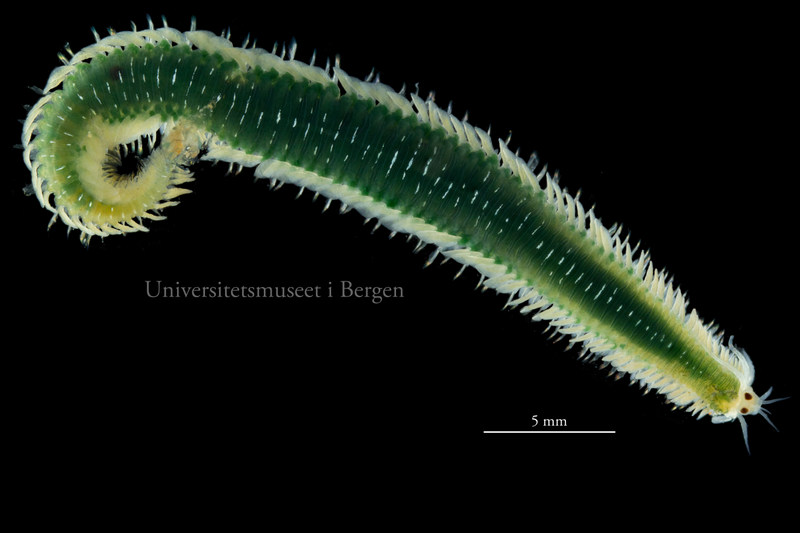
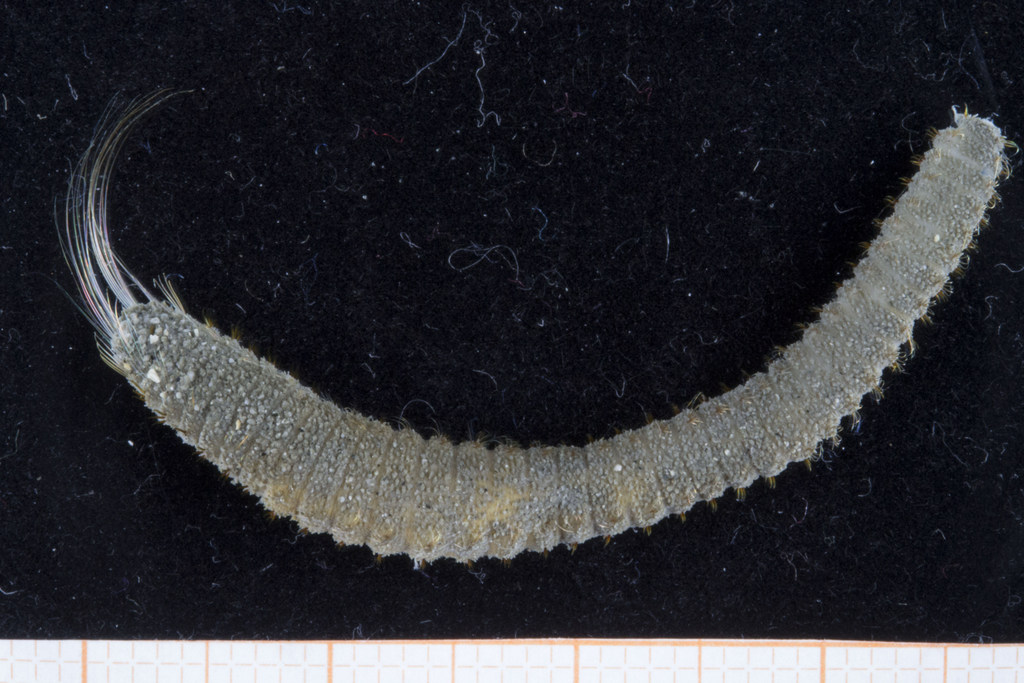
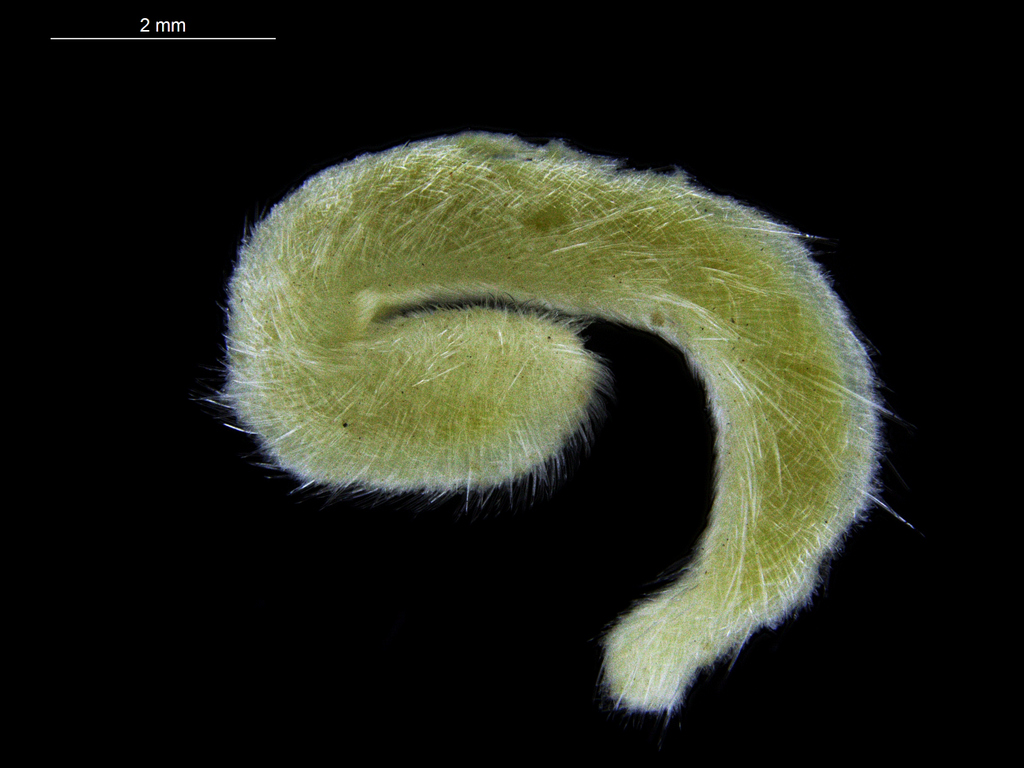
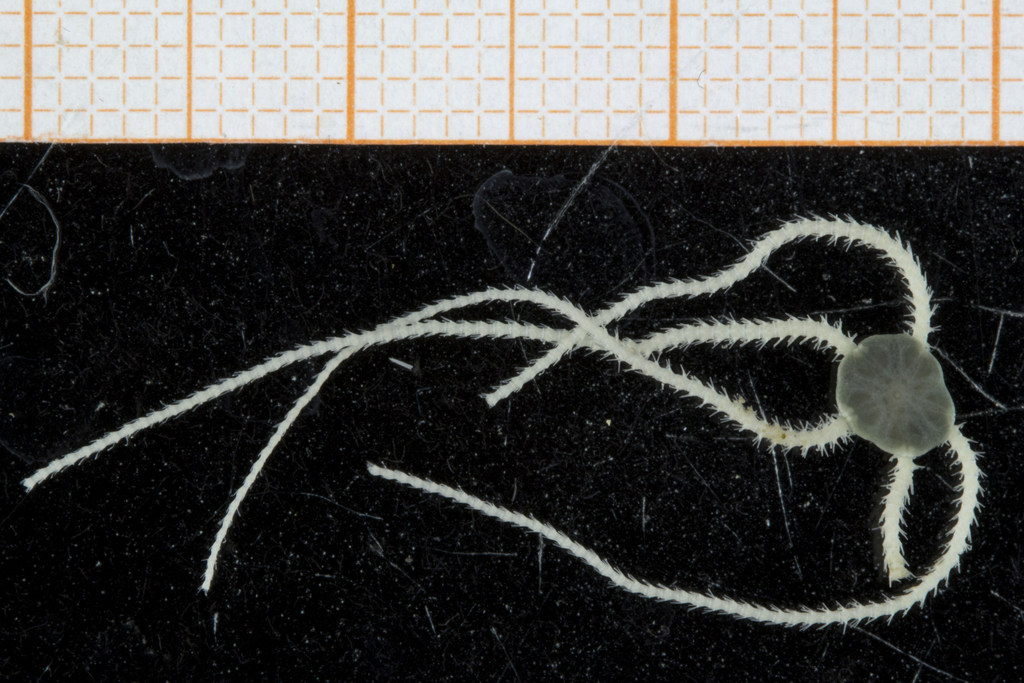
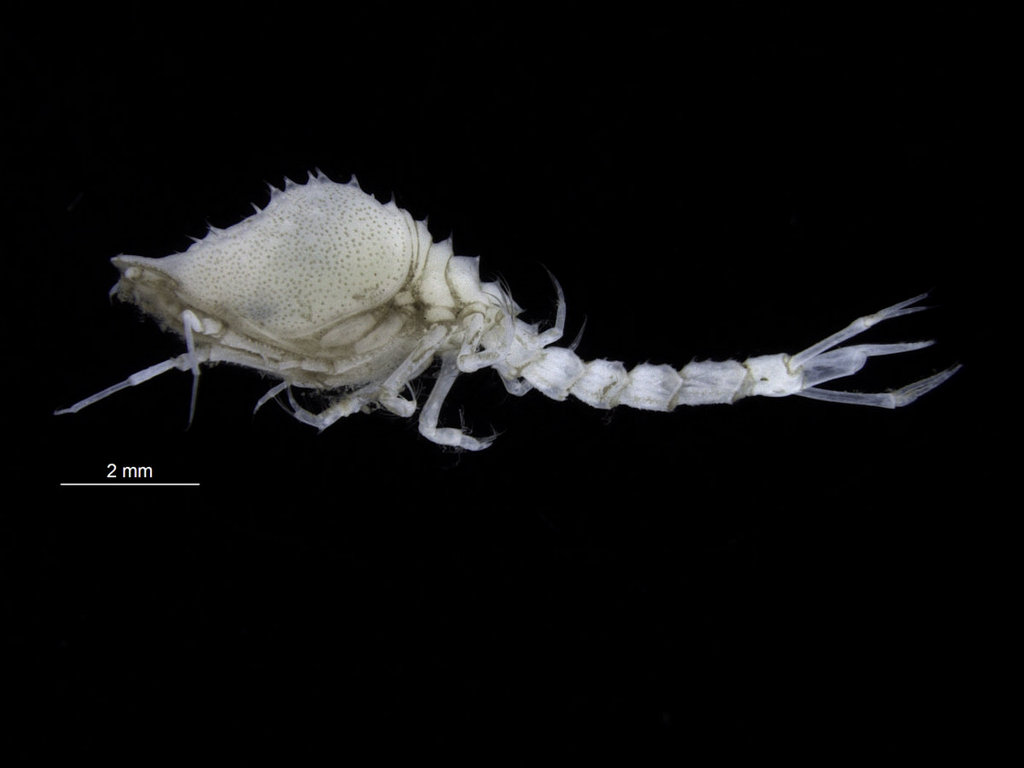
