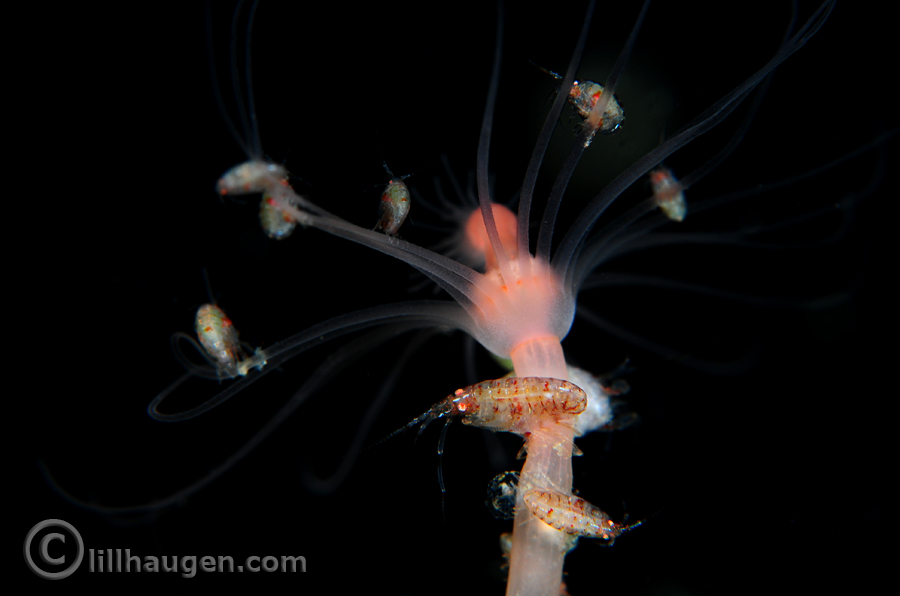
Amphipods are a group of small crustaceans where most of the species we know are benthic (bottom dwelling) and marine. But within the benthic habitat there are many niches, and one of the more intriguing is the many ways of living on or inside another benthic animal. A few species become parasitic (feeding on their host), but for the most species living like this, it does not look like eating the host is the main objective. In these cases we term the amphipods as “associated with a host”.
To document some of these associations, I have had a wonderful cooperation with an amazing underwater photographer this year. Lill Haugen has photographed amphipods associated with hydroids, and sampled the amphipods afterwards for us. Documenting this kind of association is almost impossible without the help of divers – if we are lucky enough to sample a hydroid with our normal sampling gear, the amphipods fall off. It is not easy spotting these small animals for a diver either, but Lill says that it becomes easier with practice.
This photo is from the Oslofjord, at 25 m depth. With the photos from Lill we are able to say that this particular amphipod (from the family Stenothoidae) looks like it keeps the hydroid as a family home. The parents sit on the “stem” of the hydroid, and their children sit on the tentacles of the “flower”. This might be both to provide extra protection and food for the amphipod-children. The adult amphipods are 5mm long, their children 3mm.
Earlier studies have shown that amphipods of the family Stenothoidae often associate with molluscs – we have found several different species living inside bivalves (shells). Other amphipods might associate with other crustaceans such as crabs, or with sponges, anemones or snails (gastropoda).
For most amphipod species we know nothing about their life-history and possible associations. But the more we examine them, the more we learn..
Suggested reading:
Tandberg, A.H., Schander, C., Pleijel, F. (2010) First record of the association between the amphipod Metopa alderii and the bivalve Musculus Marine Biodiversity Records, 3, e5, doi:10.1017/S1755267209991102
Tandberg, A.H., Vader, W., Berge, J. (2010) Studies on the association of Metopa glacialis (Amphipoda, Crustacea) and Musculus discors (Mollusca, Mytilidae). Polar Biology, 33, 1407-1418
Vader, W., Tandberg, A.H. (2013) A survey of amphipods associated with mollusks. Crustaceana 86(7-8), 1038-1049
Vader, W., Tandberg, A.H. (2015) Amphipods as associates of other crustacea: a survey. Journal of Crustacean Biology 35(4), 522-532
-Anne Helene