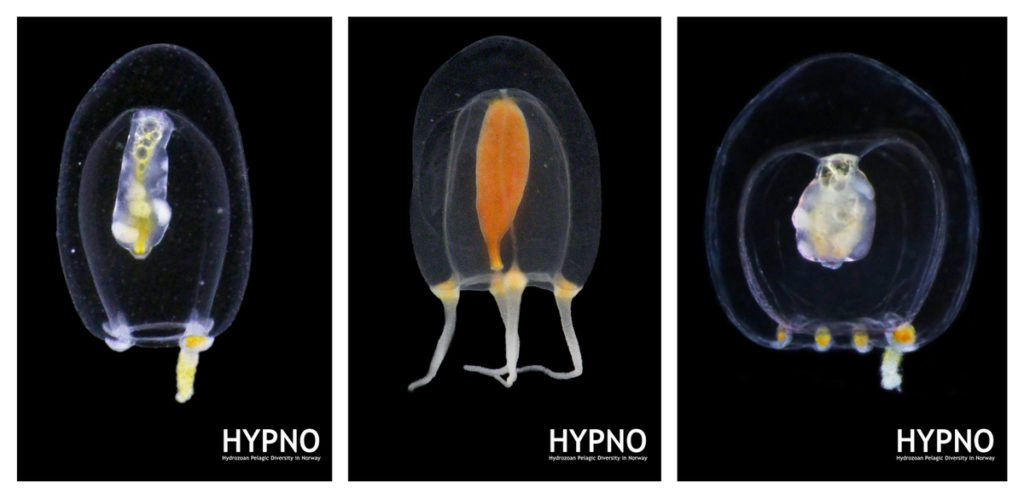
Some of the species of Euphysa occurring in Norway. From left to right: Euphysa aurata, Euphysa flammea, and Euphysa sp
My first mission as an intern was collecting some samples of Euphysa and other gelatinous organisms. Luckily, the opportunity to do so presented itself during the student cruise associated to BIO325, a course in which I participated as part of my studies at UiB.
During this cruise I used a light table to spot the tiny jellyfishes brought on board by the Multinet, then I placed them on a Petri dish and took pictures of them with a camera attached to a stereomicroscope, before transferring them to an Eppendorf tube filled with ethanol.
All these elements (the pictures of each organism, the associated sampling data, and the samples themselves) are needed for species delimitation of hydromedusae. The pictures are used to compare the morphology of different individuals and to identify important diagnostic characters (unfortunately, ethanol-fixed jellyfish are not useful for morphological analysis), while the ethanol-preserved samples are used to obtain DNA sequences.

Some siphonophore parts are very transparent, and thus they are some of the most difficult animals to spot in plankton samples.

The hydrozoan Aglantha digitale (left) was very abundant in all my samples. Other cnidarians, such as this anthozoan larva (right) were also present.
My second mission consisted on gathering the original descriptions of the different species of Euphysa. This information is necessary if we want to understand what makes each species different, and will come handy when analyzing the individuals and their pictures collected on the field. Talking about species boundaries, I had the opportunity to attend a course on “Molecular Species Delimitation” offered by the University Museum. In this course I learned how to perform the analysis of DNA sequences for species delimitation, using some common software (MEGA and R) for this purpose. These are important tools that will allow us to assess the diversity of Euphysa in Norway, and together with the morphological analyses these data will help us determine if new species have to be described.
Now the semester has ended and my internship is over. Nevertheless, I hope my help was meaningful, as I want to continue being a part of this research project in the future. I will keep myself updated with the changes in the taxonomy of Euphysa, so I’m sure I will be able to join NorHydro again when I’ll come back to Bergen!
-Francesco