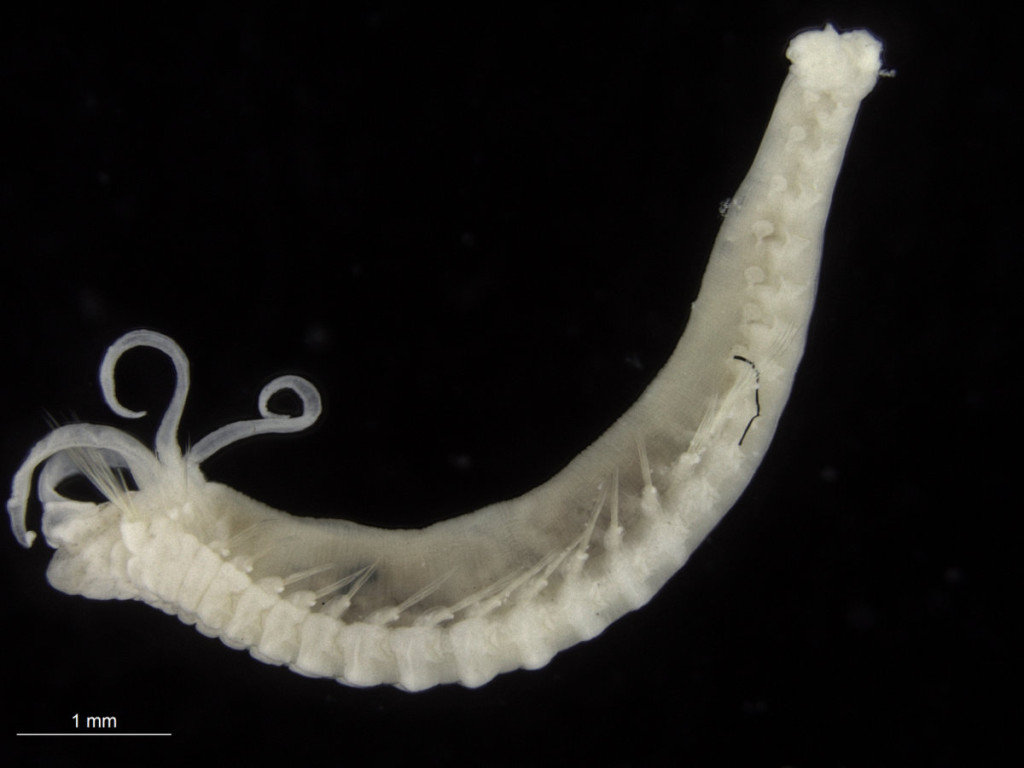
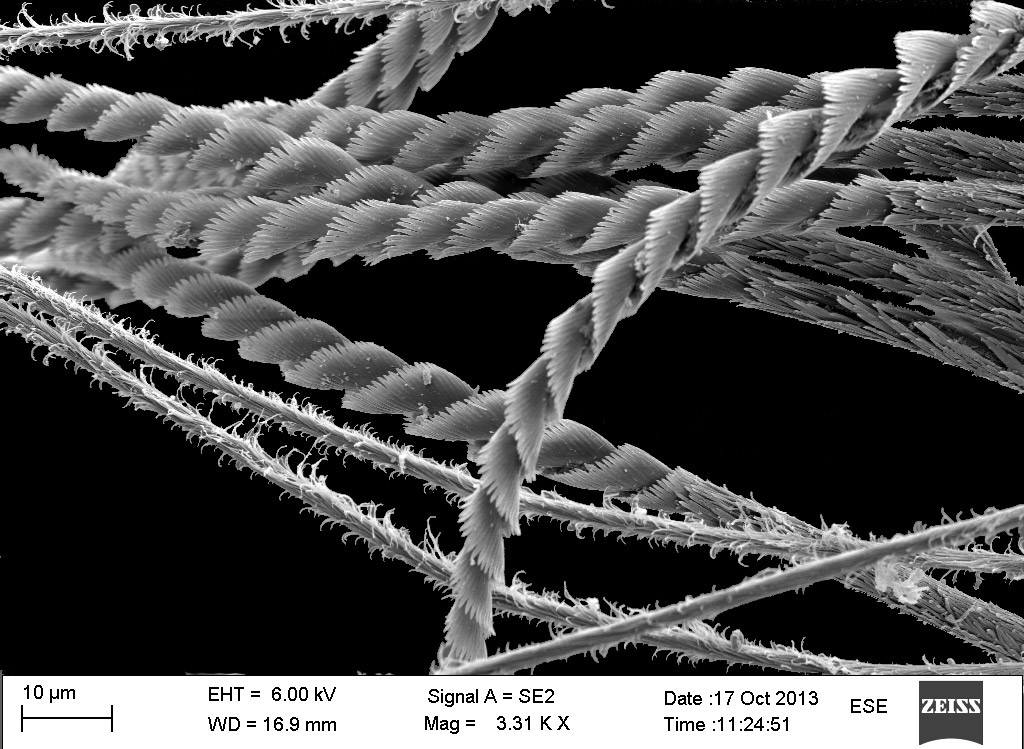
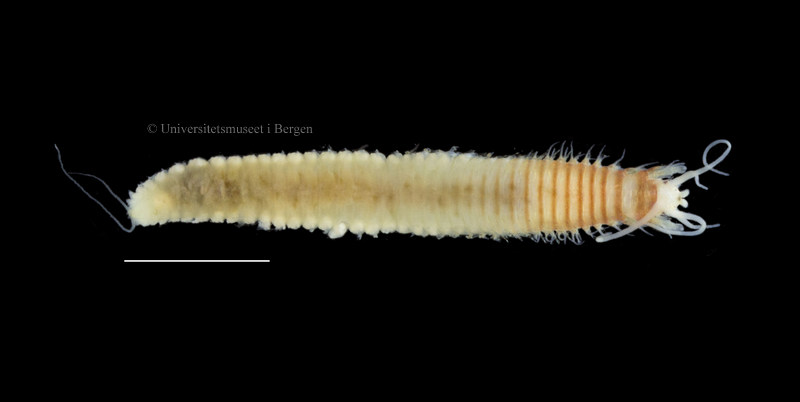
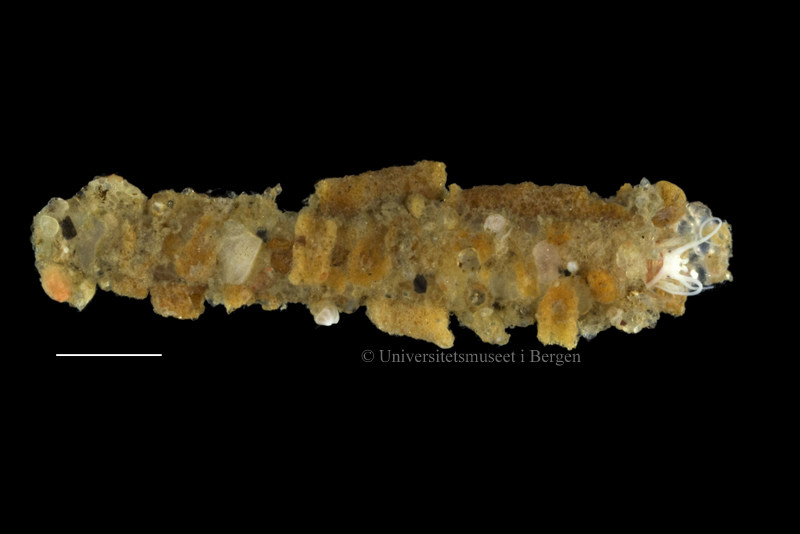
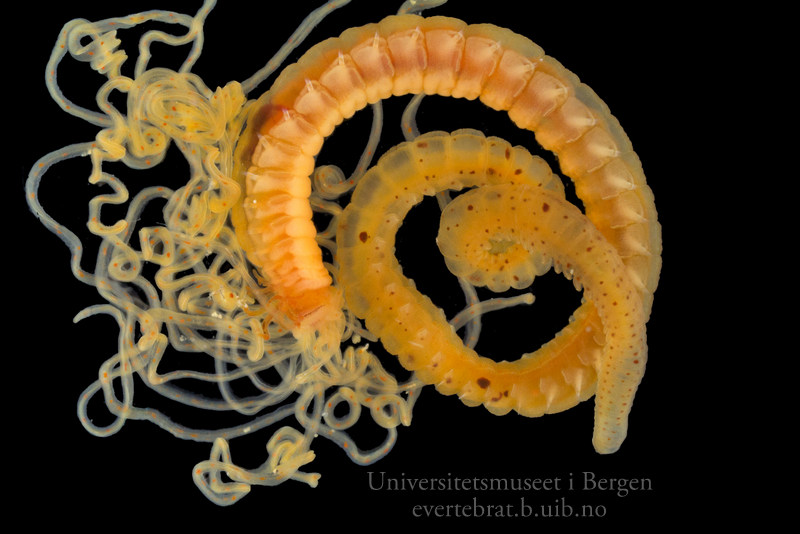
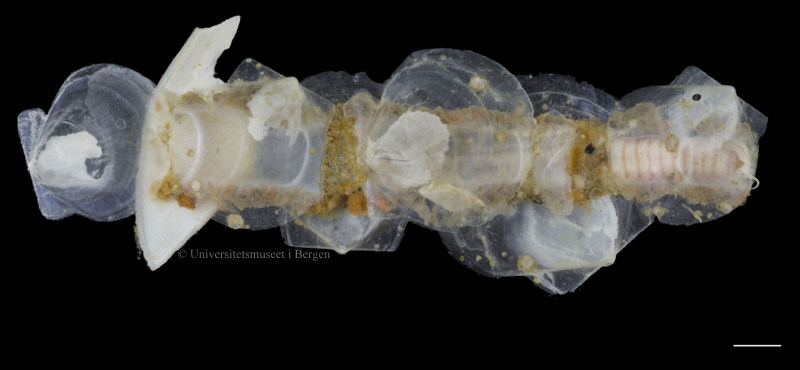
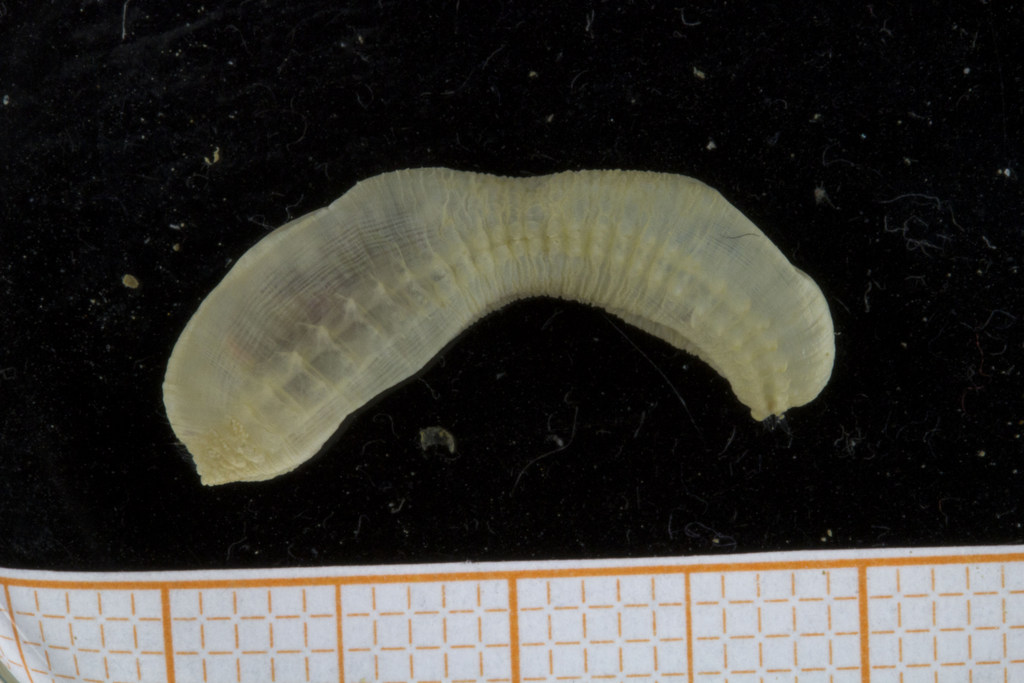
A nice and yellow polychaete just in time for Easter!
Category Archives: Photography
Friday Photo: Eumida alkyone
We went on two one-day trips with the R/V “Hans Brattstrøm” in March, here’s a collection of snapshots from the sunny day of surveying.
This is one of the species we found, and – apart from being nice and photogenic – it is also interesting as it is a rather new species, described in 2010. You can read more about that here:
Nygren, Arne ; Pleijel, Fredrik. 2010. From one to ten in a single stroke – resolving the European Eumida sanguinea (Phyllodocidae, Annelida) species complex. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution [In Press, Corrected Proof] , available online athttp://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.10.010. page(s): 8
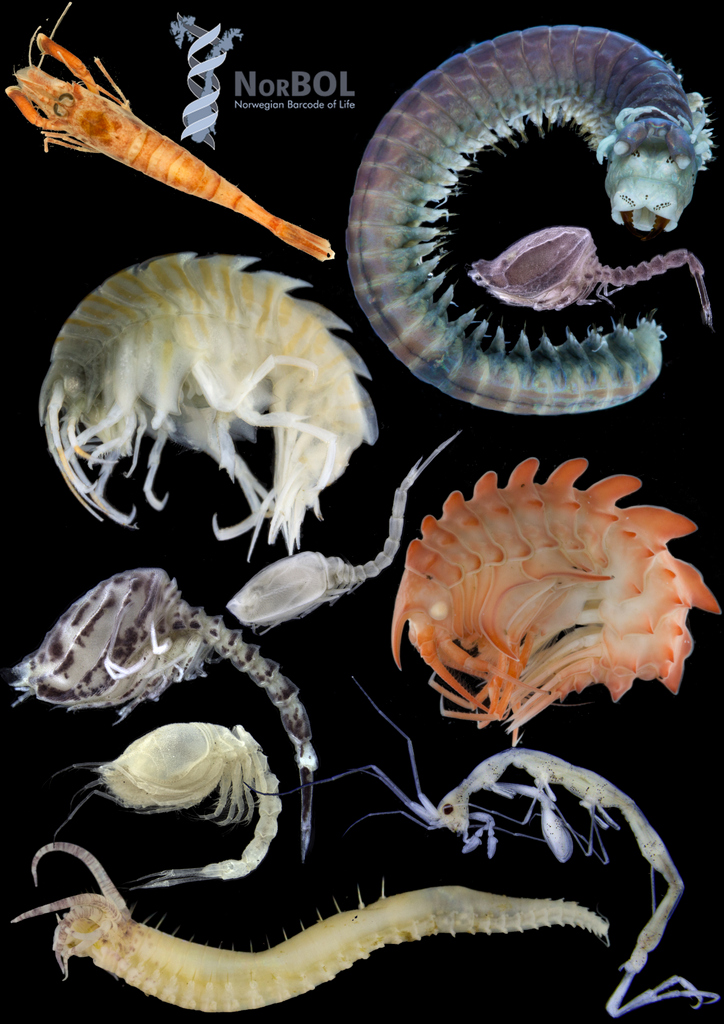
10(!) new plates ready for BOLD
We’re currently in the final stages of preparing ten plates; 9 from Norwegian waters for the Norwegian Barcode of Life project (NorBOL), and one plate of Polychaetes from the Marine Biodiversity of Western Africa (MIWA) project for submission to the BOLD database.
The shipment will consist of the following taxa groups:

…4 plates of polychaetes (bristle worms) from Norwegian waters. These have mainly been collected by the large projects MAREANO, BIOSKAG and PolySkag, and have been identified during workshops that we have arranged.
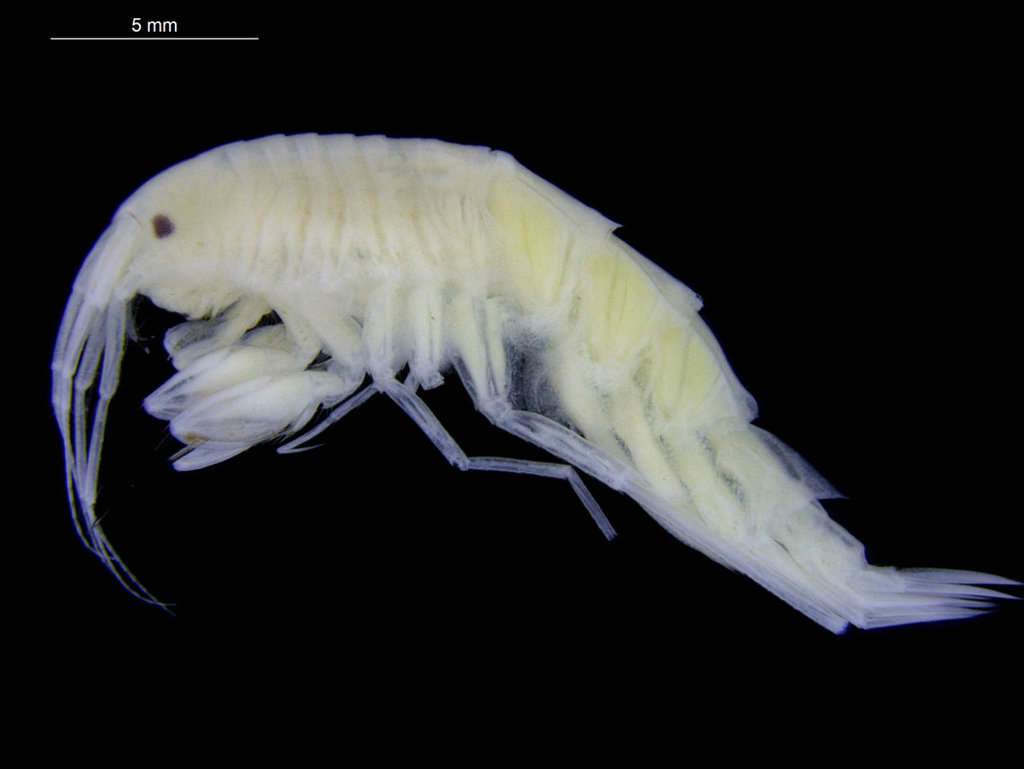

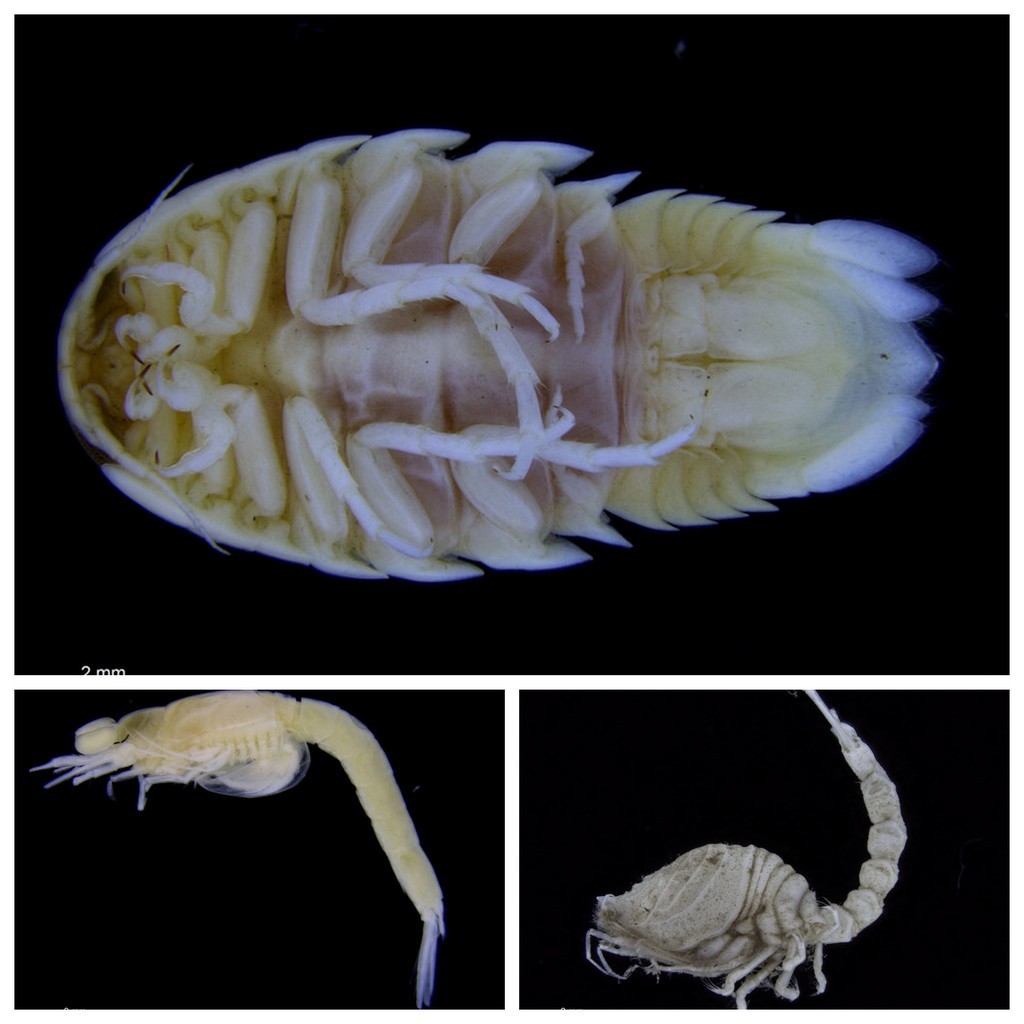
One plate of Amphipoda, mostly collected by MAREANO, but also samples collected during a teaching cruise from UNIS at Svalbard
Hopefully the sequencing will be successfull, and yield many new DNA barcodes!
More from the PolyNor workshop
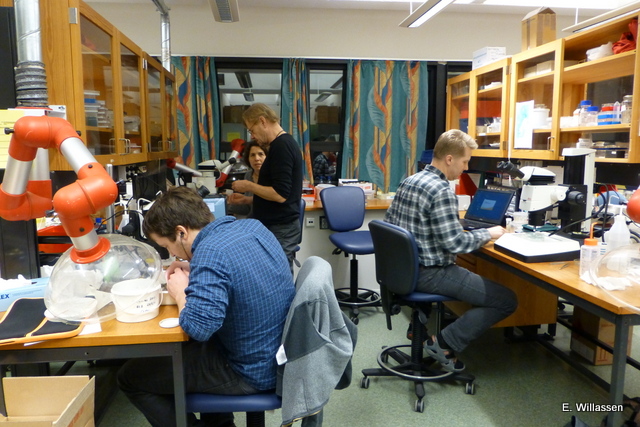
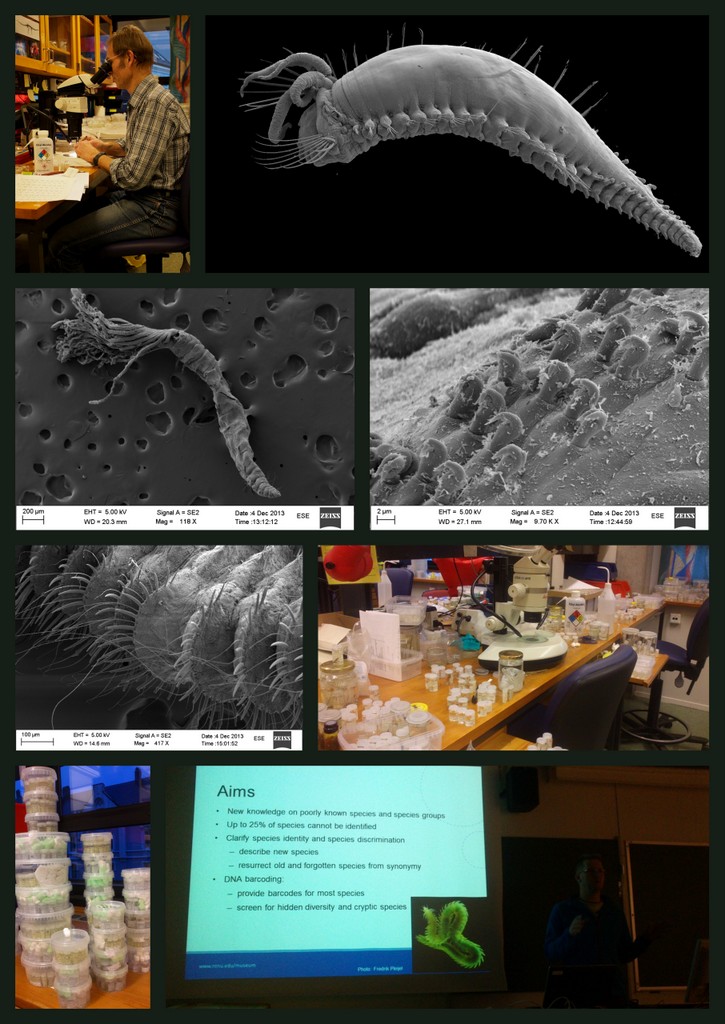
As usual, we use a variety of methods to work with our animals – these include use of stereo microscope, “ordinary” microscope, and electron scanning microscope (SEM). Below are some pictures of work in progress during today.
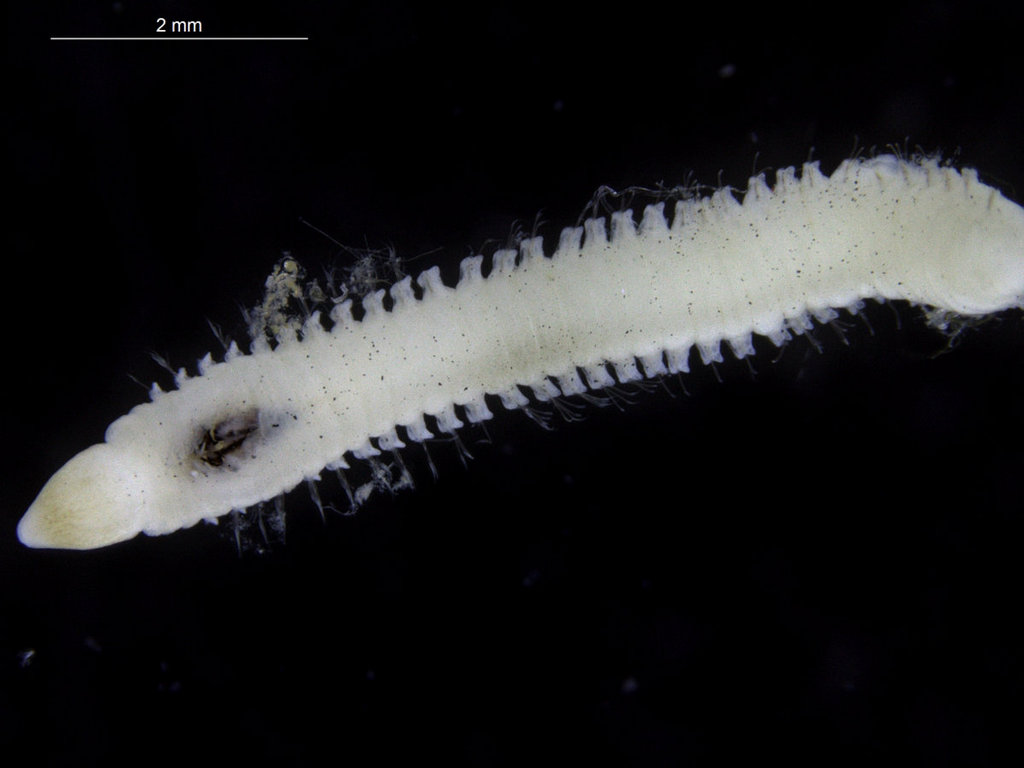
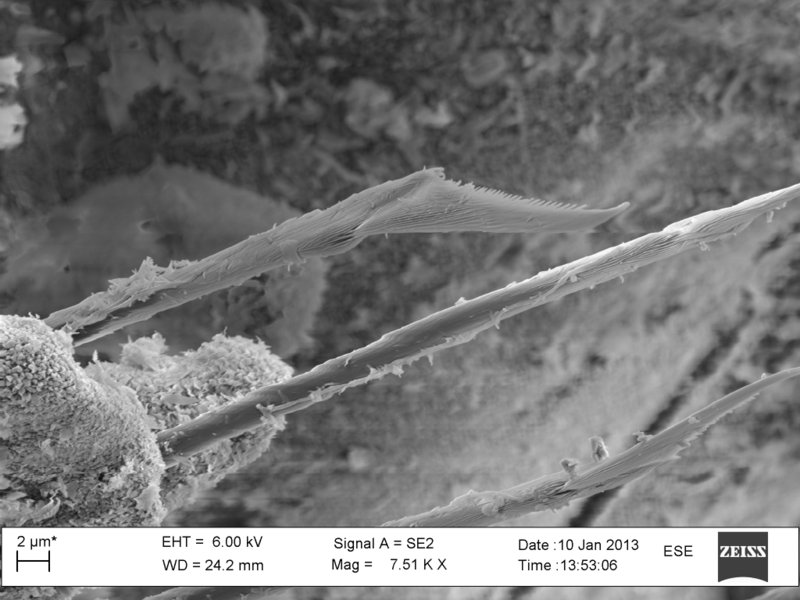
Friday Photo: the bristles of a bristle worm
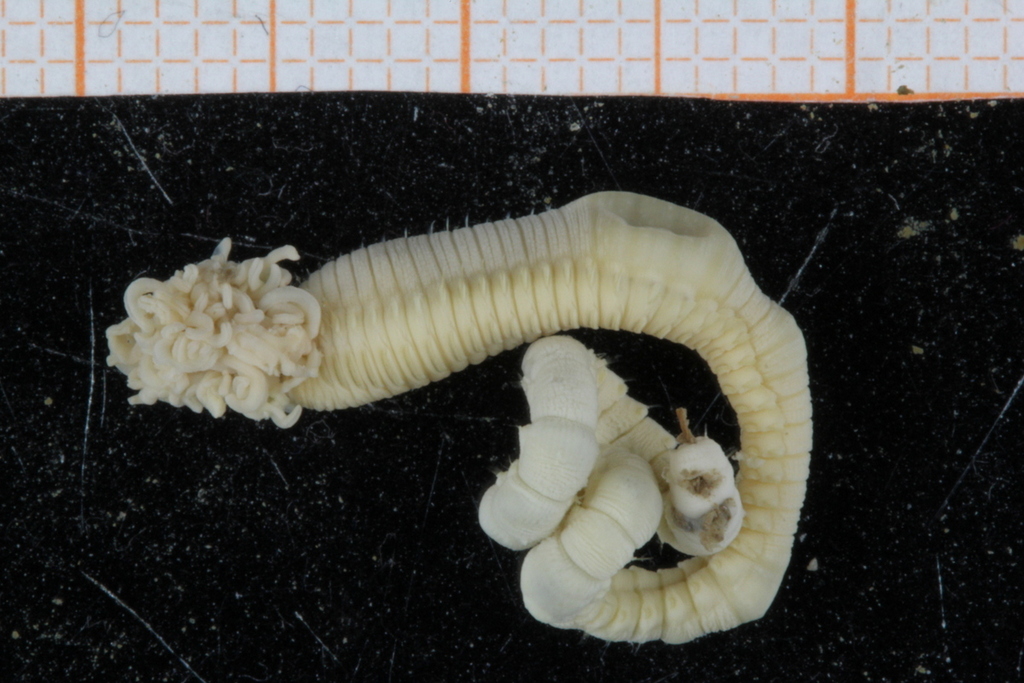
Home, sweet home
I came across these two bristle worms from the genus Nothria whilst sorting out the animals from a sample collected in the Barents sea by the MAREANO project, and wanted to show you how differently they’ve approached the choice of building materials for their tubes. They build the tube around their bodies to protect themselves from predators. Now, a Nothria outside its “house”, or tube, looks like this (scale bar is 2 mm) :
The same animal inside its tube looked like this:
And then there was this one, who had made a more select choice of building materials:
Fall cruise with MAREANO
I’m onboard the research vessel “G.O. Sars”, participating in the last MAREANO cruise of the year. We’re currently on our way back out to the sampling sites after seeking refuge in a fjord from the storm yesterday.

Sampling areas. The yellow area is finished, the brown ones are work in progress. From mareano.no
The area we’re working on is outside Møre & Romsdal, currently we’re on our way to a set of video stations whilst we wait for the sea swell to die down (it’s quite the rollercoaster here at the moment!). We have two-three full stations remaining, hopefully we’ll be able to finish those as well before the cruise ends this Friday.
“Full station” means that we in addition to videoing the sea floor for a 700m long transect with our remotely controlled video rig, the Campod 2, also collect physical samples.
This is done using a variety of gears, which collectively gives us a extensive insight in the properties of the area we’re working on. On board we have a team of biologists, geologists and a chemist. The geologists and chemist are after sediment cores, which provide a window back in time for analyses of the physical and chemical parameters of the sea floor, including the accumulation of pollution. How far back a core extends will depend on the sedimentation rate, and on how long the core we manage to extract is.
For collecting animals, we are using three main gears: the epibenthic RP-sled, the beam trawl, and the grab. These collect different parts of the fauna, and (together with the video) gives us a fair understanding of the species diversity and composition.
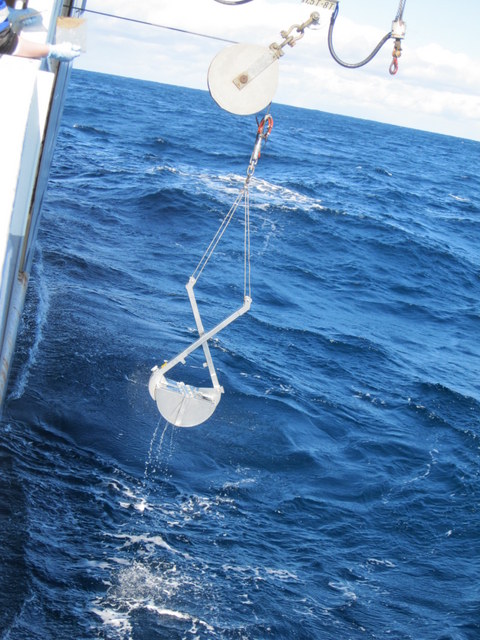

The grab (a van veen) collects a quantifiable amount of animals exceeding 1 mm in size living in the sediment. We collect two grabs at each full station.
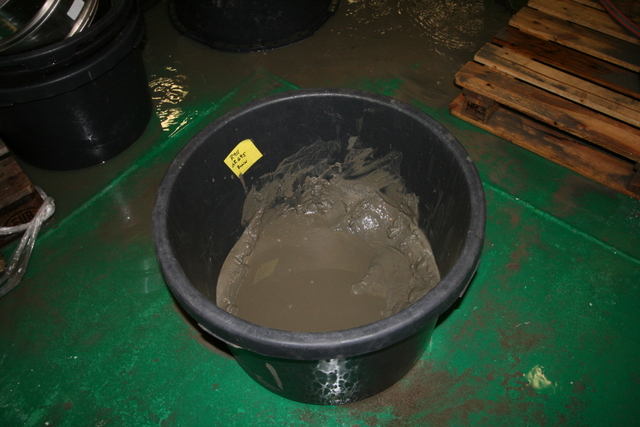

A typical grab sample. We carefully rinse the mud through a 1 mm sieve, collecting the animals within it.

RP sled (left) and the beam trawl. The sled collects the small animals living just above and in the upper layer of sediment. The beam trawl collects the macro- and megafauna living above and within the top layer of the bottom.
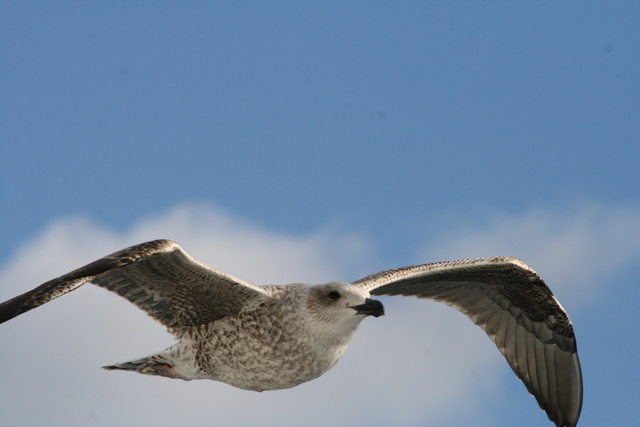

Fulmars and gulls are following us, hoping we’ll give up on the small animals and start catching fish for them
Now we’ve arrived at the next station, so I’d better get going!
Focus on West African crabs (Brachyura)
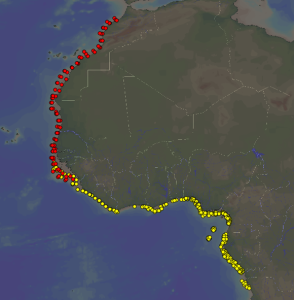
R/V Dr Fridtjof Nansen sampling stations for which benthic samples have been deposited in the Invertebrate Collections of Bergen. Red dots: the Canary Current Large Marine Ecosystem (CCLME). Yellow dots: the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem (GCLME)
Since 2005 the research vessel R/V Dr Fridtjof Nansen has been sampling benthic invertebrates on the continental shelf of the large marine ecosystems (GCLME and CCLME) of West Africa. A large bulk of the material is kept in our collection and is being processed for taxonomic and other studies by several workers.
These days we are particularly focusing on the true crabs (Brachyura) and are preparing specimens for DNA barcoding with the BOLD system. This work will produce open access data (genetics, morphology, distribution) to enhance a broader knowledge about Atlantic marine biodiversity. The project is financially supported by JRS Biodiversity Foundation.

Cronius ruber (Lamarck, 1818) caught off Guinea at 35 m depth in May 2012. (Identification E.Willassen)

A small assembly of crabs photographed and prepared for DNA barcoding. Some specimens have still kept some colors despite being preserved in ethanol
Bioskag Workshop
We began the year with arranging two workshops in January. The first of these was based on the extensive sampling done in the Skagerrak strait in recent years (2006 – today). The aim was to increase the rather poor knowledge of the invertebrate fauna of the region (link is in Norwegian).
The focal group of this workshop was the Polychaetes (bristle worms), and through the effort of the ten attendants, a lot of material was examined. You can read more about this at the blog of the Norwegian Polychaete Forum.
We are currently processing the findings from the workshop, including documenting specimens through photography and drawing. One of the tools we employ for doing this is the scanning electron microscope (SEM), which enables us to make high resolution images at a very high magnification.